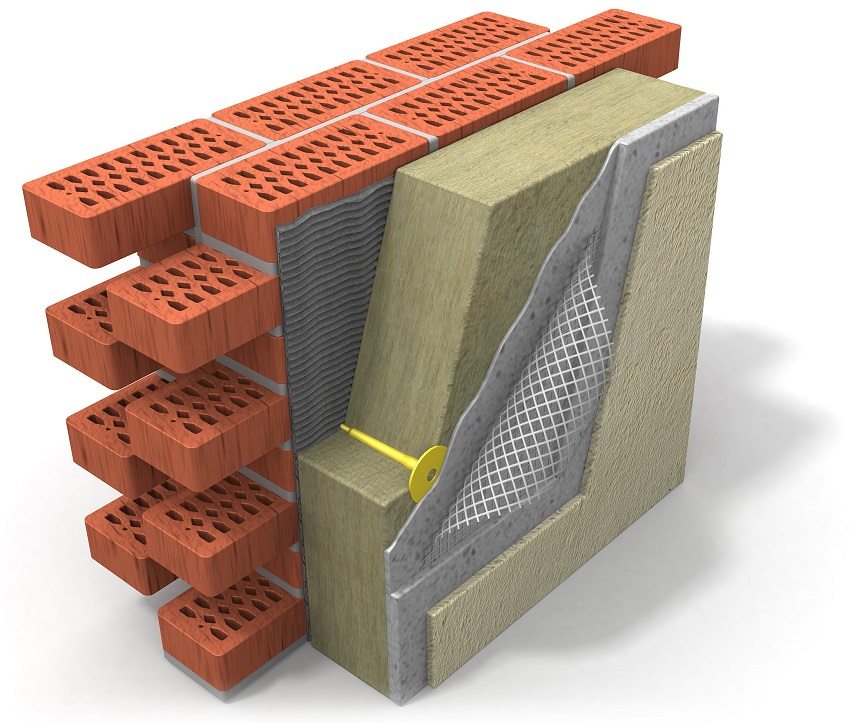
One of the possibilities for effective finishing of external walls is to cover them with decorative plaster solutions. To ensure mechanical strength, wear resistance and increase the operational life of the finishing material, during its application, a grid for plastering the walls of the facade is used. Development and production of modern reinforced mesh for wall plasters - logical development of traditional strengthening technologies facade for finishing, such as the use of shingles, often hammered in nails and the chain-link that appeared later.

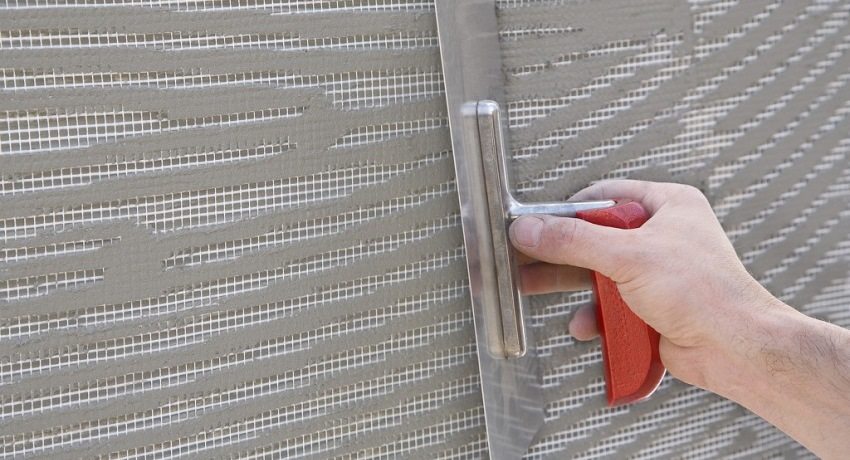
The use of a reinforcing mesh helps to maintain the strength of the decorative plaster on the facade of the building
Content [Hide]
Why use mesh reinforcement?
Mesh reinforcement when plastering external walls is used in the case of poor adhesion of the components of the finishing material with the main wall material (concrete, aerated concrete, brick or wood). In such cases, there is a possibility of peeling and crumbling of the plaster both some time after the application of the solution, and immediately. In addition, the grid anchors the draft leveling layer.
The need to use a reinforcing mesh also arises when finishing work in a recently rebuilt building, when its walls are still shrinking. Facade deformations occurring during movements lead to cracks and a violation of the integrity of the finishing coating.
What kind of mesh to use for plastering walls depends on the material of the walls, their relief, the degree of deterioration, on the presence of external insulation, the structure and thickness of the layer of finishing materials, and finally, on climatic conditions. But with a modern wide assortment, reinforcing mesh for wall plastering must meet a number of requirements:
- ease;
- no additional loads on structural elements;
- resistance to aggressive chemical compounds and corrosion resistance;
- tensile strength combined with elasticity;
- resistance to various types of loads;
- density within 150-170 g / m2 (to ensure strength and elasticity at the same time).
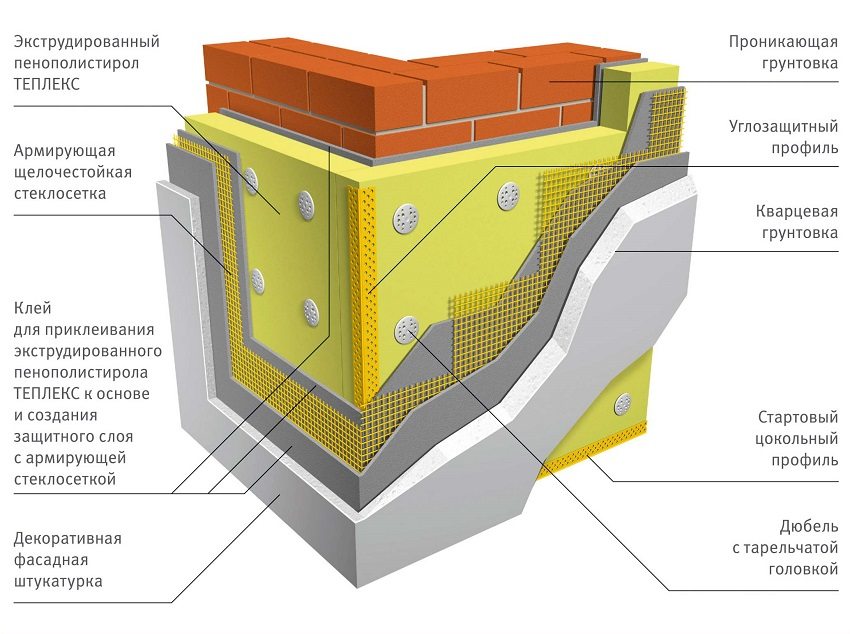
Wall insulation system "wet facade»Using a reinforcing mesh
The main types of mesh for plastering walls
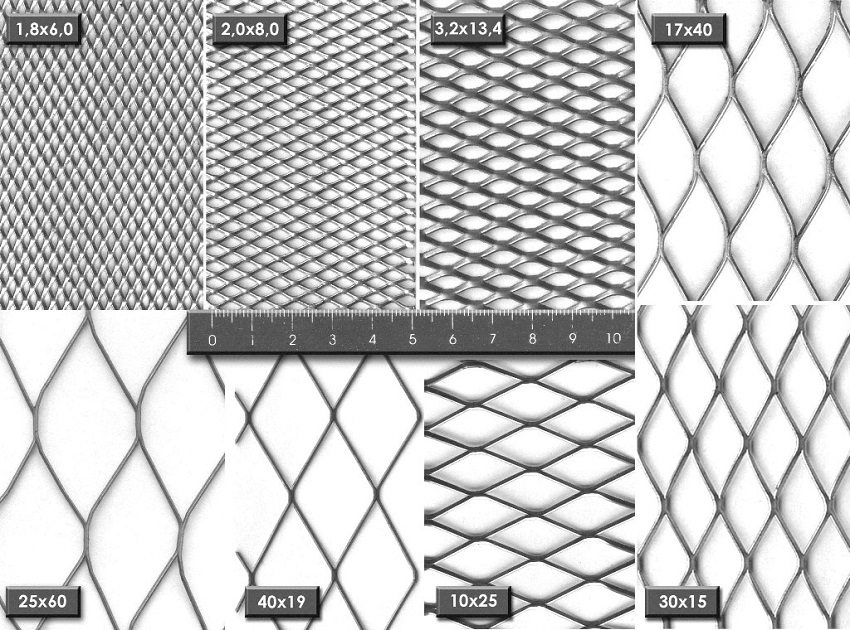
The variety of modern building and finishing materials, adhesive and leveling solutions, the use of various additives and additives in their composition has led to an expansion of the range of reinforcing products.
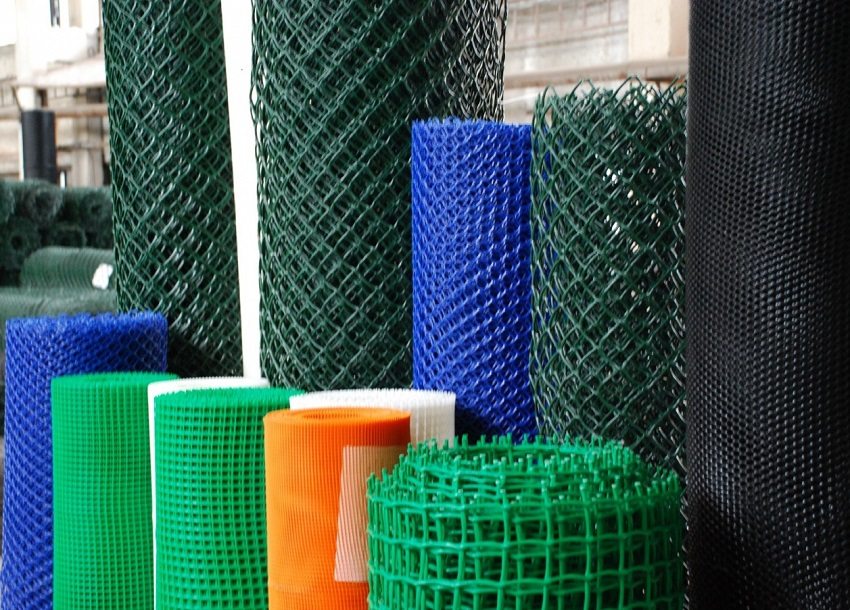
The main types of nets for plastering walls are distinguished by the composition of their material:
- metal;
- fiberglass;
- plastic;
- polymeric.
Metal grid
Reinforcement with a metal mesh for plastering the walls of the facade is resorted to in cases where the thickness of the finishing solution reaches 30 mm or more. If the plaster is planned to be applied in the thinnest possible layer, then polymer, plastic or fiberglass nets are used as a reinforcing layer for the walls.
Useful advice! By itself, the metal mesh for plastering walls is not intended for use in rooms with high humidity or for outdoor decoration. Here, it is advisable to use a galvanized mesh or with a polymer protection.
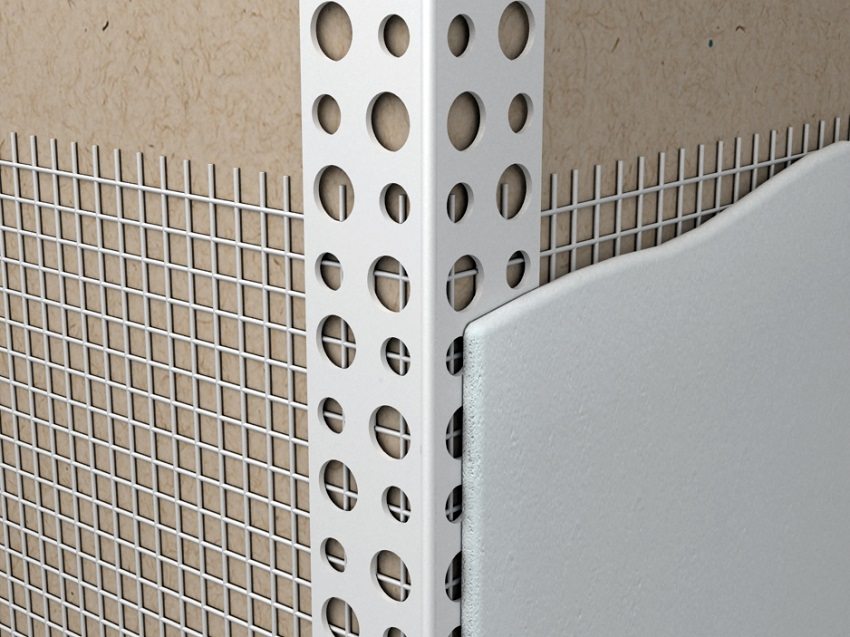

Fastening the facade mesh should be started from areas that are difficult to handle: corners, window and door slopes
There are four main types of metal reinforcement, differing in production technology and application options.
Woven mesh
Sufficiently flexible and lightweight construction, woven from very thin and strong wires of various sections. When finishing the facade it is used as a grid for plastering walls - galvanized, with a mesh size of 1 by 1 cm. Convenience of the form of implementation: in large rolls - makes it possible to use it for independently performed work.
Mesh-netting or braid
Mesh-netting is a metal wicker structure with 2 by 2 cm cells, used to strengthen walls or a facade when covering large areas with plaster. Relevant when applying a layer with a thickness of 30 mm and more. For outdoor work or in rooms with high humidity, a galvanized chain-link is used. Due to the movable system of units, it is especially preferred for wall decoration, the material of which shrinks or expands when weather conditions (temperature and humidity) change, i.e. for wooden or aerated concrete walls.
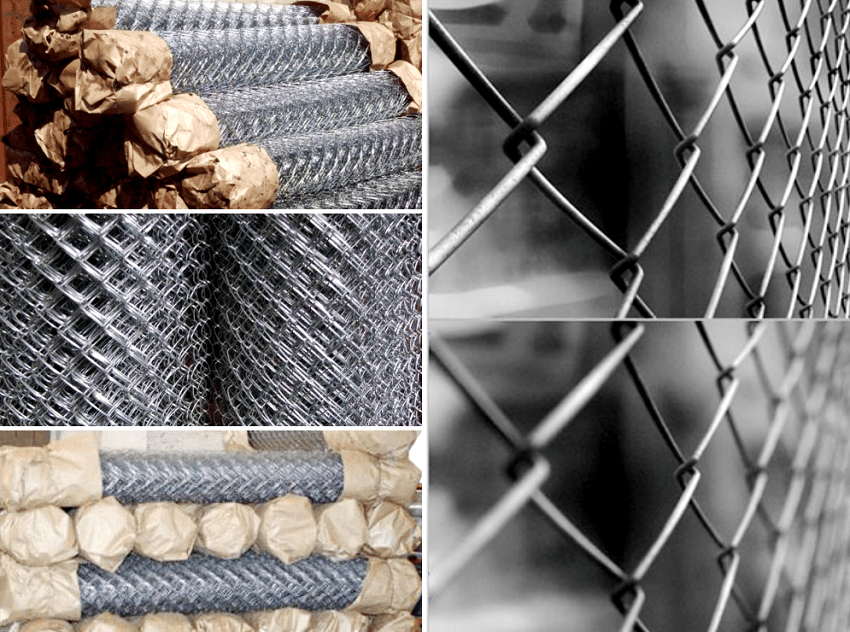

The netting is used when applying a layer plasters over 30 mm thick
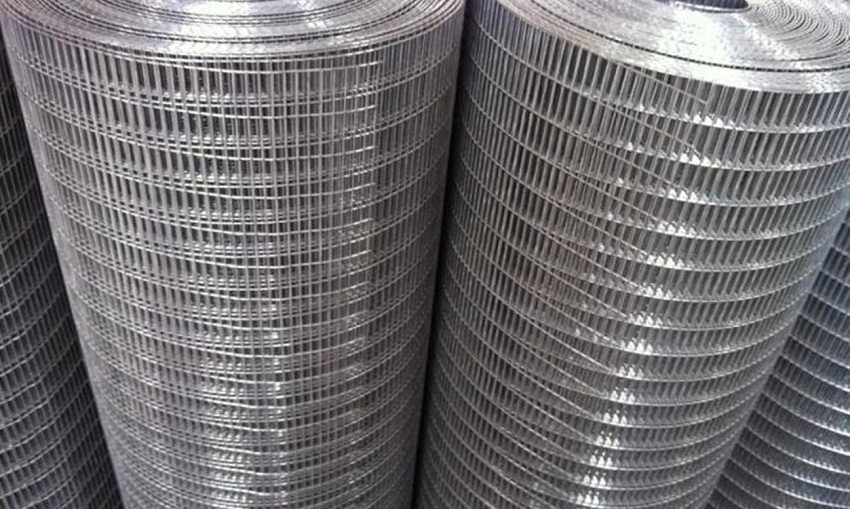
Welded mesh
When making a welded mesh, the wire is superimposed on each other perpendicularly and welded at the joints, resulting in the formation of square cells. In this case, the wire is galvanized or treated with a polymer protective compound. This reinforced structure can be used to strengthen the plaster of the facade of buildings subject to strong settlement: new buildings or located on moving soils - as well as walls made of aerated concrete.
The best results in protecting the finishing coat from cracking can be achieved when using a welded mesh for plastering facade walls with a mesh size of about 2/3 cm. This material is sold packed in rolls of a meter wide.
Expanded metal mesh
In the case when a low consumption of mortar is assumed per 1 square meter of surface, it is preferable to take expanded metal mesh for plastering the outer walls.
Such a diamond mesh is obtained from a metal sheet after punching holes of the same size in it, arranged in a checkerboard pattern, and then stretching the resulting blank.
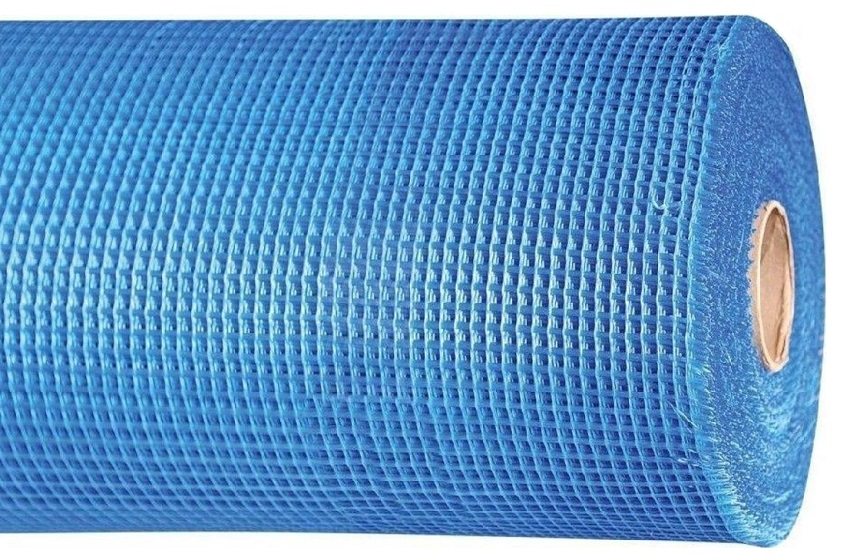
Fiberglass mesh
Along with metal ones, products made of synthetic materials are also used to reinforce walls with a mesh for plaster: polymers, fiberglass, plastic.
Fiberglass mesh is considered universal. Its fabric, being made of glass without alkaline impurities in combination with aluminum as an additional component, has increased mechanical strength. Due to this, it is able to withstand a layer of plaster of great thickness (from 30 to 50 mm). In addition, the fiberglass mesh is resistant to chemical and biological influences, in particular, to decay processes.
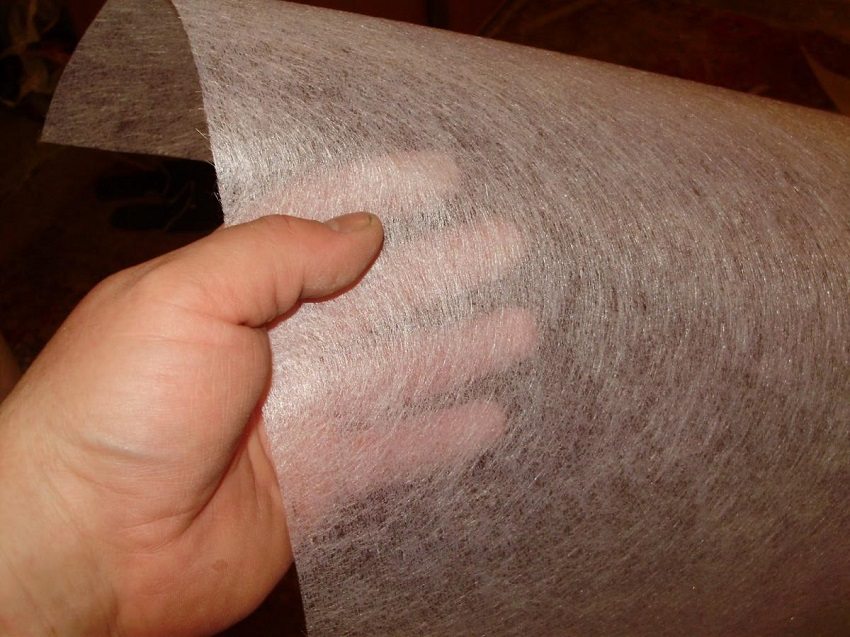
Fiberglass - effective agent against plaster cracking
It is widely used to reinforce almost all walls - especially from aerated concrete, foam blocks, bricks - with thermal insulation from most materials.
Plastic mesh
For plastering walls made of bricks and aerated concrete, plastic mesh is most commonly used, which is best suited for use on heat-insulating layers of foam or foam.
It is important! Foam plaster in most cases is made on a cement base (which has an alkaline reaction), therefore, a mixture that is resistant to alkalis should be chosen to fix the plastic mesh.
Plastic nets for plastering walls made of aerated concrete can withstand temperature drops from -40 to + 100 ° C. The walls are reinforced with a fine-mesh mesh, and the facade and basement of the building are reinforced with a mesh with large cells.
Polymer mesh
Polymer nets can be called a new word in reinforcing materials. The undoubted advantages of this reinforcing fabric are low weight, resistance to chemical attack (especially to the action of alkalis) and corrosion, elasticity and flexibility.
Heavy-duty varieties of this type of mesh are used in the construction of roads and bridges, as they are able to support the load of heavy cement compositions. Flexibility and elasticity make it possible to use polymer meshes for reinforcing complex relief structures: arches, openings, bevels.

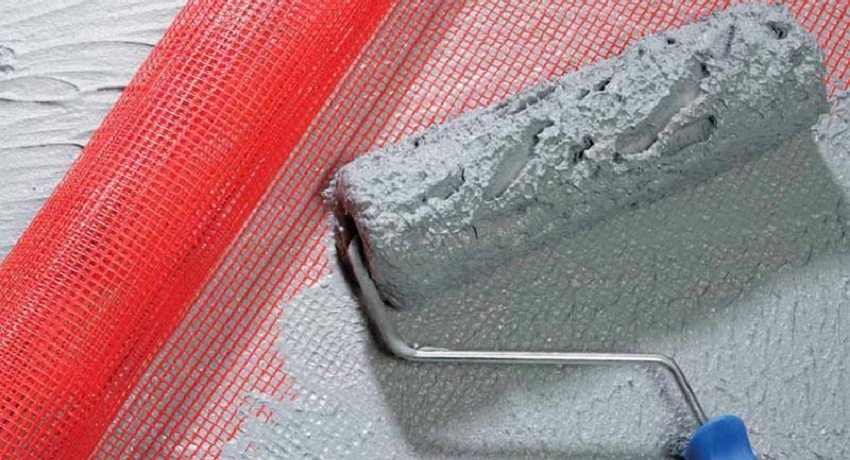
Polymer nets are resistant to chemical attack, which is very important when using a finishing solution with an alkaline medium
Polymer nets do not interfere with the propagation of a magnetic field, due to which they are indispensable for finishing work on conductive communications.
Related article:
|
Polymer nets are one of the optimal solutions for reinforcing walls and facades under plaster made of most existing materials: brick, silicate blocks, foam concrete, aerated concrete.
Which mesh for reinforcement to choose?
The range of currently produced reinforcing materials is very wide, and most of them are quite versatile.

Polymer nets are the optimal solution for reinforcing walls and facades under plaster from most existing materials
Useful advice! Fastening the facade mesh should start from areas that are difficult to handle: from corners, arches, window and door slopes, as well as areas with embossed details.
You can formulate the basic principles of choosing a reinforcing mesh:
- metal meshes are recommended for use with a layer thickness of 30 mm and more;
- for exterior walls or in rooms with a humid microclimate, grids with galvanized or polymer coating are used;
- grids with a movable structure of nodes (chain-link) are relevant for walls made of aerated concrete, gas silicate bricks, wood, changing from the effects of heat, cold and moisture;
- for buildings subject to strong settlement, welded metal mesh is used;
- when applying a finishing plaster coating on insulators from a polystyrene group, plastic or fiberglass nets are preferable. In this case, they are applied to a layer of quick-drying solution;
- a fiberglass mesh is used if the plaster is applied with a layer of less than 30 mm. It is preferable to use it for wall decoration textured plaster;
- polymer meshes are the most versatile, especially their use for reinforcing aerated concrete walls.
It is possible to use most of the above-mentioned reinforcing nets for plastering walls when doing construction and repair work on your own. Photo materials, videos and manuals will provide the consumer with the necessary information.