It has been noticed that the majority of young construction specialists immediately dismiss the phrase "natural ventilation", as images of fans appear in their collective head, recuperators, all kinds of supply and check valves and other parts that are saturated with any scheme of mechanical ventilation. The problem is that comparatively young, but rather experienced foremen rarely see this very natural ventilation of buildings as a model (most of them are self-taught).

Proper arrangement of natural ventilation is an easy way to ensure a healthy microclimate in your home
Content [Hide]
The advantages and disadvantages of natural ventilation
Both natural and artificial ventilation have both advantages and disadvantages. To understand why natural ventilation should be preferred over mechanical ventilation when installing with your own hands, it is necessary to consider in detail the principle of the first device.
Until the 90s, the ventilation device in residential buildings was natural, but most did not really find it: the fashion for plastic windows, all kinds of insulation and elements of a "smart home", the natural ventilation scheme was pushed to the periphery, where it was built in the old fashioned way for decades.
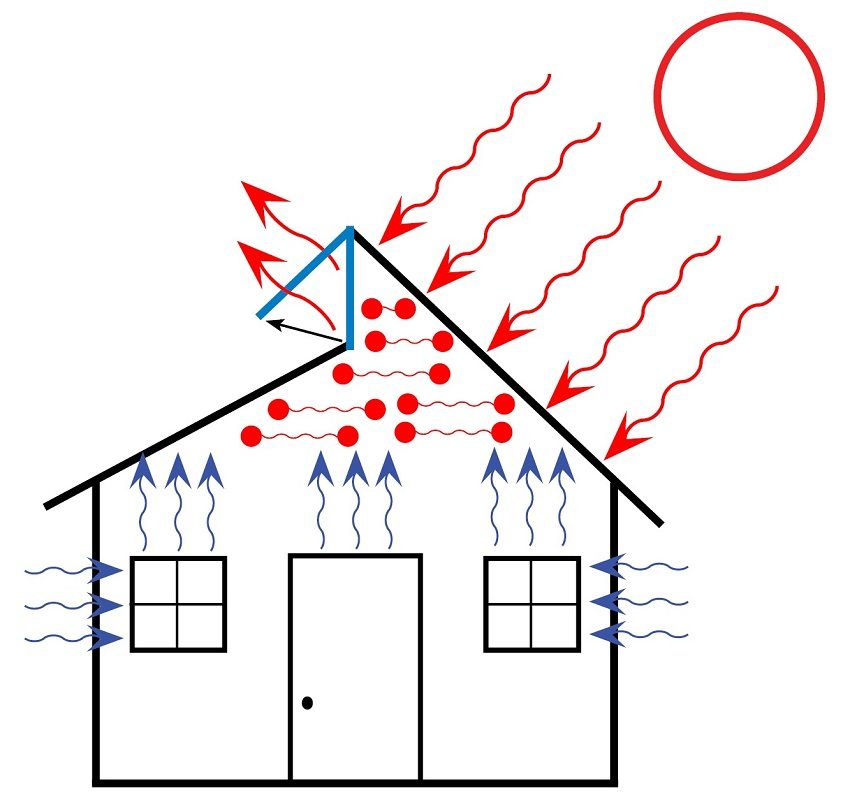
Interesting! Natural ventilation is a ventilation system in which there is no forced motive force: a fan or other mechanical device. Air draft in such a scheme arises due to the pressure difference, and the working principle of natural ventilation is based on the difference in temperature indicators in the building and on the street. The more significant this difference, the better the air exchange in the premises is provided.
Wooden windows blew through slightly, a half-centimeter gap under the door provided natural draft. Required 30 m3/ hour per day were provided by themselves, so they rather looked for a way to reduce the inevitable supply ventilation drafts.
The advantages of properly organized natural ventilation are obvious: it does not require special costs, works by itself and softens the temperature regime in the room. There are also enough disadvantages: the old ventilation was provided with old technologies. Now, especially when trying to do everything with your own hands, you need to carefully calculate the air flow, otherwise you can fall into an extreme: drafts or a lack of oxygen will be provided.
It is believed that such work should be done by a master.But the low cost of natural ventilation in comparison with artificial allows you to establish it yourself. In case of an error, it will be much easier and cheaper to fix it.

Properly organized natural ventilation does not require special costs, it works by itself and softens the temperature regime in the room
Types of natural ventilation
According to the principle of the device, natural ventilation is divided into two main types:
- Channelless natural ventilation.
- Duct natural ventilation.
Channelless ventilation includes manual ventilation: fresh air is supplied through open vents or windows in rooms and in the kitchen, and exhaust air masses are removed through exhaust grilles in the kitchen and in bathrooms.
Important! It is possible to calculate natural ventilation only if its system is implemented in a duct method.
For a channel-type natural ventilation device, it is necessary to make a duct system in the walls and ceilings. The calculation of the circuit and its installation is quite feasible with our own hands.
Natural ventilation: calculation principles
If you want to make a ventilation system in the house with your own hands, you need to make a simple calculation of natural ventilation. Knowledge of SNiPs is not required - the basics of arithmetic and a few basic constants are enough.
Helpful advice! The intensity of air exchange is regulated by five SNiPs common to the entire Russian territory, and a sufficient number of regional standards. But to calculate the natural draft of ventilation in a private building, you can do without them.
You need to know that an inflow of 30 m is considered the norm3/ hour per person, plus another 30 "just like that" for the kitchen. Therefore, it makes no sense to think about the area and layout of the building if it is a private house. Depending on the latitude, the standard thrust can be taken equal to 20 m3/ hour for the north up to 40 m3/ hour in the south. In the north, the air is much denser and colder, so it is undesirable to unnecessarily load the heating with intensive air exchange. In the south, air density is lower, and human metabolism is faster. All doors should have a gap of 1 to 2 cm at the bottom, respectively.
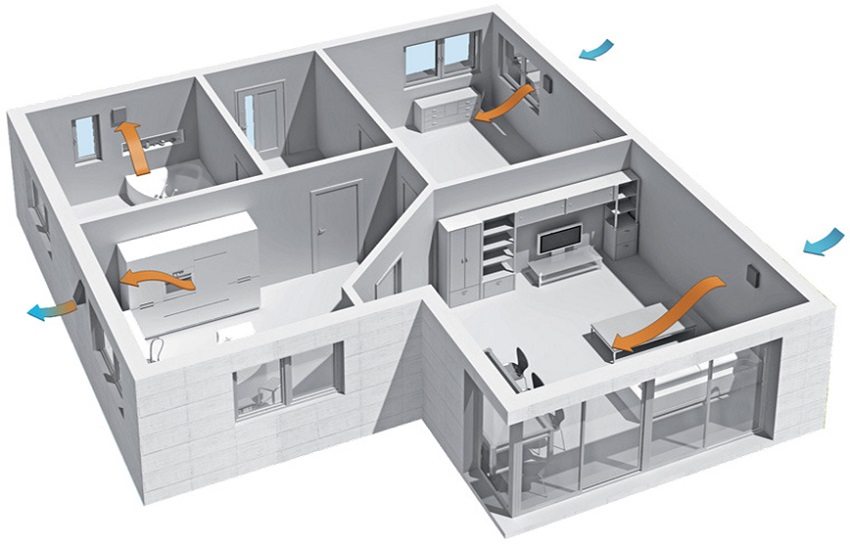
Conventionally, all premises are divided into "dirty" - this is a kitchen and a bathroom in the first place, then utility rooms, storage rooms, insulated basements and capital attics. "Clean" are all living quarters.

To arrange natural ventilation of a channel type, it is necessary to make a duct system in the walls and ceilings
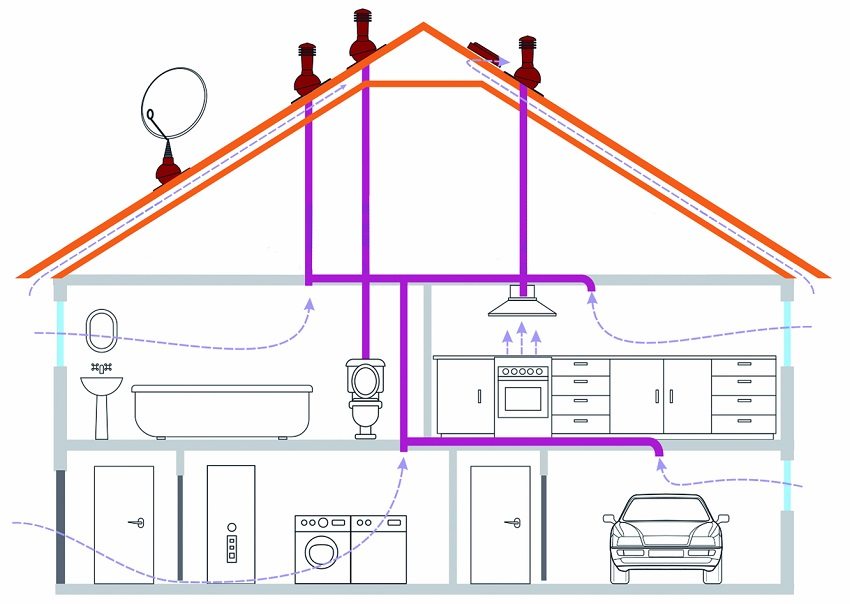
If we discuss the question of how to make natural ventilation very briefly, then the principles are very simple. Air is removed from dirty rooms using an exhaust hood. In clean rooms, they equip an inflow, but in no case install an exhaust hood: this will only provide a draft and a large loss of heat in the cold season. The air must pass through all rooms in the building in a common flow (or several "parallel").
If any work is often carried out in the garage, then both supply and exhaust are needed there. And do not forget about the "trunk" for the exhaust pipe with access to the street.
"Dirty" premises
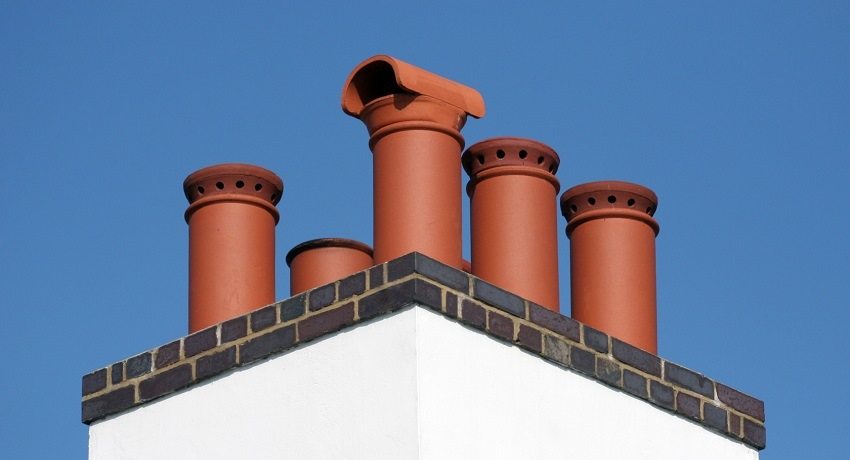
Exhaust natural ventilation in the kitchen and in the bathroom should be more powerful due to odors, moreover, these rooms are always located as far as possible from residential ones. That is, in any case, it is at least necessary to equip vertical channels for both the kitchen and the bathroom, and the higher they are, the better.In 99% of cases, typical layouts of private houses have already been tested according to the most convenient scheme: all channels of each room are brought together into one common shaft located in the middle of the building. This will not only reduce the loss of available space, but the shaft will also exit at the highest point of the roof, and the height will provide traction quality. An additional plus: you will not need to make too high pipes on the roof - this will facilitate their maintenance.
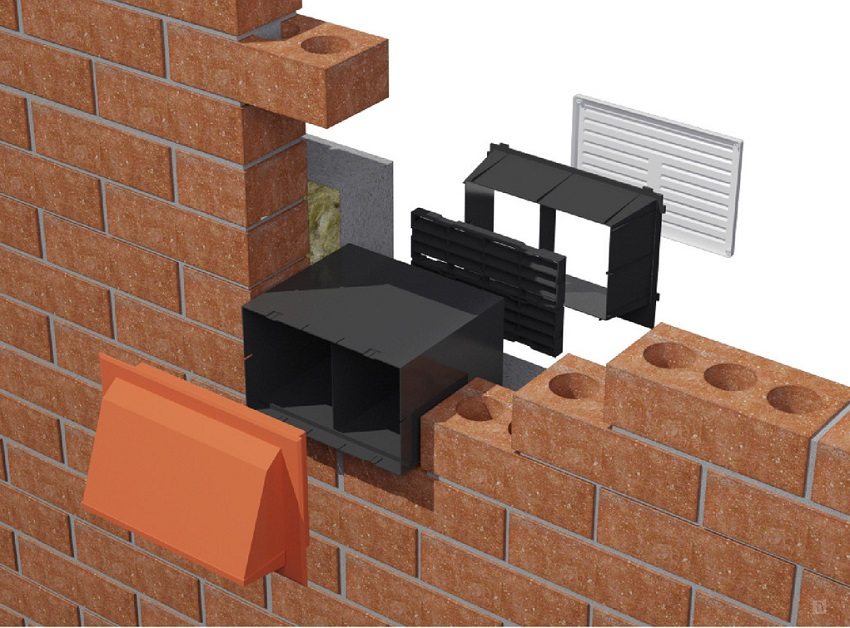
If the house is brick, then there is an even more logical and cheaper option: the mine itself is the channel / canals. And if frame house, wooden or it is simply reconstructed (that is, a brick shaft in the middle of a building cannot be made without a complete "defeat"), then usually plastic pipes made of polyvinyl chloride or sewer pipes are used. There is no difference, since the temperature regime of the pipes will be almost natural.
The shaft-pipe brought out to the roof of the building must be sheathed with insulation. This will prevent the pipe from collapsing due to temperature changes - in any case, the hood from the kitchen will have a significant difference with the external atmosphere, and it is the inner surface of the mine that will expand. At the same time, this will significantly reduce the amount of condensate. A cap must be made on top of the pipe to protect it from snow and rain.
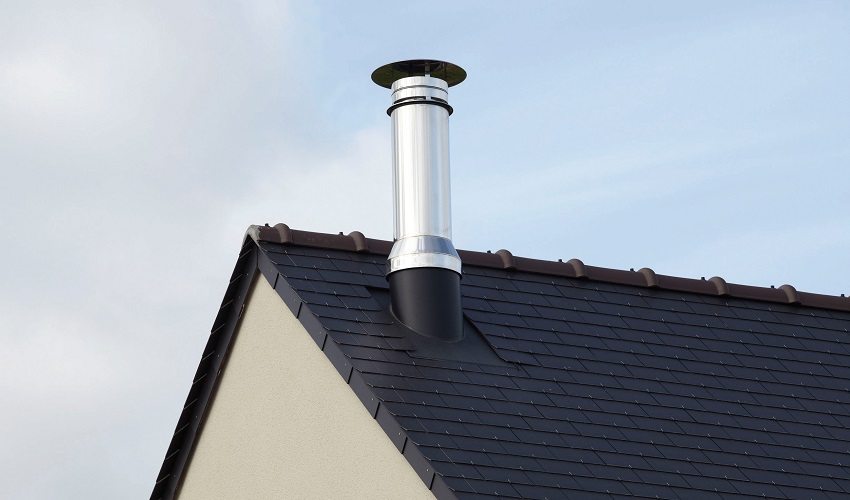

The chimney is brought out to the roof of the building and covered with a cap to avoid precipitation
If the house is not high or located in southern latitudes, then the thrust may be insufficient. Under different weather conditions, a reverse draft effect may occur, then the presence of a real fireplace or even a water heater with its own built-in outlet can lead to unpleasant consequences. In this case, fans are installed at the outlets of the channels, which will turn on when using the hood in the kitchen, water heater or fireplace.
"Clean" rooms
In residential premises, only supply valves need to be installed, and even then not always. The air should go from the natural ventilation inlet valve to the door, but not circulate inside the room - the hood cannot be installed, as it will provide a constant, but invisible draft.
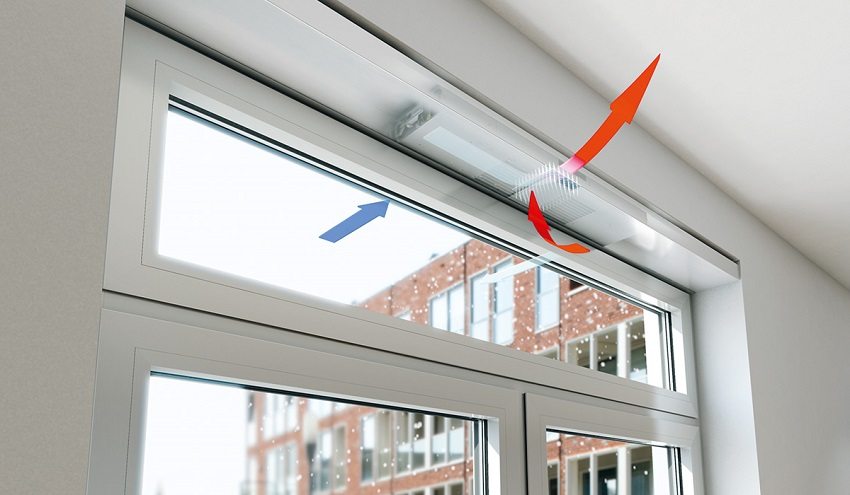
First of all, it is necessary to pay attention to the windows and vents - this is the main natural flow of air. Classic wooden windows and with closed vents let in from half to normal air volume each. But modern frames are impregnated with a fireproofing compound and repeatedly coated or even kept in varnish. The modern composition of rubber and tin upholstery for glass turn such windows almost into a plastic double-glazed unit - complete thermal and sound insulation. It remains to use the vents.
But the vents give too much heat loss and are too discretely regulated by the serif latch. Therefore, there are frames into which ventilators are inserted, allowing air to pass through the microchannel system, almost like in a recuperator, which gives a constant air flow with a temperature increase of 20 ° C.
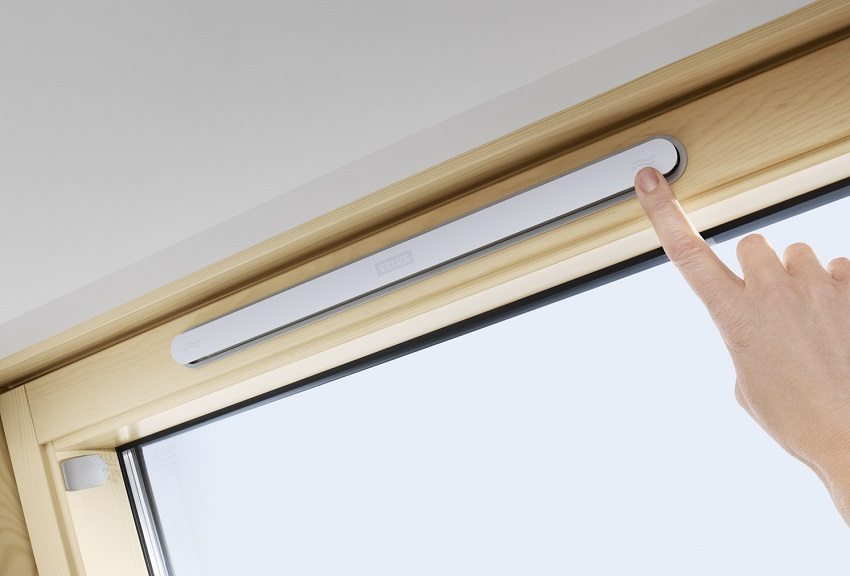
However, if you want a more accurate (10-20 times) regulation of the incoming air flow, valves for the supply flow can be installed under the ceiling in the outer wall. In the old models, they are equipped with a lid with a vigner, and in the new ones they use the already familiar shutters. Their convenience is that, unlike the vents, on each of the valves you can set the required minimum gap once, after which the vents will only be required on a particularly hot day.
Garage, basement and special rooms
The garage is characterized by an abundance of too strong odors if used regularly.In theory, it would be nice to equip it with a forced draft, but if the temperature inside is not at all important, then it is quite possible to establish a natural one.
Related article:
|
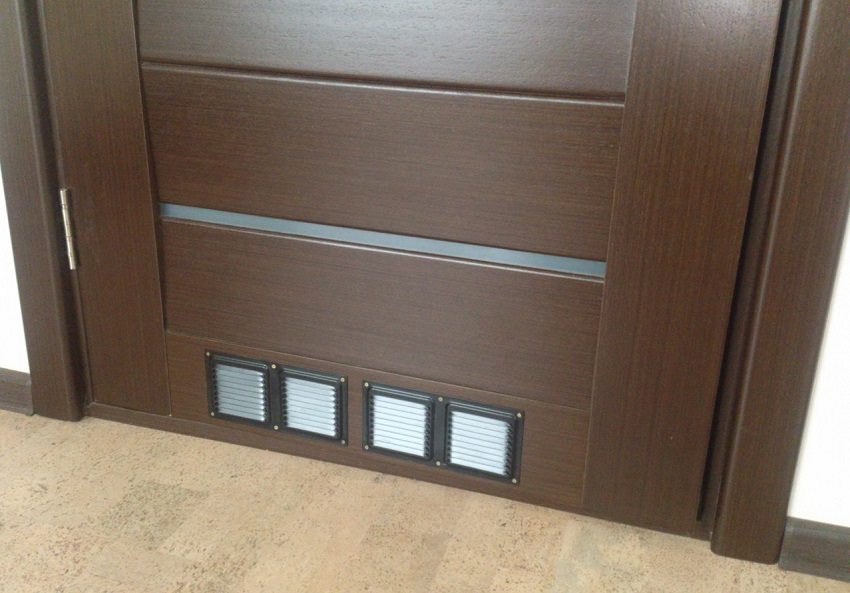
At one of the walls we make several holes at a height of 30-50 cm under the ceiling level for inlet valves with curtains. On the opposite side, one or more outlet valves are installed, naturally also from above.
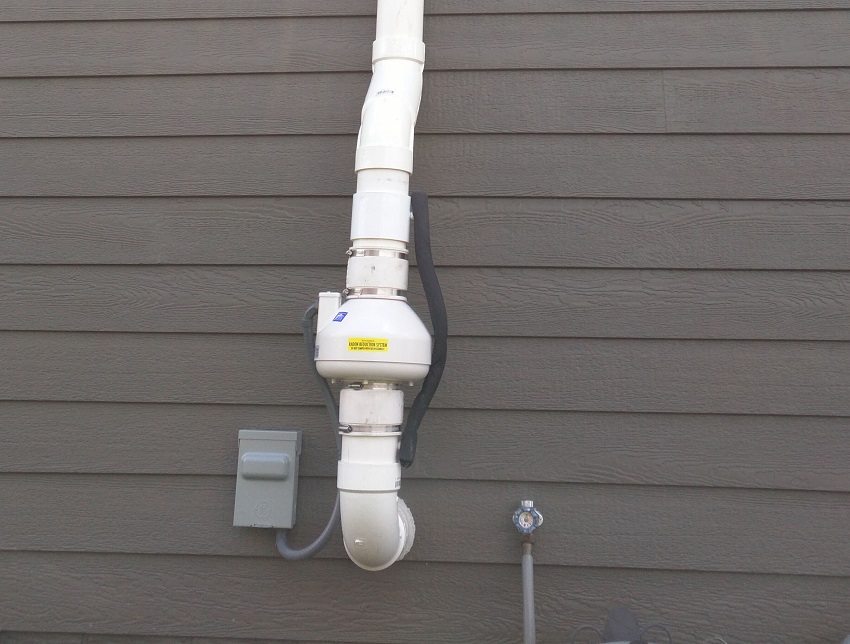

If the natural draft is not enough to ensure ventilation, then it can be forcibly increased using fans built into the air duct
The supply valves are located on top, so inside the garage we install duct pipes to them vertically downwards, and it would be nice to stuff glass wool inside the pipe. Of course, this is a "recuperator" from the times of dinosaurs, but in winter, autumn and spring, a few additional degrees of air temperature can provide a quick warm-up of the engine and non-freezing of locks.
Check valves for natural ventilation are arranged a little more complicated than classical ones: it is also useful to connect a short pipe down to them (20-30 cm will be enough) and insert a drain valve at the bottom. In winter, during active work in the garage, condensation will quickly accumulate inside.
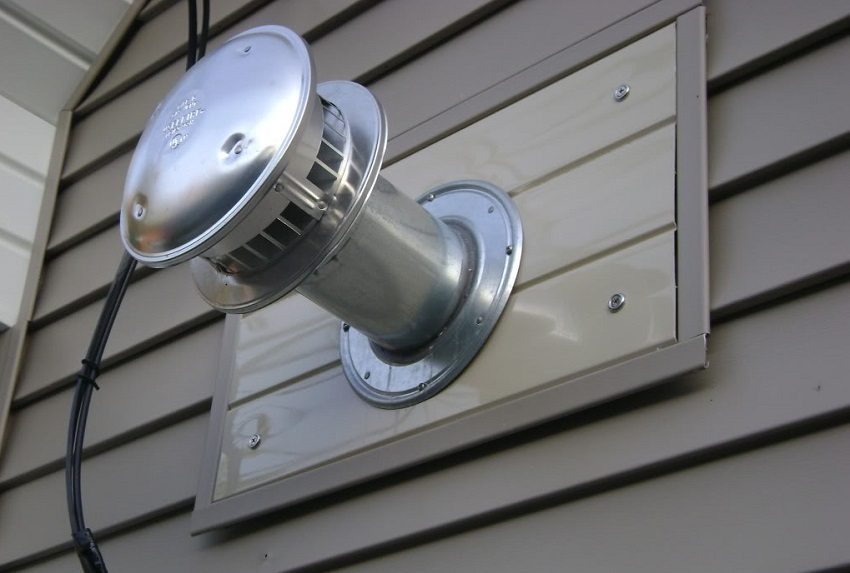

The damper for natural ventilation is equipped with a non-return valve to regulate the direction of the air flow
With a fireplace and water heating, everything is simple - cold outside air is supplied from below under the fireplace itself to the flame. This will improve oxygen flow to the flame and provide excellent traction. It's also simple with vonografi: the pipe from the supply valve should stretch to the far corner from the tank and release air at the very floor - there is no point in taking heat away from the water heater.
The basement can be both technical (workshop) and "food". It is logical to "design" the workshop as a garage, and the food cellar should be cool, but dry. To do this, the inlet valves are inserted into the floor of the first floor behind the grating - the warm air of the living room will provide the temperature in the cellar by only 3-5 degrees below.
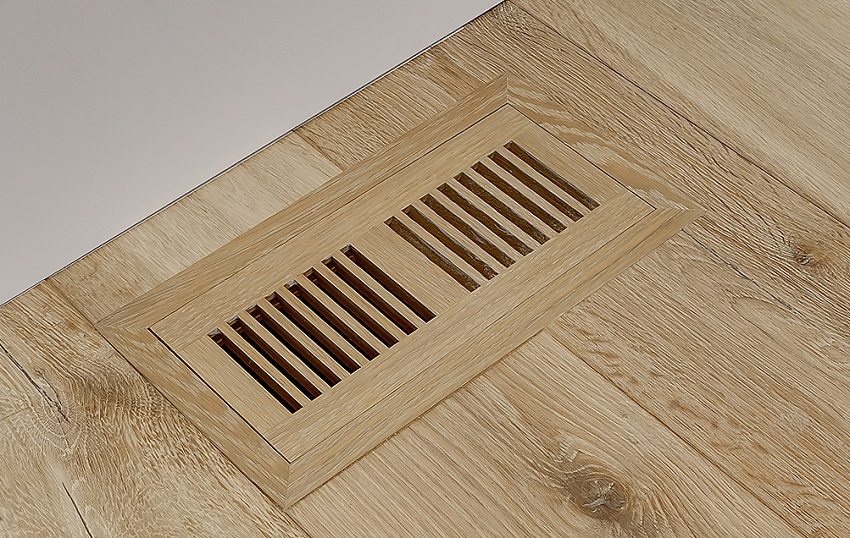

For ventilation of the basement, you can install ventilation grilles in the floor of the first floor
As can be seen from the above, there is nothing in principle complicated in the device of natural ventilation with your own hands. Of all active equipment, in some cases only a fan is required. But there is one more little trick, natural for a brick mine, but which will have to be done in a wooden or frame building: if all pipes from all rooms are brought together for "exhaust", then the total pressure difference between the internal and external atmosphere will be greater, which will give more a little extra traction.