The requirement for reliable protection of a person from damaging effects electric current has always outstripped the possibilities of science and technology to create protective devices that satisfy this goal. Today, innovative developments in the electrical industry fully meet all the criteria for devices of this type. The article reveals the issue of such a device as an RCD: what it is, its purpose, principle of operation, choice and application.
Content [Hide]
Means and methods of electrical protection: modern devices and features of their work
As soon as the use of electric current entered our lives, it immediately became necessary to protect against its damaging effects on human health. First of all, this is the implementation of insulation of conductive parts of the wiring and parts of current receivers.
But complete isolation is impossible, since technological breaks and contact groups are present in any electrical circuit. There is always a possibility of disruption (destruction) of the insulating layer of conductive elements and their mechanical damage, and most importantly - statistical regularity in violation of safety regulations, instructions and rules for the operation of electrical equipment, both at the production and household level.
Electrical protection: insulation and grounding
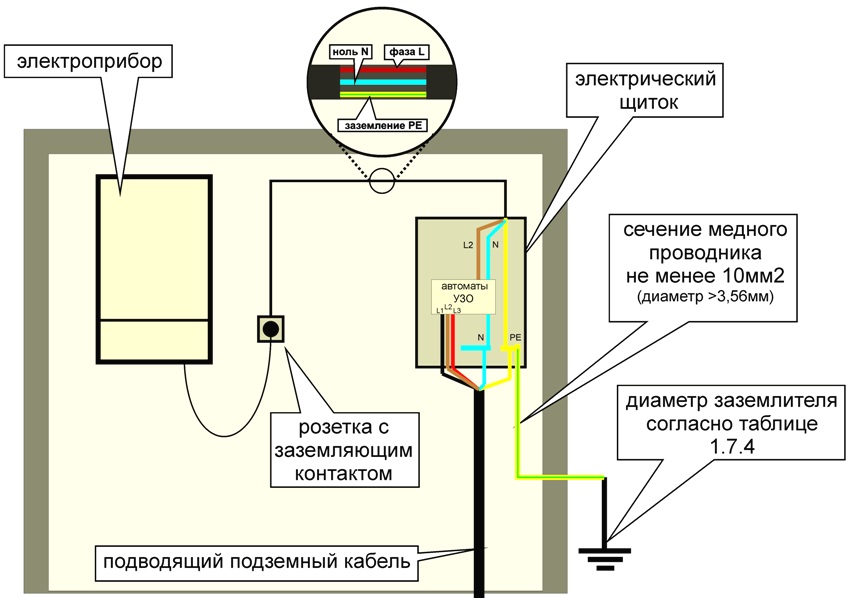
One of the most effective ways to protect against the damaging effects of electric current is to organize a ground loop. The ground loop is an artificial conductor connection to the ground (the so-called PE conductor) of neutral conductive housings or parts of electrical mechanisms, with a resistance not exceeding 4 ohms. The listed elements of electrical equipment may be energized due to a short circuit to the case of a phase conductor or lightning current.
The main purpose of the ground loop device is to exclude the possibility of electric shock to a person or an animal in case of touching the body or part of the electrical equipment mechanism, which is energized due to a phase electric current short circuit on them.
Note! In AC networks with grounded neutral and voltage up to 1 kV (this is the format of residential power supply), grounding as the main protection against electric shock with indirect contact is not used, since it is not effective.
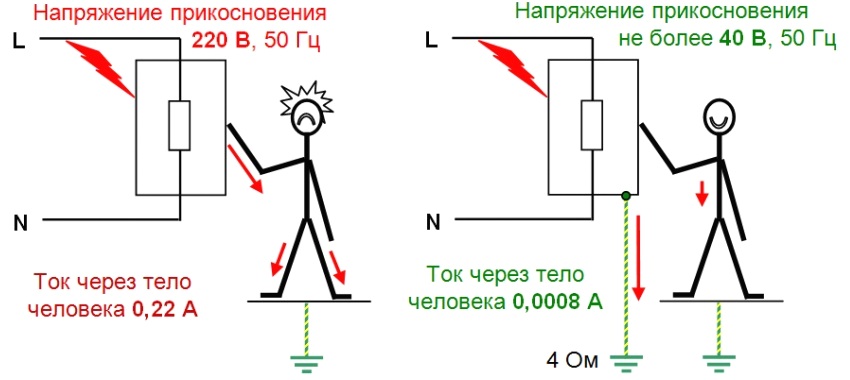
The passage of electric current through the human body in the event of an impact in a system with ground (right) and without ground (left)
The problem of the most effective protection against the effects of electricity on a person was solved by the so-called differential current devices (UDT) - this is a large segment of control and protective devices for various purposes and design features. The classification of the UDT segment is quite extensive: from the control method, type of installation and the number of poles, to the possibility of regulation and time delay of the tripping differential current.
Consider what an RCD is. The decoding of this abbreviation is a residual current device. Requirements for the installation and use of UDT are given in the supplemented editions of the PUE - rules for the installation of electrical equipment and in the IEC 60364 series of standards for electrical installations of buildings and the effect of current on humans and livestock IEC 60479-1.
Historical background of RCD development
Germany was the innovator in the development of RCDs. The first operating prototype of the protection device was designed and manufactured in the thirties of the last century. The smallest possible differential current transformer was used as a leakage current sensor, and a polarized magnetic relay with a sensitivity of 100 milliamperes (mA) and a response rate of no more than 0.1 seconds was used as a control element.
The threshold for recording the differential current in the prototype was about 80 mA. At that time, it was impossible to develop a control relay with a sensitivity of less than 80 mA due to the lack of materials with the required electromagnetic characteristics. And only in the middle of the twentieth century a new constructive solution for the RCD was proposed. The design took into account mechanisms to eliminate false positives from discharges during a thunderstorm and significantly increased the differential current sensitivity to 30 mA.

The first models of protection devices included a differential current transformer and a polarized magnetic relay.
The overall dimensions of the RCD have also undergone changes: from the size of a parcel box to a modern format that can be installed on a DIN rail in modern electrical cabinets.
Technical experts in electrical and electronic engineering are already predicting the future. They firmly believe that artificial intelligence will soon be in charge of systems such as protection against electric shock.
It will be able to perform not only measuring and control functions, but also by video and audio monitoring of the object given to it, make instant decisions on any accidental situations and, if necessary, notify the rescue services.
RCD: what is it and how it works
Residual current devices (RCDs) are among the most popular of the protective UDTs operating in a domestic environment. The RCD works as a protector of a person from electric shock and as a preventive mechanism to prevent accidental ignition of wiring cables and plug-in cords of electrical appliances.
The functional idea of the device under consideration is based on the laws of electrical engineering, postulating the equality of the incoming and outgoing currents in closed electrical circuits with active loads.
This means that the current flowing through the phase wire must be equal to the current flowing through the neutral wire - for single-phase current circuits with two-wire wiring and that the current in the neutral wire must be equal to the sum of the currents that flow in the phases for a three-phase four-wire circuit.
When in such a circuit, due to accidental touch of a person to the uninsulated parts of the conductive elements of the circuit or when the bare part of the wiring (due to damage) contacts with other conductive objects that form a new electrical circuit, a so-called current leakage occurs - the equality of the incoming and outgoing currents is violated ...
This violation can be registered and used as a command to disconnect the entire electrical circuit. On this process, the RCD was designed. And the "leakage" current in the framework of electrical engineering began to be called differential current.
The RCD can register very small "leakage" currents and act as a circuit breaker mechanism. Purely theoretically, the principle of operation of the RCD looks like this (where Iin - input current of the neutral wire, Iout - phase wire output current):
- Iin = Iout (system balance without disturbance, RCD in standby state);
- Iin > Iout (the balance of the system is disturbed, the RCD registers the appearance of a differential current and turns off the supply network).
RCD will definitely protect
When an RCD is installed in the power supply network, this means that protection is provided against:
- shorting the phase wire to the body of the appliance. In a large number of cases, these are heating elements of washing machines, water heaters and heaters. Moreover, breakdown can occur only when the thermal element heats up under the influence of current;
- improper wiring, when unscrupulous electricians bricked up the "twisting" of wires in the plaster without using a back box. If the wall is wet, a differential current will leak into the wall from this twist and the RCD will de-energize the line all the time until the plaster is completely dry or the connections are properly repaired;
- improper installation in the electrical panel, when seemingly small but "useful" changes made to the circuit change the current distribution and lead to the loss of high efficiency of the device. This will be discussed in more detail a little later.
The RCD can be triggered for reasons that are not striking from the first inspection of the connection diagram for household appliances. If you use a gas stove with electric ignition of gas, or a washing machine is connected with a hose in a metal case to a water tap, or when neighbors have grounded the water supply or heating system, then a current leak will again appear in the electrical circuit, due to which it will work RCD. In such cases, a thorough engineering analysis is required.
Boundary conditions of the RCD
The rules very often have exceptions. This principle has not bypassed the universal qualities of the residual current device in question.
The RCD will not react when a person or animal is energized, but there will be no earth fault current. Such a case is possible when touching simultaneously the phase and neutral conductors, which are under the control of the RCD, or with complete isolation with the floor. RCD protection in such cases is completely absent. An RCD cannot distinguish between an electric current passing through the body of a person or animal from the current flowing in a load element. In such cases, safety can be ensured by mechanical protection measures (complete isolation, dielectric housings, etc.) or a complete de-energization of the electrical appliance before its technical inspection.
The RCD, completely dependent on the supply voltage suitable for the network object, is in working condition only if the specified network is fully operational. The situation can become dangerous when the neutral wire breaks “above” the RCD, and the phase wire remains energized. Then, in the wiring, the phase wire can become a factor of electric shock, and the RCD, due to its own incapacity, will not be able to turn off the mains power.
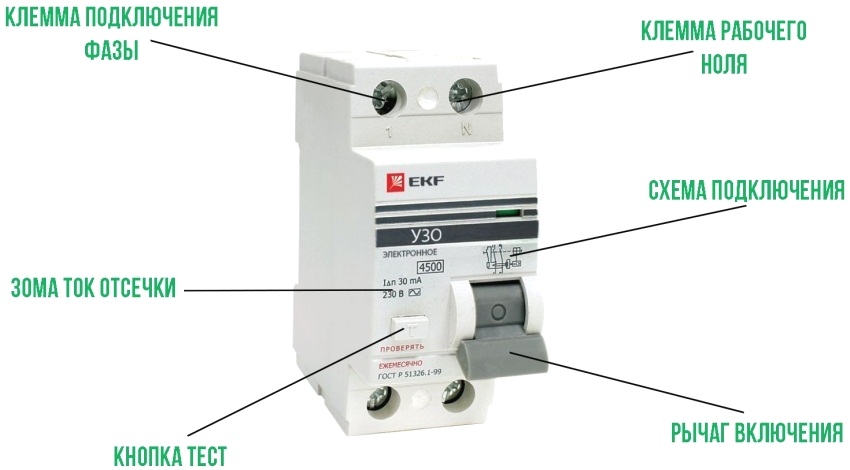
The RCD can "hang" in the standby state if the main contact rod is jammed in the solenoid or when the secondary winding of the control device fails, and does not work at the right time. In order to check the operating state of the RCD, there is a test mechanism. If you regularly carry out a test check of the device (and for this you just need to press the "T" button - test), the risk of breakage of the RCD will have a minimal probability.
Application and how to connect an RCD
The main application in the domestic environment is the use of a large number of connected devices and equipment in electrical groups of bathrooms, kitchens and outlet groups. This does not mean that it does not make sense to use an RCD on a common incoming network. This selective scheme is dictated only by the efficiency of management and marketing expediency, since RCDs for small currents are much cheaper at the price of devices with higher power.
However, in some cases, if we consider dormitories, clubs, etc., it will be more reliable to use a general selective RCD due to the massive and simultaneous use of almost all elements of electrical equipment. The selective type RCD differs from the usual one by the long delay time of the tripping differential current (i.e. the trip time) and is one of the most used devices. When an ordinary local RCD is triggered in any circuit, the general selective RCD does not turn off all the wiring at once, but allows you to stop the power supply of only a separate group.
For example, if a breakdown of the equipment insulation occurs at a disco and the case (for example, the amplifier) is in contact with the phase wire, then at the moment the operator touches the amplifier, the local RCD is triggered and disconnects only the group of amplifying equipment, and the selective general RCD will not turn off all power and such groups like general lighting, toilets and cafes will work as usual.
The mechanism for connecting an RCD to an operating network is similar to connecting a circuit breaker with the only difference that when a single-phase machine requires tightening two terminals, then on an RCD - four.
If, when a person touches a bare section of a wire or the body of equipment that is under phase voltage, the electricity instantly turns off, then the RCD has worked.
Important! In AC systems, additional protection by means of an RCD should be provided for outlet groups with a rated current of up to 20A (washing machines, boiler, ovens, etc.) and mobile (portable) equipment and power tools with a rated current of up to 32A, which are used outdoors.
Basic principles of the RCD mechanism and comparative analysis of analogues
The physical processes occurring in the mechanisms of operation of many modern electromechanical or electronic devices may be completely incomprehensible to us. Not everyone has knowledge of engineering and technical disciplines and, naturally, is unable to understand and describe the physical basis of the principles of operation of a particular device. But the principle of use (operating rules), built on safety elements, makes it possible to apply the most complex inventions in our daily life.
Related article:
LED ceiling lights for home: the essence of harmonious lighting
Luminaire selection criteria.Types of overhead lighting devices. Types and prices of built-in models. Review of LED chandeliers.
Each device has a technical passport, in which the purpose and the principle of operation are always described in an easy-to-understand language, and whenever it is required, measures for installation, connection and correct operation are prescribed in it. In our case, an attempt was made to describe the principle of operation of a trip protection device (RCD) in the most accessible way and to give the reader the opportunity to independently make decisions in choosing one or another device, if necessary.
The principle of operation of the RCD and design features
To perform its protection function, the device consists of a differential current transformer minimized in size, a control "tracking" magnetoelectric relay, a control solenoid for the main contact group and additional diagnostic elements - the "Test" button and elements of actuation mechanisms.

RCD consists of a differential current transformer, a magnetoelectric relay, a solenoid and a "Test" button
The physical side of the work is as follows.
When the RCD is turned on (pressing the contact closure button), the solenoid turns on and holds the rod of the contact group in the same way as an electromagnet. Since at the same moment the terminals of the winding of the solenoid itself and the terminals of the supply wires come into contact. But in the power circuit of the solenoid, transit opening contacts are installed, which are controlled by a magnetoelectric relay and the relay is given the function of self-disconnecting the RCD.
The outgoing and incoming current of the network, flowing in the corresponding windings of the transformer, due to the generated EMF (electromotive force), creates two equal, but oppositely directed magnetic fluxes in the magnetic circuit (core).
Due to the complete compensation of magnetic fluxes, no EMF occurs in the secondary winding wound on the core and supplying the control relay, and the relay is in a passive state.
At the moment a person or an animal touches the bare part of the phase wire or the case of any household appliance, to which a phase breakdown has occurred, an additional differential current will flow through the input winding of the transformer.
Violation of the equality of the incoming and outgoing currents instantly creates an uncompensated magnetic flux in the transformer core. And as a consequence, the instantaneous appearance of EMF in the secondary winding connected to the relay as its power source.
The relay, having received power, immediately triggers and cuts off the power to the solenoid (transit terminals open), which holds the main contacts in a closed position.
The contacts open, the solenoid de-energizes and releases the spring-loaded rod of the contact group, and the mains power supply is interrupted. The more sensitive the monitoring relay is to small values of the differential current, the more effective the protective function of the RCD.
Note! Protection functions such as disconnecting the power supply in the event of a short circuit and overcurrent are not provided in the RCD. In practice, the installation of an RCD usually involves the joint use of a circuit breaker ("machine"), directly designed for the possibility of short circuit and current overload.
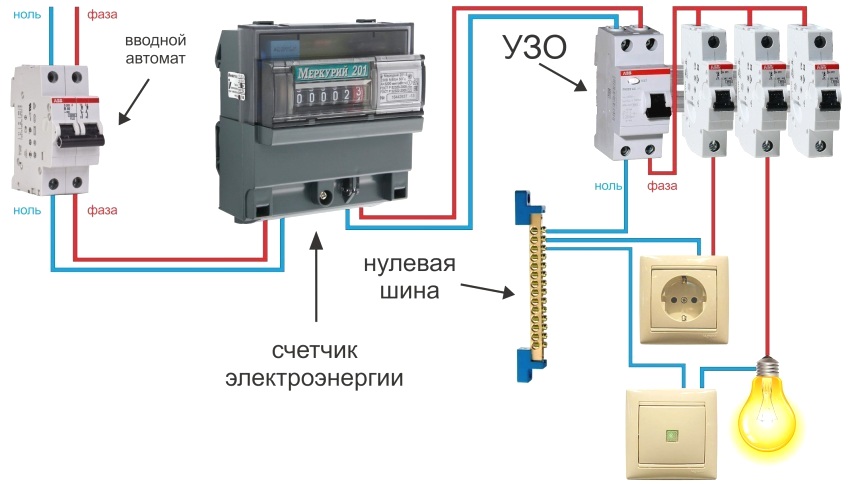
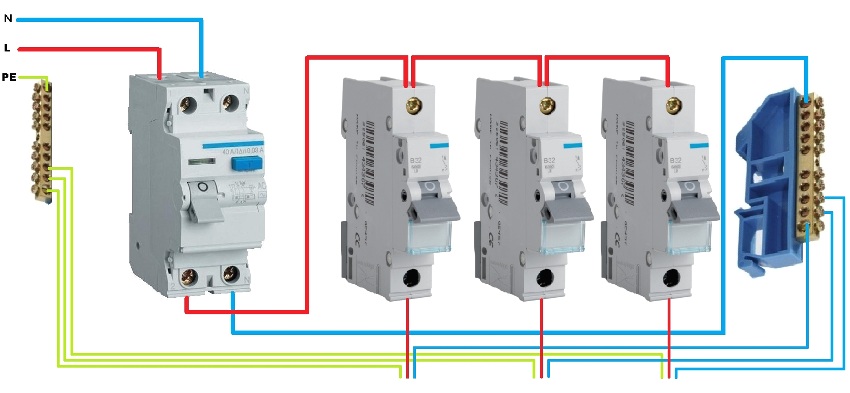
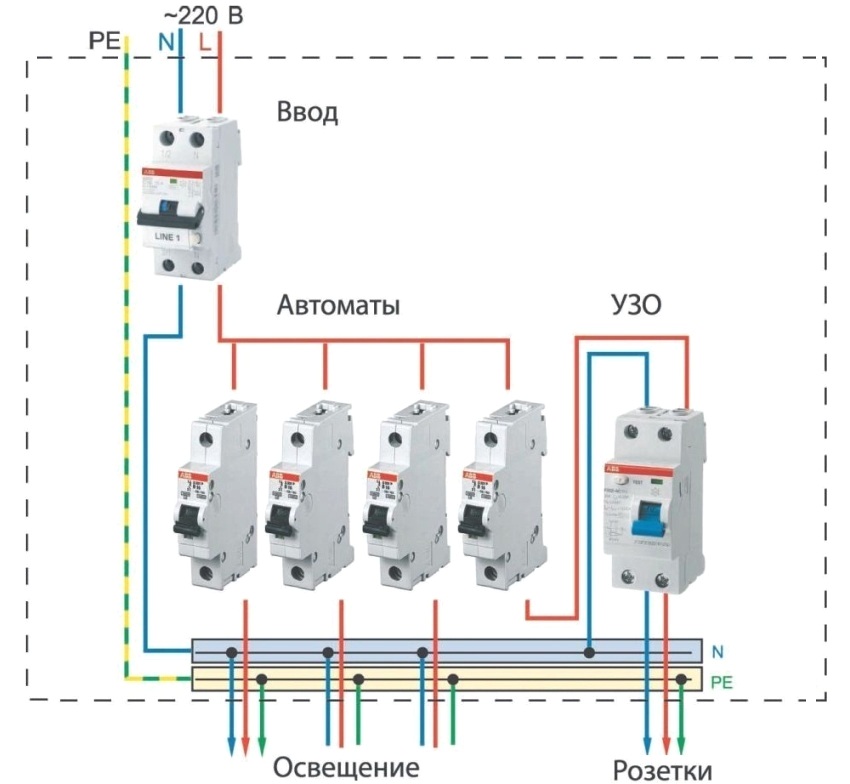
The correct connection diagram for the RCD and the machine. Installation errors
Both devices have the same mounting design for installation in control panels for electricity metering and distribution. The task is reduced only to the correct connection to the mains and to each other:
- Basic option: central machine → metering meter → RCD.
- Preferred: central machine → metering meter → selective type RCD → group machine → group RCD.
In this case, the recommended connection sequence is shown, but it is also necessary to take into account the correctness of the connection diagram itself:
- under no circumstances connect the neutral wire to the ground terminal after it leaves the RCD. In this case, periodic occurrences of a differential leakage current are possible, leading to false positives;
- incomplete phase connection of the RCD. If the neutral wire from the supply network passes in transit past the RCD, then the arising current in the neutral wire will be perceived as differential, which will lead to the constant operation of the device;
- do not allow the connection of the neutral wires of the sockets, which are under the control of the RCD, with the ground wire (terminal). In this case, even an outlet that is not connected to the consumer will create a differential current;
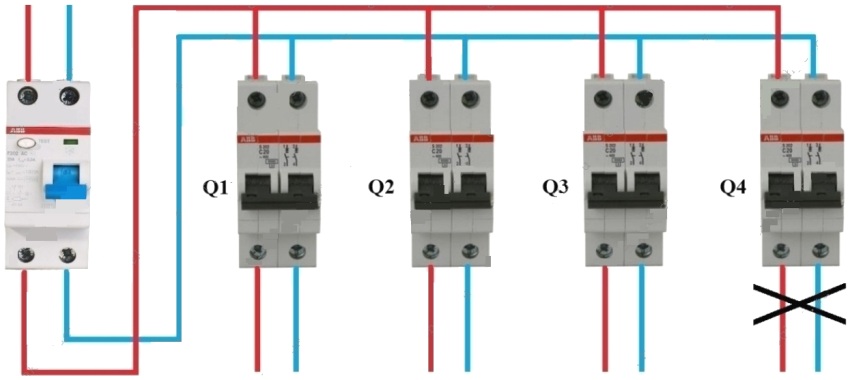
- with group use of RCDs, neutral wire jumpers on the incoming terminals are not allowed. This will trigger all RCDs at the same time.
Useful advice! When connecting a four-pole. those. three-phase RCD into a similar network, it is necessary to strictly comply with the phase marking with the marking terminals of the device. Otherwise, the test mode will not be objective.

When connecting the RCD, it is impossible to allow the connection of the neutral wires of the sockets to the ground terminal
RCDs with extended functions
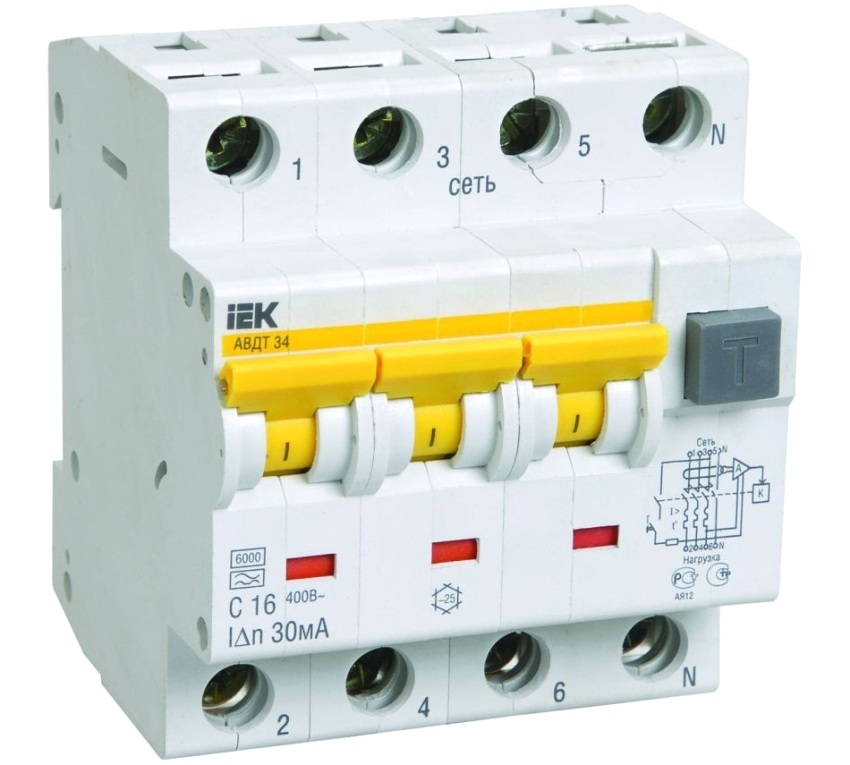
The market for residual current devices (residual current devices) is very diverse. It is necessary to single out from a number of analogs competing with RCDs the so-called differential automatic device, belonging to the class of circuit breakers controlled by differential current - RCBO.
To answer the question in an accessible form: difavtomat, what is it? - it is necessary to remember that its main feature is the combination of the main function of an RCD and a circuit breaker. Also, the difference between an RCD and a differential machine is that the RCD itself needs protection against short circuits in the network and overcurrent (naturally, for this, a circuit breaker is installed in a pair), and the difavtomat is able to protect itself.
It should be noted that new RCBO models have entered the market - electronic and with an auxiliary power supply. They differ from electromechanical structures by the presence of an electronic board with a differential current amplifier, which makes it possible to record leaks of the order of 10 mA and operate even if the neutral wire of the incoming network is broken, when the phase wire remains energized. A conventional RCD or RCBO will not work in such a situation when a person comes into contact with an open phase section.
Another novelty in the line of residual current devices is the so-called multifunctional protection device. What is UZM becomes clear from familiarization with its purpose. This device serves to completely turn off the equipment when the voltage parameters in the network go beyond the operating limits (less than 180V and more than 260V), as well as to protect the operating equipment from voltage surges that "burn" the windings and electronic elements of devices. These surges can be caused by electromagnetic pulses or short circuits of phase wires to zero in a three-phase network.
RCD or differential machine: how to distinguish and what to choose
There is no unambiguous algorithm allowing to give preference to one or another device. The reason is the multivariate feature of the choice. Consider the main factors that affect the choice of an RCD or RCBO.
Is it possible to place this or that device in the main panel... In practice, the overall overall size of the RCD and the circuit breaker is larger than the overall size of the difavtomat.
What is the purpose of making changes to the electrical circuit... If it is necessary to protect high-power equipment (kitchen stove, boiler, washing machine, etc.) from a possible "shock" by electric current, a differential automaton, which clearly monitors the load current, is optimal.
If it is necessary to protect against electric shock for a group of outlets or a lighting line, in which the power can be increased over time, it is advisable to use an RCD. The RCD has a large power reserve, and the differential automatic device, due to overload, will need to be replaced with a more powerful one.
Qualitative assessment... Practice has proven that devices that combine many functions of various devices are very often inferior in quality to single devices. This also applies to such a multifunctional device as a differential circuit breaker, which is inferior in quality and service life to an RCD and a circuit breaker.
Breakdown situation... In a situation where an RCD or a circuit breaker stops working, either one or another device needs to be replaced. But when the differential machine does not work, even due to failure of one function, you have to replace it with a new one. In this case, the costs are much higher.
Power supply stability... If the RCD fails, it is enough to install jumpers between the circuit breaker and the power supply network (bypass the RCD) and the power supply is restored. But if a difavtomat breaks down, you will need either a spare difavtomat or a spare circuit breaker. So an early prompt resumption of power supply may be questionable.
Useful advice! If it is necessary to select the correct differential current device (RCD or RCBO), it is necessary to use an engineering approach and an economic assessment even when one or another type of device is already at hand.
There remained the question of the external difference between the RCD and the RCBO.
Labeling the front of the device. Example 1: "ABB 16A 30 mA" - we have an ABB RCD (manufactured by ABB) with a rated current of 16 amperes and a lower differential current of 30 milliamperes. Example 2: "CHNT C16 0.03A" - before us is a difavtomat, manufacturer CHNT with a rated current of 16 amperes and a characteristic of a class C electromagnetic and thermal breaker with a differential current of 30 milliamperes.
Specified wiring diagram on the title side. For RCDs, the diagram shows a differential transformer (oval loop), a control relay (square) with a loop on the oval contour and a test circuit in the form of a dash-dotted line. For a difavtomat, the circuit is very similar to an RCD circuit, only there are additional figures in the form of a small arc and a stepped line - these are designations that differ from RCDs, electromagnetic and thermal breakers.
Application and installation of RCDs: designations on wiring diagrams
Most of the control and management devices installed in the power supply network have a small list of parameters required for their correct selection in the electrical circuit.
The selection of the RCD is made according to the rated load current and the threshold for fixing the differential leakage current. Practice recommends a value no higher than 30 mA. Installation of an RCD into an electrical network is carried out on the basis of an engineering analysis of the elements existing in the network and installation possibilities. The circuit for connecting the RCD to the network should take into account all possible switching errors and exclude them. Only when properly connected to the power supply circuit, the RCD will provide maximum efficiency in triggering the protective mechanisms of the device.
Selection parameters and connection diagram for RCDs without grounding
Knowing the principle of operation of an RCD, with a standard two-wire electrical network, represented only by phase and neutral wires, and not having a ground loop, it is possible and necessary to install an RCD in accordance with the protection requirements. The correctness and installation diagrams of the RCD were discussed earlier.
The answer to the question of which RCD to put in the apartment is with a calculator in hand. It is necessary to sum up the power of the pieces of equipment and equipment installed in the apartment, and divide the sum by the number 220. Thus, in a rough approximation, we calculate the rated current, according to which the choice of the RCD will be made. This calculation is based on the mathematical dependence of the electrical power on the mains voltage (220V) and the current that occurs when the load devices are powered:
M = U x I,
where М - power, U - voltage, I - current.
Example: you need to select an RCD to protect a group of electrical appliances in a kitchen unit. This line contains the following household appliances:
- Electric oven 2000 watts
- Microwave 1200 W.
- Food processor 700 W.
- Refrigerator 800 W.
- Small household appliances about 600 W.
Let's summarize the power consumption: 2000 + 1200 + 700 + 800 = 5300 W. We calculate the current by the formula: I = M / U = 5300/220 = 24.09A. We select the closest rated RCD with a large value - 25A.
For in-depth calculation of currents in distribution lines, knowledge of the basics of higher electrical engineering is required.
In addition to the rated load current and the differential current sensitivity threshold, in some cases, when choosing an RCD, you need to pay attention to one more criterion - the category of the leakage current. This in most cases applies to alternating and impulse current in the network.
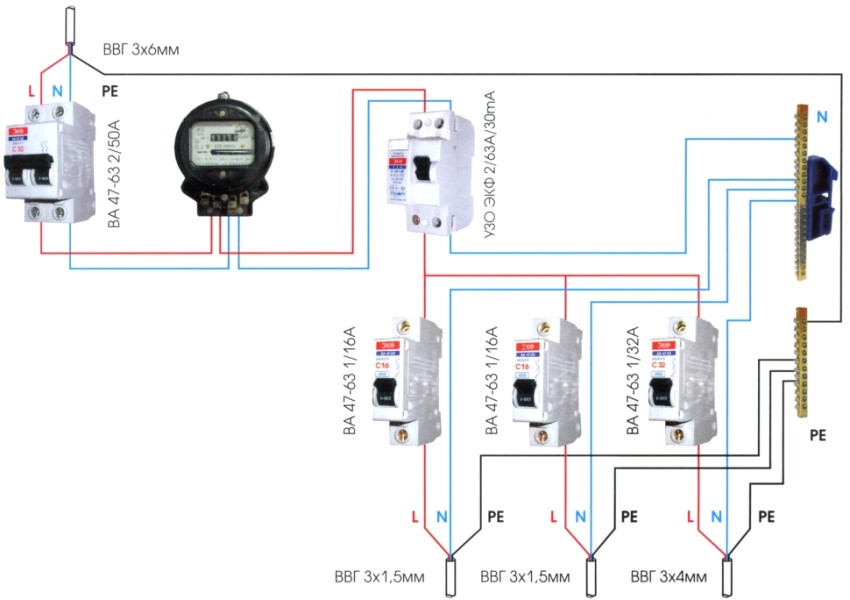
Connection diagram of RCDs and machines using the example of an apartment electricity meter
Category AC assumes the operation of an RCD in an alternating current environment of differential leakage. This category is the most common and can be used in all types of AC networks. In what cases the RCD works - it was discussed above.
Category A has the lowest threshold of sensitivity (about 10 mA) for differential current and is capable of detecting a separate component of the current amplitude (the so-called half-wave). An RCD with this category of leakage current reacts not only to an alternating current configuration, but also to a pulsed one. Such RCDs are becoming a priority application, since more and more household appliances, especially lighting elements, are transferred to pulsed current power supplies.
The main trend of the European market is the expansion of the impulse equipment segment. This, of course, will lead to an increase in the number of pulse current RCDs used. But since receivers of active current (fully alternating) will remain in domestic use for a long time, RCDs of the AC category will occupy a fairly wide space on the market shelves.
Returning to the issue of the absence or presence of a grounding circuit in the power grid, it is necessary to emphasize that even if there is grounding, it is even more necessary to organize protection against electric shock by installing an RCD in the network.
The basic principles of the RCD connection diagram in a single-phase network have already been discussed earlier. The connection diagram for an RCD with grounding is no different from a circuit without grounding.
Useful advice! If the power grid has a ground loop, it is necessary to check and ensure the correct circuit when connecting the RCD, when not a single neutral wire in the wiring should be mated with a wire (terminal) of the ground loop.
Graphic designation of the RCD on the power supply diagram
The main directives included in GOST 2.755-87 ESKD "Conventional graphic designations in electrical circuit diagrams of switching and contact connections" and GOST 2.710-81 ESKD "Alphanumeric designations in electrical circuits" prescribe graphic and letter designations of such devices as RCDs. But there are no strict regulations for the different designation of differential current devices.
As we already know, all differential current devices are represented by a breaker and control element mechanism - a differential current transformer.Therefore, the designation of an RCD in the diagram is represented by two standard graphic designations - a circuit breaker and a transformer that records a differential current. You can see the graphic designation of the RCD in single line diagrams and other drawings.
Three-phase RCD connection diagram
This type of device is usually called a four-pole device and the specificity of its connection to a three-phase network is completely similar to connecting a two-pole RCD. The terminals for connecting the phase wires and the neutral wire are indicated on the body of the device. Also, a passport is attached to the device, which presents standard diagrams for connecting a four-pole RCD to a three-phase network.
Different manufacturers sometimes have differences in the location of the zero terminal on the device case - to the right or to the left, and the connection of the phase wires requires only matching the designation at the input and output.
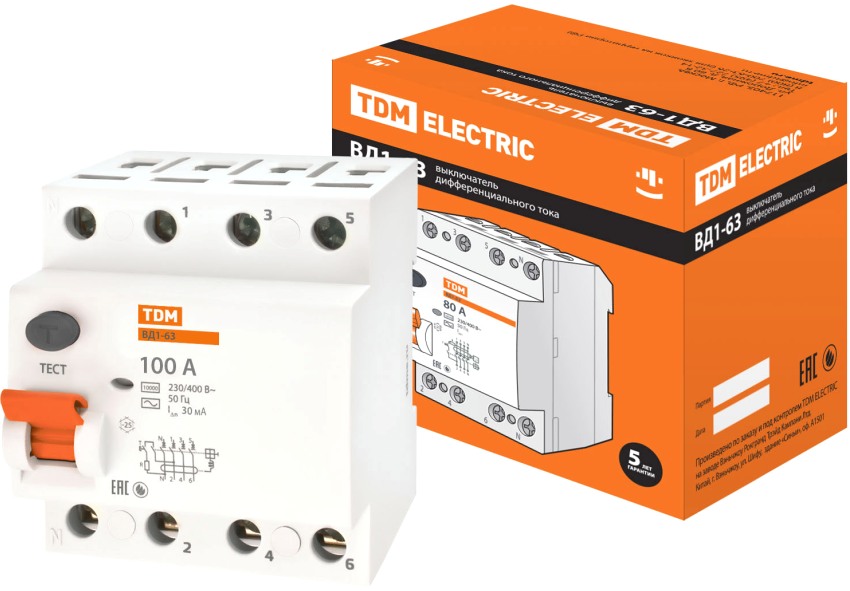
Four-pole three-phase RCDs are used for large differential leakage currents and their main purpose is only to protect the electrical wiring from fire. To organize the protection of people from electric shock, it is necessary to install two-pole single-phase RCDs with leakage current regulation equal to no more than 30 mA on each separate group of equipment.
Model range, manufacturers and prices of RCDs
The market segment of UDT products is represented by a number of foreign brand companies, as well as domestic manufacturers. Today, preference is given to trademarks from Italy, Poland, Germany and Spain, as their products have received the best consumer assessment in terms of quality, reliability and price-quality ratio. The existing market for differential current devices UDT allows you to produce a wide selection of certain types of devices, providing a diverse range of goods both in price and quality.
The table lists the products of the most common UDT manufacturers and shows the market prices they offer:
| product name | Trademark | price, rub. |
| RCD IEK VD1-63 single-phase 25A 30 mA | IEK, China | 442 |
| RCD ABB single-phase 25A 30 mA | ABB, Italy | 536 |
| RCD ABB 40A 30 mA single-phase | ABB, Italy | 740 |
| RCD Legrand 403000 single-phase 25A 30 mA | Legrand, Poland | 1177 |
| RCD Schneider 11450 single-phase 25A 30 mA | Schneider Electric, Spain | 1431 |
| RCD IEK VD1-63 three-phase 63A 100 mA | IEK, China | 1491 |
| IEK circuit breaker VA47-29 25A | IEK, China | 92 |
| Legrand 404028 25A circuit breaker | Legrand, Poland | 168 |
| ABB S801C 25A single-pole circuit breaker | ABB, Italy | 441 |
| RCBO IEK 34, three-phase С25 300 mA | IEK, China | 1335 |
As can be seen from the comparative table, the price of a 25A 30 mA RCD (the most demanded on the market) depends on the manufacturer. So the price of ABB 25A 30 mA UZO is higher than its Chinese counterparts, but lower than that of such manufacturers as Legrand or Schneider Electric. Taking into account such criteria as quality and cost, buying a 25A 30 mA RCD is preferable to ABB, and the necessary circuit breaker can be purchased from China or Legrand.
Useful advice! Having made the decision to install an RCD in a home network, but not having experience in wiring similar devices, use the services of a qualified electrician.
Summing up this excursion into the world of differential current devices, in particular, a residual current device (RCD), we will focus on the important points considered.
One of the most effective means of protecting people and animals from the damaging effects of electric current is the installation of residual current devices in the power supply network - RCDs.
The RCD has the function of responding to the differential leakage current that appears when a person comes into contact with the bare part of the wiring or the case of any electrical equipment.It can be under phase voltage due to damage to the insulation of the phase wire and its contact with the case. The RCD also reacts to a current leak in places where the insulation of the wiring is damaged, when this can lead to heating and fire.
However, the RCD does not react to short-circuit phenomena in the wiring circuit and to excess power in the current circuit. In this regard, the device must be installed in tandem with an automatic switch ("automatic"), which reacts to short circuit and power overload.
The most important thing is to always follow the safety rules and caution when working with electrical appliances and equipment. As often as possible, visually inspect open current-carrying electrical wiring elements and connected pantograph elements.