Any construction, regardless of its size, always begins with the development of the project. Its goal is to design not only the appearance of the future structure, but also to calculate the main heat engineering characteristics. After all, the main task of construction is considered to be the construction of solid, durable buildings that can maintain a healthy and comfortable microclimate without unnecessary heating costs. Undoubted help in choosing the raw materials used for the construction of the building will be provided by the table of thermal conductivity of building materials: coefficients.
Content [Hide]
What is thermal conductivity?
Thermal conduction is the process of transferring heat energy from heated parts of a room to less warm ones. This exchange of energy will continue until the temperature equilibrates. Applying this rule to the enclosing systems of the house, it can be understood that the heat transfer process is determined by the time interval during which the temperature in the rooms is equalized with the environment. The longer this time, the lower the thermal conductivity of the material used in construction.
To characterize the conductivity of heat by materials, such a concept as the coefficient of thermal conductivity is used. It shows how much heat in one unit of time will pass through one unit of surface area. The higher this indicator, the stronger the heat transfer, which means that the building will cool down much faster. That is, when constructing buildings, houses and other premises, it is necessary to use materials whose heat conductivity is minimal.
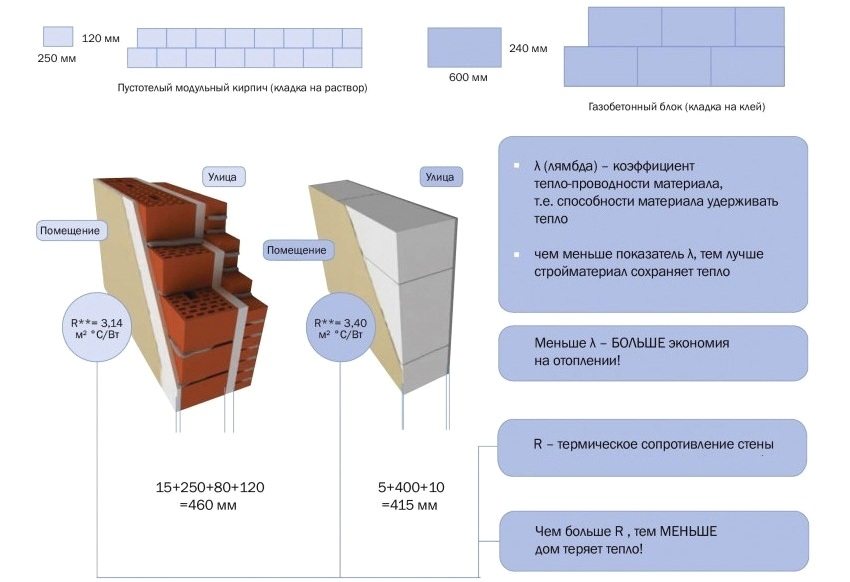
Comparative characteristics of thermal conductivity and thermal resistance of walls built of bricks and aerated concrete blocks
What affects the value of thermal conductivity?
The thermal conductivity of any material depends on many parameters:
- Porous structure. The presence of pores suggests heterogeneity of the raw material. When heat passes through such structures, where most of the volume is occupied by pores, cooling will be minimal.
- Density. High density promotes closer interaction of particles with each other. As a result, heat exchange and the subsequent full equilibration of temperatures occurs faster.
- Humidity. When the ambient humidity is high or the walls of the building become wet, dry air is displaced by droplets of liquid from the pores.Thermal conductivity in such a case increases significantly.
Application of the thermal conductivity index in practice
In construction, all materials are conditionally subdivided into heat-insulating and structural materials. Structural raw materials are distinguished by the highest rates of thermal conductivity, but it is they who are used to build walls, ceilings, and other fences. According to the table of thermal conductivity of building materials, when erecting walls made of reinforced concrete, for low heat transfer with the environment, the thickness of the structure should be about 6 meters. In this case, the structure will turn out to be huge, cumbersome and will require considerable costs.
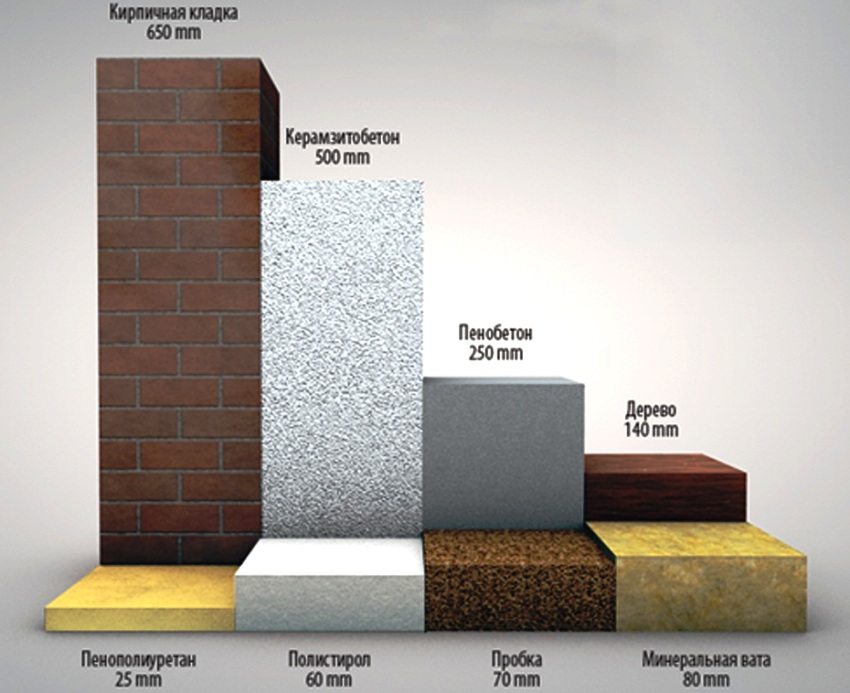
An illustrative example is at what thickness of different materials their thermal conductivity coefficient will be the same
Therefore, when erecting a building, special attention should be paid to additional heat-insulating materials. A layer of thermal insulation may not be needed only for buildings made of wood or foam concrete, but even when using such low-conductive raw materials, the thickness of the structure should be at least 50 cm.
Need to know! Thermal insulation materials have minimal thermal conductivity values.
Thermal conductivity of the finished building. Thermal insulation options for structures
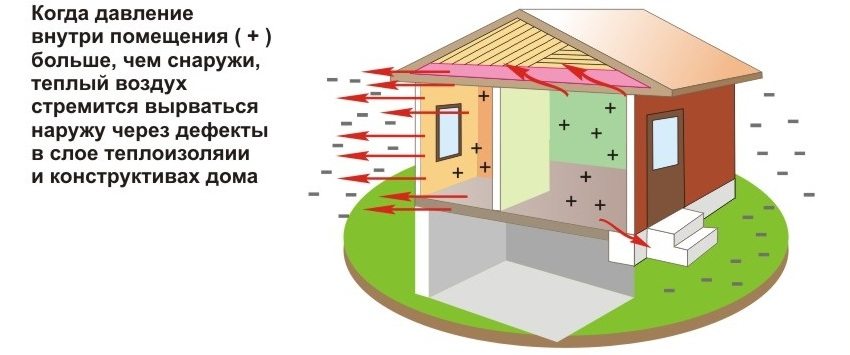
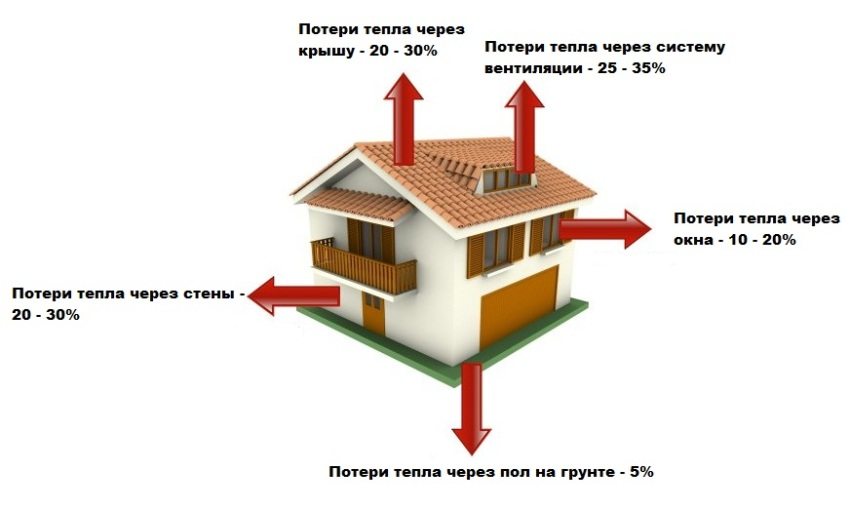
When developing a construction project, it is necessary to take into account all possible options and ways of heat loss. A large amount of it can go through:
- walls - 30%;
- roof - 30%;
- doors and windows - 20%;
- floors - 10%.
With an incorrect calculation of thermal conductivity at the design stage, residents can only be content with 10% of the heat received from energy carriers. That is why houses built from standard raw materials: brick, concrete, stone are recommended to be additionally insulated. An ideal construction according to the thermal conductivity table of building materials should be made entirely of thermal insulation elements. However, their low strength and minimal resistance to loads limit the possibilities of their use.
Need to know! When arranging the correct waterproofing of any insulation, high humidity will not affect the quality of thermal insulation and the resistance of the building to heat transfer will be much higher.
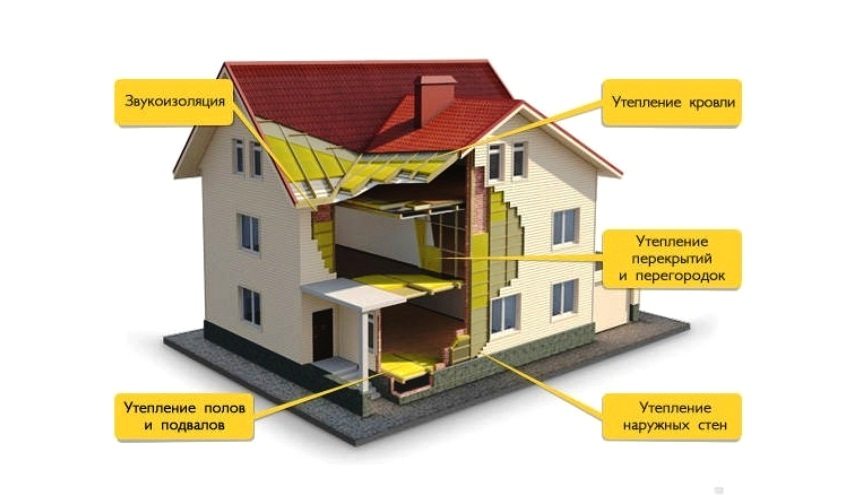
The most common option is to combine a supporting structure made of high-strength materials with an additional layer of thermal insulation. These include:
- Frame house... When it is built with a wood frame, the rigidity of the entire structure is ensured, and the insulation is laid in the space between the racks. With a slight decrease in heat transfer, in some cases, insulation may also be required outside the main frame.
- House made from standard materials. When making brick walls, cinder blocks, insulation should be carried out according to outer surface constructions.
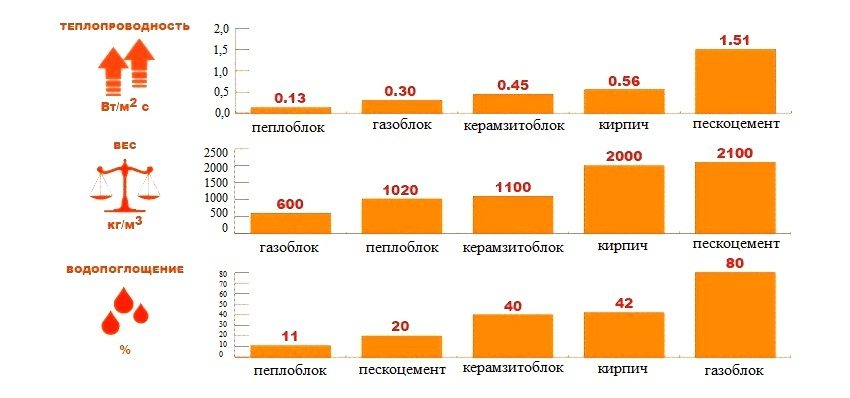
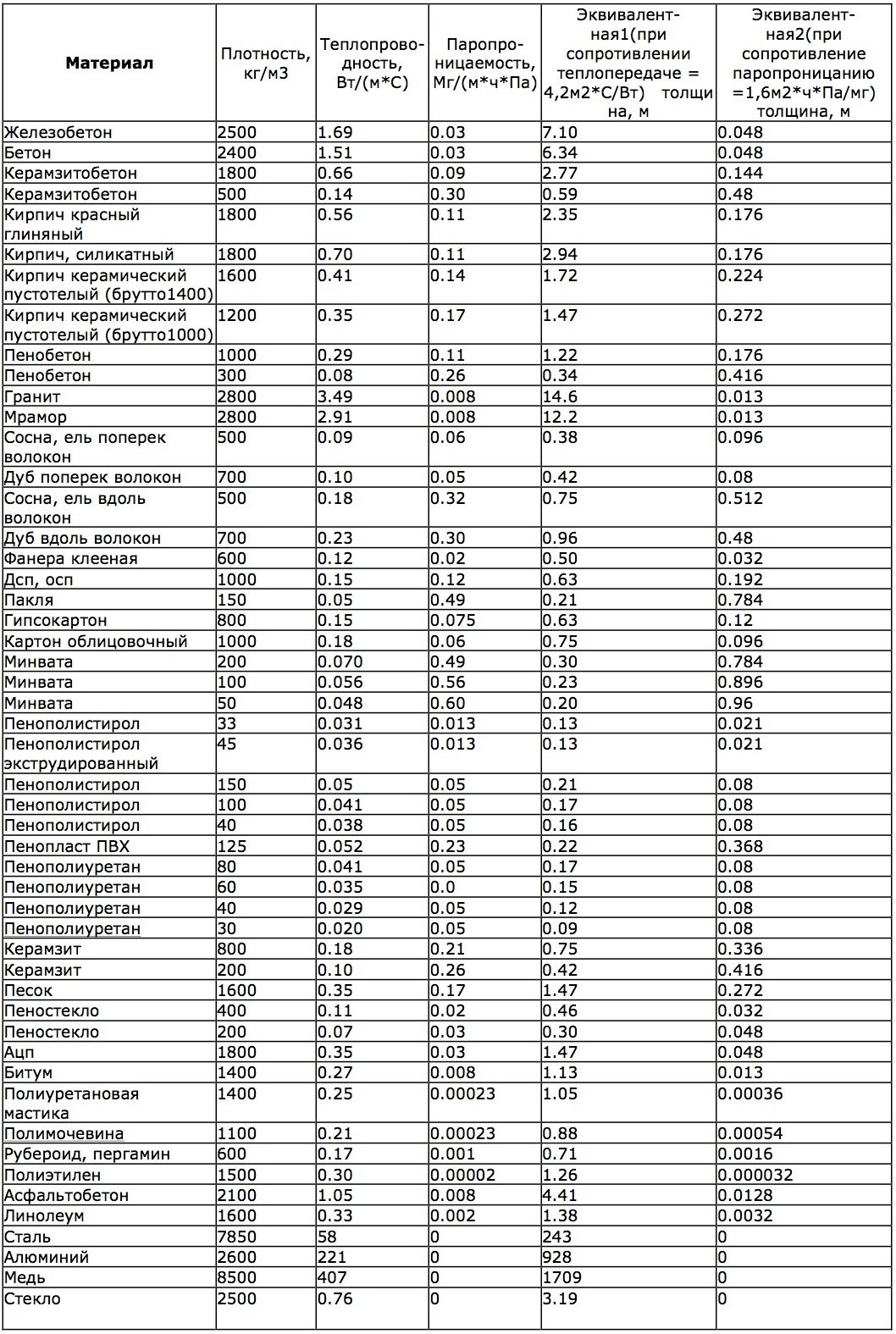
Thermal conductivity table of building materials: coefficients
This table contains the thermal conductivity of the most common building materials. Using such reference books, you can easily calculate the required thickness of the walls and the used insulation.
Table of thermal conductivity coefficient of building materials: