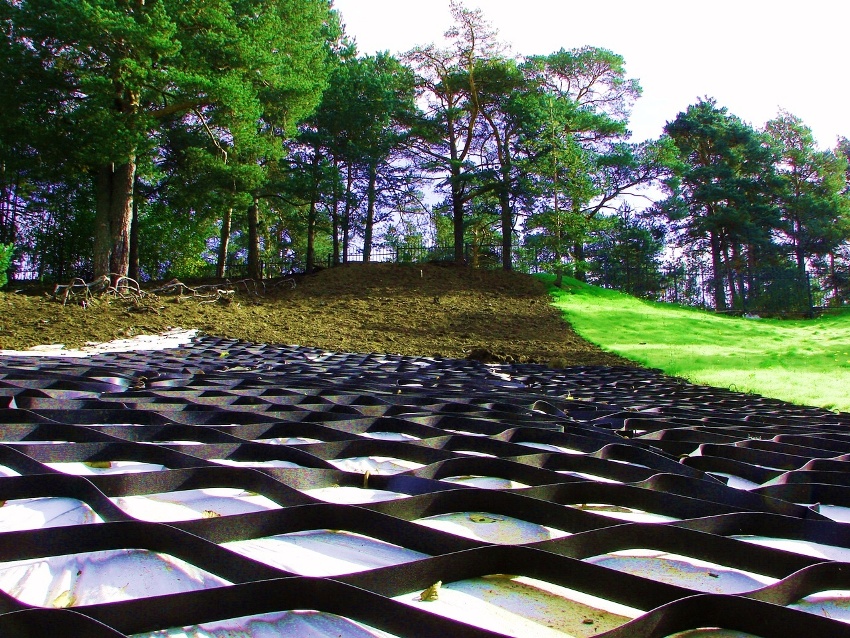
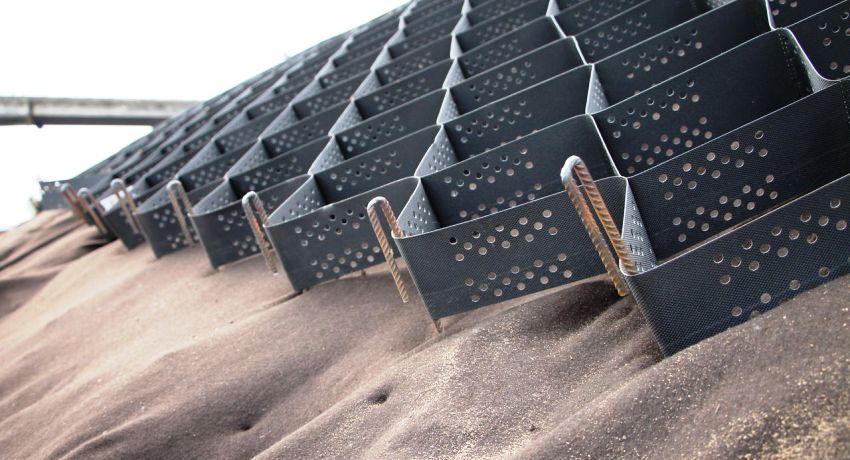
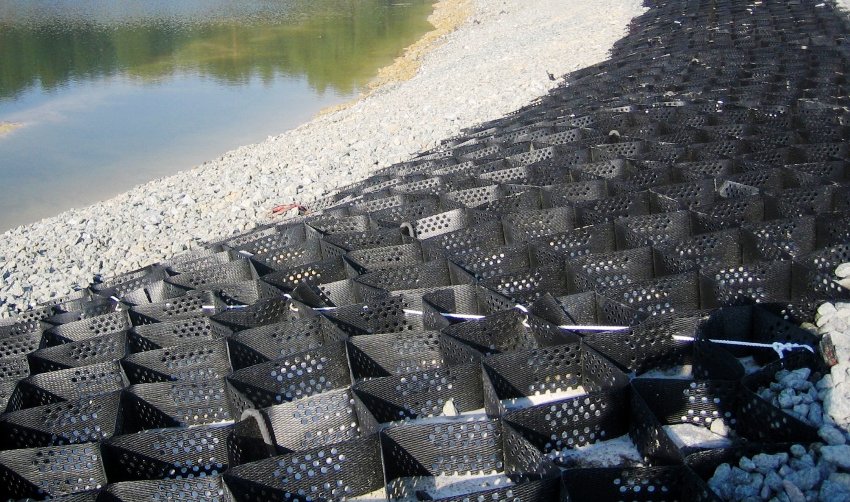
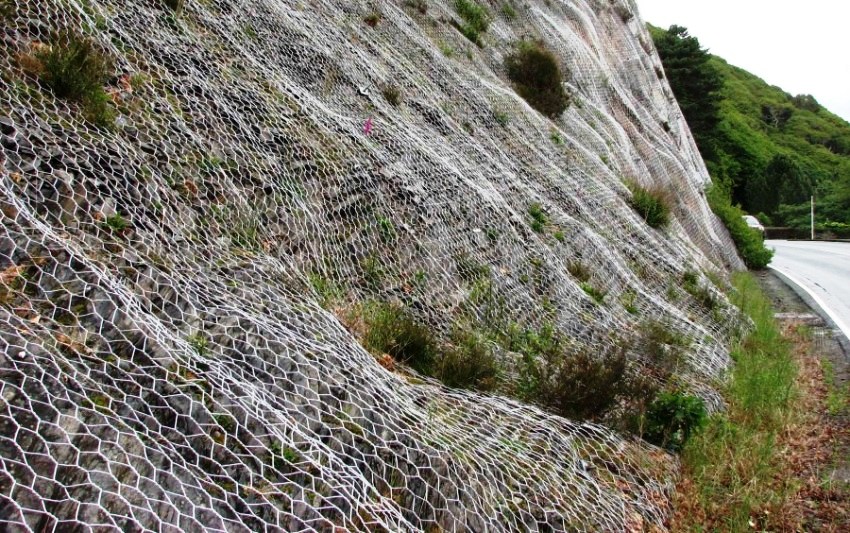
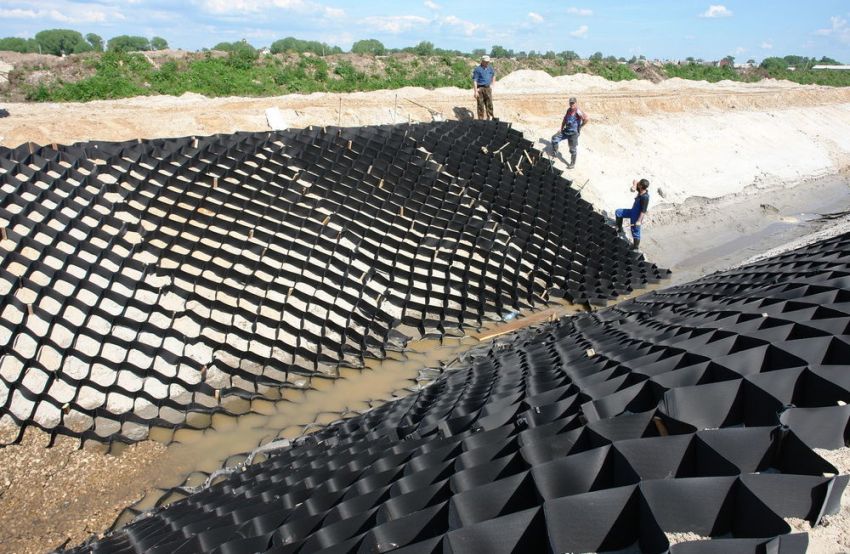
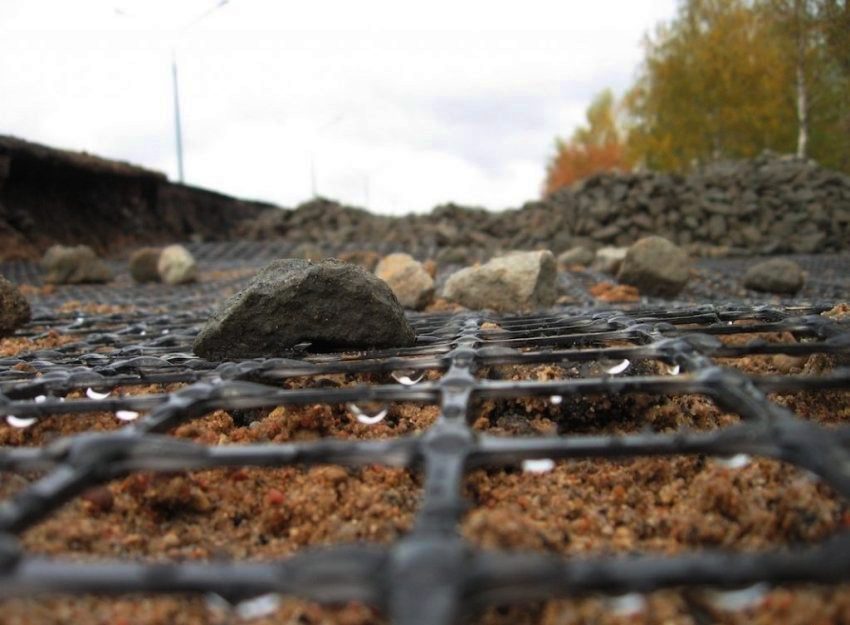
During earthworks, freshly dug embankments, pits and slopes crumble, especially after heavy rains. The slope reinforcement geogrid is one of the best solutions when you need to quickly and effectively eliminate this problem. Cell structures, geosynthetics and reinforced soil plates solve the problem in different ways. Let's consider the capabilities of geogrids in detail, comparing with analogues.

The geogrids have a high level of elasticity, are neutral to aggressive environments and are non-toxic
Content [Hide]
- 1 The main characteristics of the polymer geogrid
- 2 The main purpose and application of geogrid for reinforcement
- 3 Existing analogues of geogrid for earthworks
- 4 Combined strengthening of crumbling slopes
- 5 Classification of road slopes in terrain
- 6 Geogrid for slope reinforcement: application possibilities
- 6.1 What is preferable to choose a geogrid
- 6.2 Functionality of universal geotextile reinforcing mesh
- 6.3 Reinforcement of the slope and embankment with a geogrid for road construction
- 6.4 Geogrid to strengthen the slopes of parking lots and gas stations
- 6.5 Cultivation of the hardened surface with geotextile fabrics
- 6.6 Application of a geogrid for natural and artificial reservoirs
- 6.7 Does the polymer geogrid affect the overall eco-balance of the reservoir?
- 6.8 Strengthening road slopes using geogrids
- 6.9 How to choose a material for road reinforcement
- 6.10 How geomats and geogrids are applicable for summer cottages
The main characteristics of the polymer geogrid
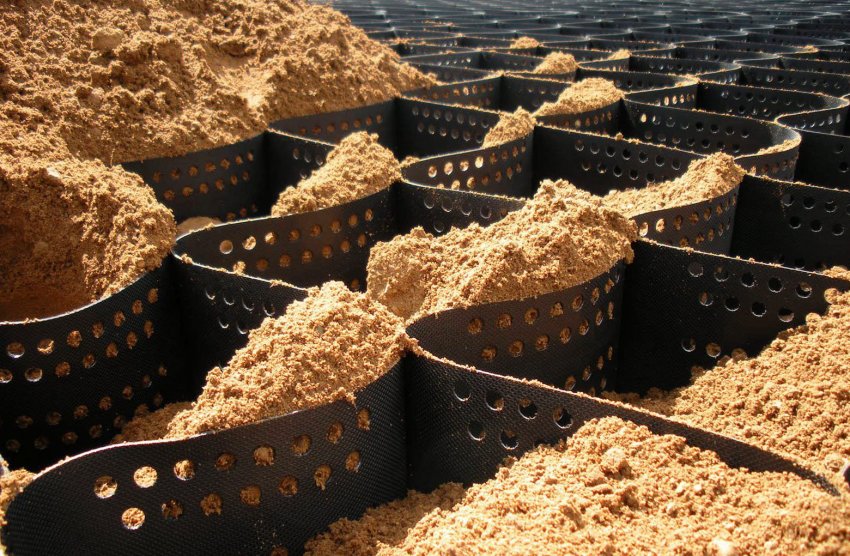
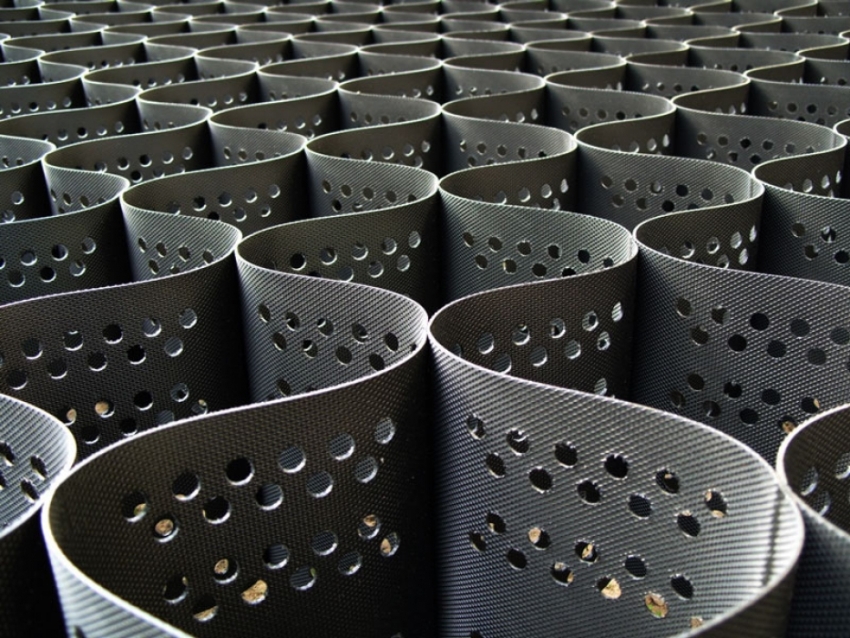
For those who have no idea what a geotextile geogrid looks like, a cursory glance is enough to understand the simplicity and practicality of this invention. It can be characterized as the simplest cellular base, consisting of fairly strong polymer threads. Another option is geotextile or ribbon fiber mesh.
Geogrids are polymeric canvases made of non-rotting materials. The tensile transformation results in a three-dimensional cellular structure reminiscent of a checkerboard or honeycomb. Raw materials for their production:
- PP polypropylene;
- polyester PET;
- carbon fiber;
- high density polyethylene HDPE;
- innovative raw materials PVA.
High-strength synthetic fibers are coated with a protective layer of polyvinyl chloride (PVC) to protect against UV damage. By the type of production, geotextiles are classified:
- woven;
- thermally bonded by extrusion (there are 1-axis and 2-axis).
European manufacturers use similar raw materials at Bonar enterprises (Slovakia).Construction supermarkets have Armatex®RSM and Armatex®M - a composite geogrid for reinforcing slopes, the price is quite acceptable.
It is interesting! The plastic material is interesting in that, when stretched, cells are formed for filling with soil or crushed stone with sand, increasing the coverage area.
The geogrid is produced from polyethylene tapes - on the same basis as polymer products for construction. Due to its tensile strength and resistance to weather and climatic factors, 3D geosynthetics are not subject to rotting and destructive changes in the ground. They will always be in demand - durable polymer fibers are not destroyed by moisture and frost.
Rigid extruded geogrids are also produced from another, less elastic raw material - polypropylene. They are pulled out after a short heating. In specialized retail outlets, you can buy Tenax®LBO and Tenax®TT geogrids for strengthening slopes - offers from Tenax (Italy). Ultraviolet rays and temperature changes, increased acidity or alkalization of the soil, as well as aggressive microflora do not cause significant harm to geosynthetics.
The main purpose and geogrid application for reinforcement
Steep and relatively gentle slopes, hills and ravines are typical of the landscape of most countries. Moscow and Rome, as you know, are built on hills, new objects today require strengthening the slopes with a geogrid. The products are designed for heavy loads - biaxial modules are designed to be stretched in two directions.

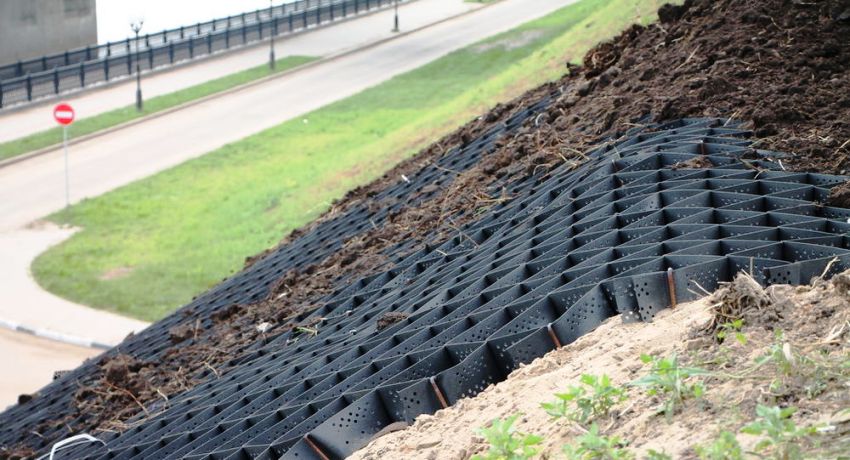
The main field of application of geogrids is road and bridge construction and reinforcement of unstable soils
Uniaxial rigid HDPE structures are used for retaining walls and stabilizing nearly vertical structures. They have the longest service life - up to 50-100 years.
Without fixing a geogrid or a polymer mesh, the excavation line will lose its design outlines, the excavated soil will settle. Reinforcement will more reliably arrange:
- pit for an artificial reservoir;
- almost vertical slope;
- paved country paths;
- artificial fences and embankments;
- terraces in landscape design;
- private territory with a slope;
- construction of access roads;
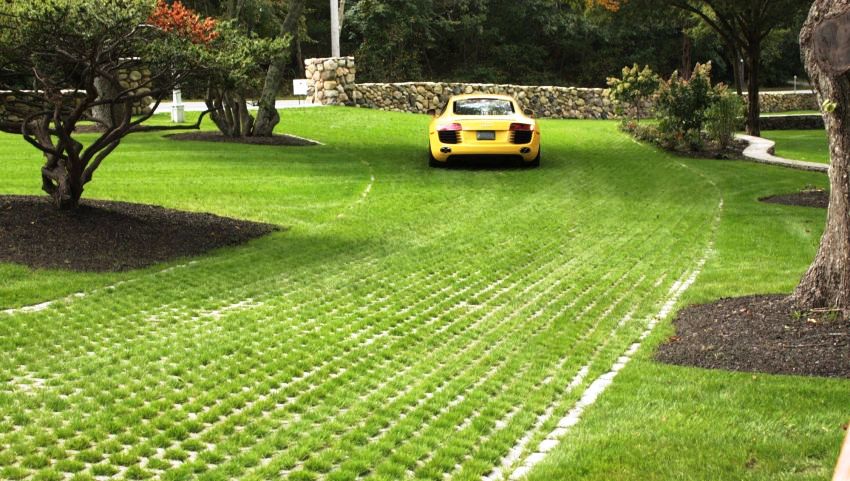
- sloping lawns with 3D geosynthetics landscaping;
- parking lots and adjacent areas in hilly terrain
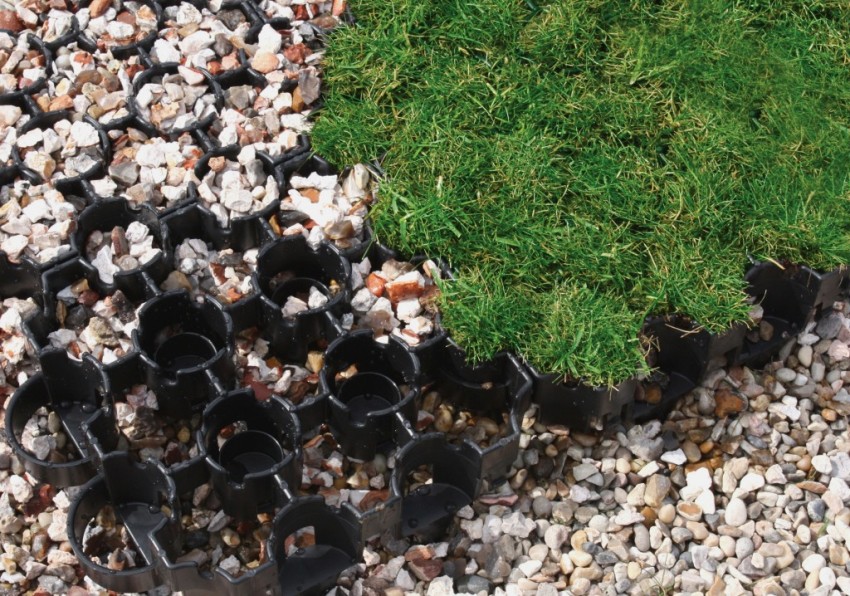
The cellular structure of polymers is an excellent basis for the design of gentle slopes. The surface is formed by filling the windows with natural or artificial aggregates. The net for laying is stretched over the surface, obtaining a honeycomb structure, which remains to be fixed with anchors and filled with a substrate:
- pebbles;
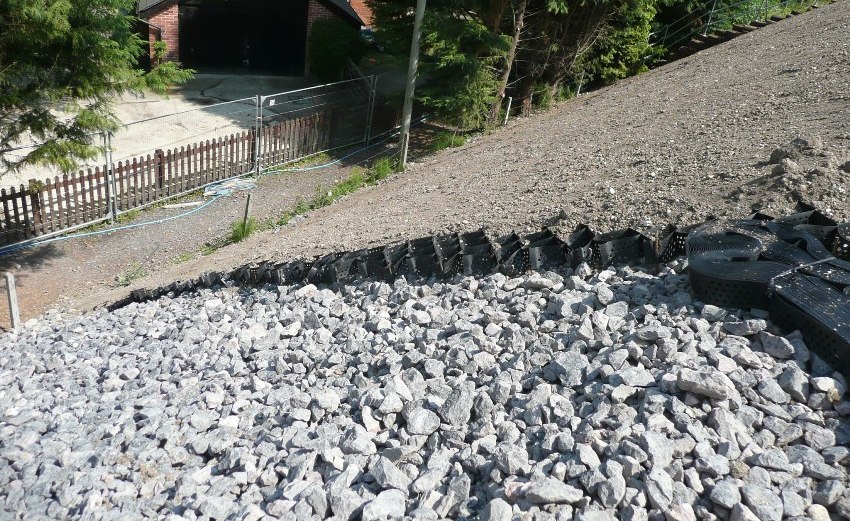

With the help of a polymer geogrid, it is possible to stabilize weak foundations, strengthen slopes and embankments
- expanded clay;
- sand;
- crushed stone (different fractions);
- soil from excavation, etc.
So far, nothing better has been invented for volumetric reinforcement of slopes, with the exception of concrete geoplates for slopes (reinforced soil products). Their cost is much higher, loading and transportation is more difficult.
Benefits of geosynthetic mesh gratings
Polymer volumetric geogrid for reinforcing crumbling and unstable soil has a lot of positive qualities:
- rolls are easy to store and transport, honeycomb relief is obtained by stretching;
- wide range of applications for infrastructure facilities on soils with unsuitable characteristics;
- installation of geopolitics expands main and railway embankments to increase their throughput;
- trenches and road beds after reinforcement serve flawlessly for decades;
- large-scale excavation work to stabilize the soil is carried out without significant costs, as it was before the invention of polymer panels (a geogrid for strengthening slopes at a price of 32 rubles / m² is quite economical);
- the layer of crumbling rocks decreases;
- the use of grids makes it possible to tighten the road construction schedule;
- the reliability of highways, junctions and complex bridge structures is significantly increased;
- solving complex technical problems in difficult conditions of engineering and geological developments.
It is important to note that the welded seam of polymer tapes demonstrates a load of about 7-8 kN / m, as a rule, it does not come to such tests. The soldering is made by the extrusion method - with short-term temperature exposure, increasing the strength.
Existing analogues of geogrid for earthworks
Geomat is a three-dimensional structure resembling a layer of fibrous polymers, multilayer polypropylene (one-on-one grating). Best remedy for soil erosion, installation is very simple. Suitable for planting vegetation on the surface - the roots penetrate the structure, allow moisture to pass through.
Geomats, like other lawn coverings, do not deteriorate due to temperature extremes and negative effects of seasonal temperatures. Based on laboratory tests, it can withstand -300 ° C to + 1000 ° C. The polymer layer does not ignite, does not collapse under the influence of increased soil acidity.
A similar material is biomats, consisting of plant components (mainly coconut coir, quilted with jute). Wide rolls are environmentally friendly, so the soil structure and suitability for fouling do not change after the slopes have been strengthened. A layer of soil and decorative stones is poured on top of the laid roll onto an inclined landscape design site.
Note! Biomats are not recommended to be installed in frosty weather. Excessive moisture and excessive watering are unfavorable for them.
Geotextile is a dense synthetic non-woven material of high strength, which has many advantages. It is used in suburban areas to strengthen the soil - as one of the "layers" and as a mesh for the lawn.
Excellent frost resistance, the material is not subject to destruction by excess moisture in the soil and atmospheric precipitation. Pathological microflora does not develop under its cover. The material tolerates stretching up to 120% of its own area, but surface leveling is recommended before installation. 3D geosynthetics are easy to cut and fit.
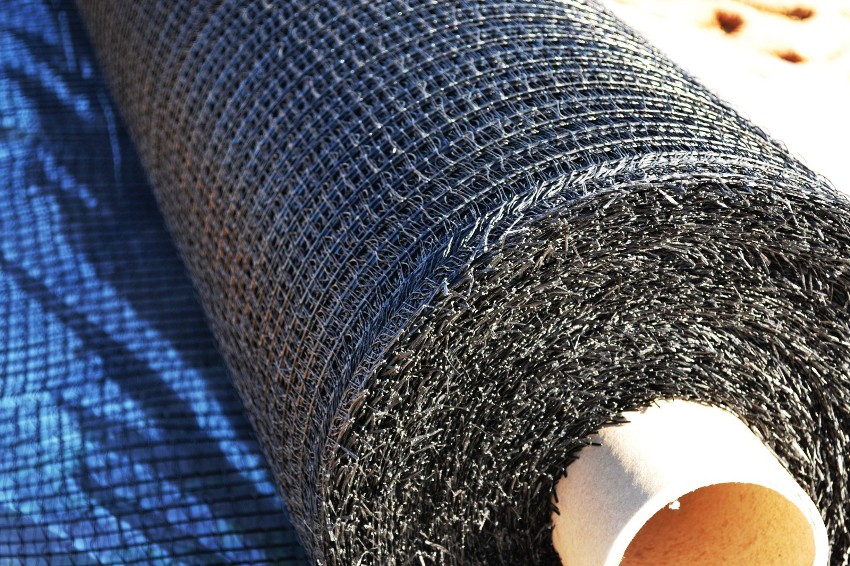

Geomat is a polymer structure, unique in its properties, consisting of several layers, randomly arranged lattices
The geogrid made of synthetic fibers (polyester, polyethylene, fiberglass) is multifunctional and comfortable. Flexible and plastic panels are not afraid of seismic fluctuations and temperature changes. It is easy to transport in the form of rolls and lay on crumbling soil. The coating compresses the soil, reinforces the slopes, protecting the artificial relief from destruction.
The mesh device of the geogrid does not impede the circulation of moisture and air in the surface layers of the soil. From above, you can sow lawn grass, sprouting, it additionally strengthens the slope. The material is used to seal dams and artificial reservoirs, bridge cones and fresh ravines after landslides and mudflows.
To strengthen the complex relief of the slopes, reinforced soil plates are also used to resist landslide processes on unstable soils. With their help, loads are stabilized on almost vertical surfaces along roads and embankments of interchanges.
Armor-ground geoplates - guaranteed stabilization of loads during road construction.They are designed to improve the properties of loose soils, therefore they are used to fasten load-bearing structures. The products provide an aesthetic volumetric reinforcement - the plates have uniform cells that trap bulk materials in which plants germinate.
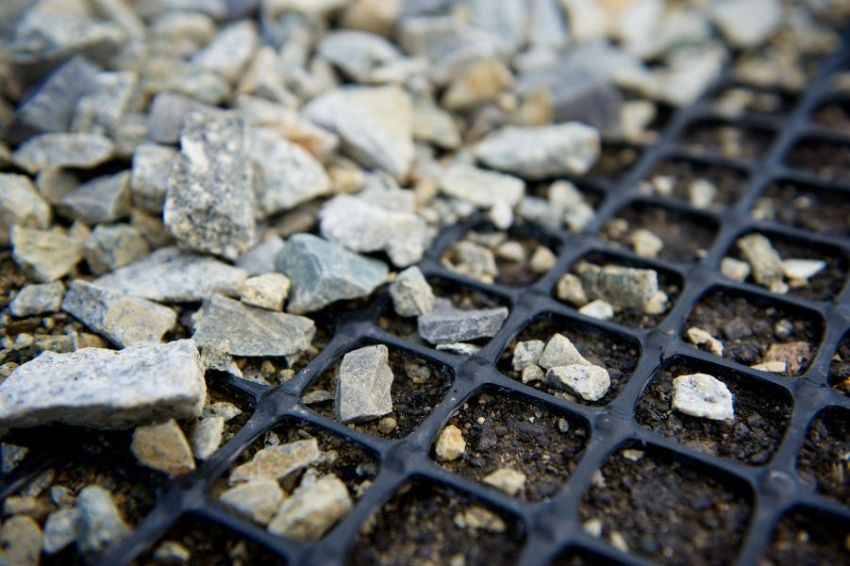

Geogrids are used to reinforce the foundations of pavements made of coarse-grained materials, embankment slopes
Combined strengthening of crumbling slopes
Combi decking combines different types of slope reinforcement, including geogrid rolls and stones. For greater surface aesthetics, stones or pebbles are sorted by size, color and composition.
The technology for laying the geogrid with the combined method is approximately the same. Stones are poured over geomats, fixed with anchors 30 cm long. Then textiles or mesh are laid, then stones (possibly in several layers) fixing the layers with polyurethane.
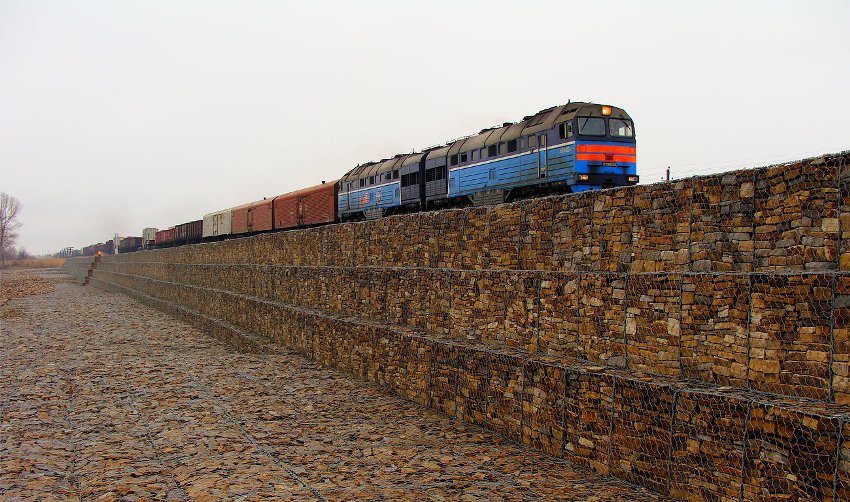
Gabions are heavy structures to prevent rockfalls and mudflows in the mountains. It is good to lay them at the base of inclined sections along the highways, which have been used for about a century. These are ordinary blocks of metal reinforcement filled with stones of different sizes. Recently, they have been actively used for decorative purposes - in landscape design. Metal meshes fill:
- cobblestone;
- large rubble;
- sea pebbles;
- chipped stone.
Technical gabions are applicable as any type of slope stabilization, especially where other types of reinforcement are not applicable. Eco-friendly and inexpensive filler has a long and reliable service. Such reinforcement of slopes is advantageous in that the filling can be taken almost underfoot.
Helpful advice! Prepare the site by marking the boundaries of the installation. Be sure to compact the soil after each layer of the slope reinforcement geogrid, removing the anchor at the end of the next step.
We offer panels with a tape from 50 mm to 200 mm. The size of the cells also varies, you can choose for your soil filler - 160x160 mm, maximum 410x410 mm. Ultrasonic welding is used to join the tapes in a checkerboard pattern. The strength of polyethylene tapes is very high - about 10-15 kN / m (the indicator varies with different thickness of the panel).
Related article:
Geogrid for parking: innovative material of a new generation
Varieties of products. How to choose a geogrid for parking. Review of manufacturers. Geogrid installation sequence.
Composite geogrids perform the same function - reinforcing unstable soils and crumbling slopes. Cells when stretched increase the format of the panel. This type combines the properties of a geogrid and geotextile (a secondary role is assigned). It is both a separator and a filter that increases the adhesion of the layer to the surface - it is important for the reinforcement of asphalt concrete layers of highways, car parks and gas stations.
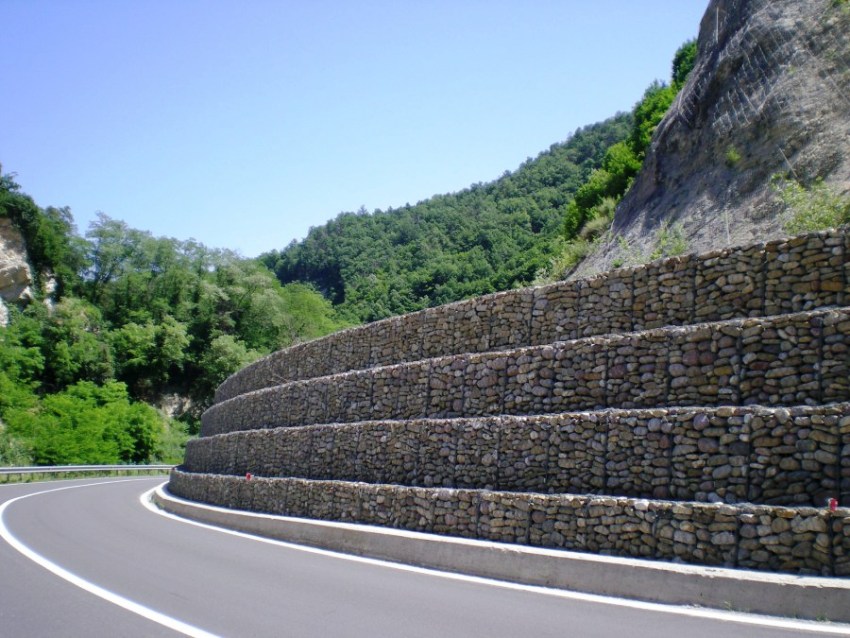

Technical gabions are used to stabilize slopes of various types, where it is impossible to use other materials
Classification of road slopes in terrain
Ravines and small hills are typical of the European lowlands. Using a combination of synthetic geogrid and natural bulk materials, it is easy to strengthen the slopes. This will help to minimize the effects of erosion, rockfalls, shedding of embankments and slopes.
Slopes have their own classification by shape, area and steepness. In length, they are long (over 500 m), medium length (from 50 m to 500 m) and short (within 50 m). In terms of steepness, the slopes are:
- very steep> 35 °);
- steep 15-35 °;
- slopes of medium steepness - within 8-15 °;
- gentle (up to 4-8 °);
- very flat (2-4 °, visually not always noticeable).
The way slopes are reinforced depends on various factors, including the natural topography, soil density and the degree of slope.
Gentle slopes with a slope of 8 ° do not need reinforcement. This happens in a natural way - the soil is overgrown with grass, trees and shrubs. Substantial compaction is not required, the roots, deeply embedded in the soil, hold together stones that are not visible, but they are always in the ground. In this case, the strengthening of the slopes with a geogrid is required in rare cases.. Natural overgrowth with vegetation or sowing lawn grass with shrubs is enough to prevent the site from slipping due to adverse weather and climatic factors.
Important! A quick effect of strengthening the soil (after changing the topography of the site) can be achieved after planting fast-growing plants with a root system branching at the surface.
Artificial terraces with steps and hedges are a good alternative to geogrid mounting. They are relevant on gentle slopes, where it becomes steep when descending to a reservoir. In wet soil, willow branches will take root, in the southern regions - blackberry shoots, which quickly grow, strengthening areas with a slope. In landscape design, alpine slides or rockeries with easily rooting plants are more appropriate.
Medium slopes - with an angle of inclination within 8-15 °. A slight slope interferes with natural fouling - not every plant will gain a foothold in an area where there are frequent showers. Here it is possible to sow grass only after laying the geogrid, on top of the reinforcing elements. Elastic cells for natural fillers are especially relevant on radial and conical slopes, where other reinforcement methods are not suitable.
Helpful advice! In landscape design, geomats are most relevant - on areas subject to erosion by rainfall streams. Applicable are porous layers of welded polymer fibers that allow air and moisture to pass through, which is beneficial for the sod layer.
In rainy climates, the problem of soil washout from the middle slope is solved after fixing with geogrids. However, there may be problems with filling cells from natural bulk materials. Fine-grained crushed stone is suitable for compaction of the slope, after filling a small layer of soil, lawn grass is sown. The descent to the artificial reservoir can be strengthened in the same way. But you will need a directing chute to drain the water, blocking natural washout.
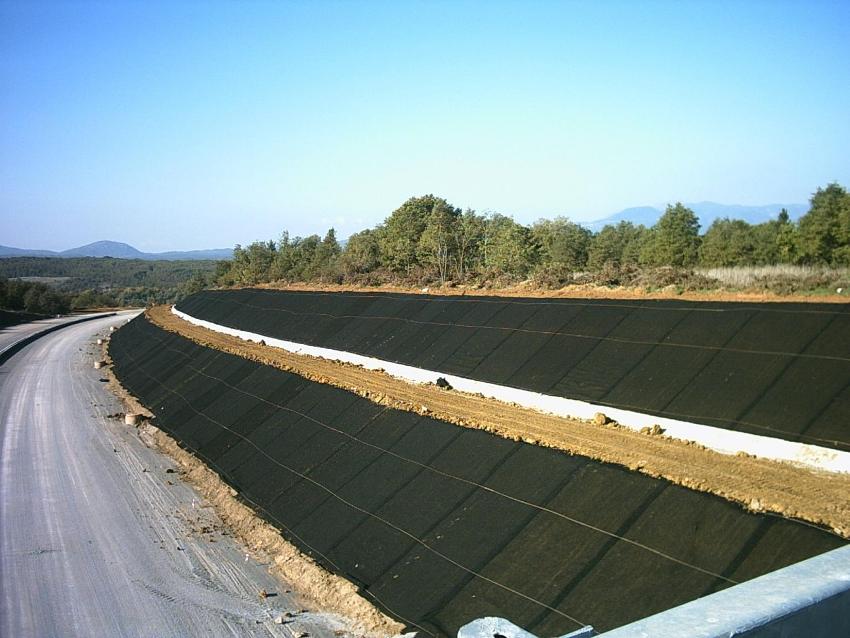
Steep slopes in areas within 15-35 ° need strengthening, especially after excavation. Here you can not do without laying a durable non-woven geotextile, which serves as an excellent barrier against soil erosion and destruction by water flows.
On difficult turning sections of roads and on a suburban area, all fastening methods are good, especially in a combined way. Gabions and geoplites, as well as all geomaterials, including geogrid and geomats, can be used. Filling the grid cells with stone chips and soil from the excavation is also applicable for stabilizing coastal areas using the 494 Proudhon geogrid.
Styling geogrids for strengthening slopes of different steepness
When there is a need for reinforcement for landscaping at an angle, a volumetric geogrid is laid. The cells are filled with a substrate mixed with fertile soil under the seeds of lawn grass. They will quickly sprout and strengthen the crumbling slope of a small steepness, additionally "nailed" with roots to the base.
Wind and water erosion quickly destroys recent embankments and ravines, especially when it is a cliff or body of water and the slope is steep enough. Polymer fiber geotextile will cope with the task. If the base does not have reliable support on the site or on the turn of the roadway, it must be strengthened:
- supports made of reinforced concrete slabs;
- masonry.
The canvases are fastened with special anchors, additionally fastened to the surface of the embankment along the edges. In the cells under the natural growth, a mixture of crushed stone, sand with soil, or one or the other can be filled in.
Helpful advice! Fertile filler and fine crushed stone must be added under the lawn grass, creating favorable conditions for fouling of an inclined surface.
High-quality installation of the geogrid, in addition to protecting the slope from collapse, counteracts erosion by groundwater. This is true in hilly areas where the horizon fluctuates. From freezing of the soil after autumn showers with subsequent sharp thawing, there is a danger of changing the relief. The consequences of temperature changes are noticeable on the soil in spring, when paved paths and alleys in parks and squares in some places "creep" without reinforcing the embankment or trench.
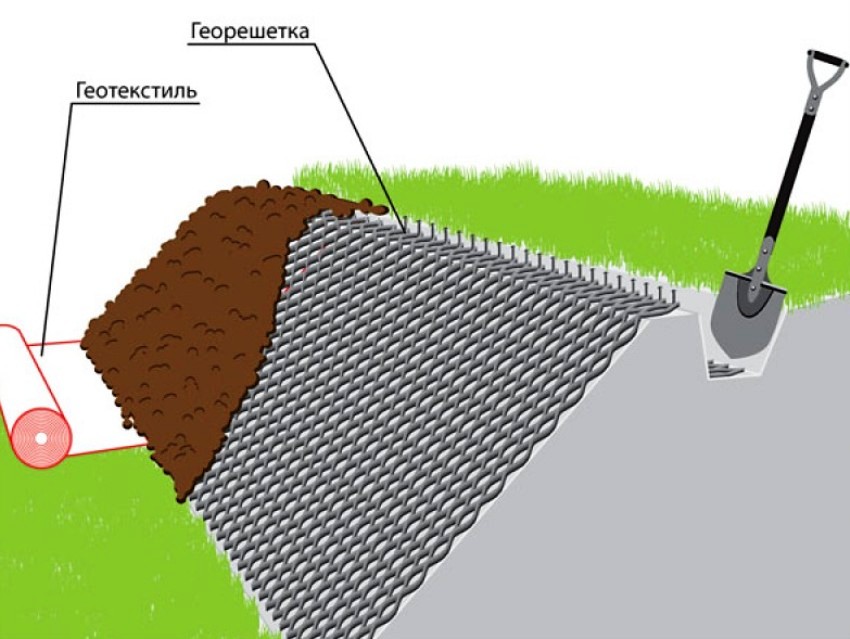
The best solution is a multi-layer "sandwich" with geotextile and a cushion of sand and gravel. If necessary, using a natural slope, a preliminary excavation of 50 cm is made. Near the path, gutters are arranged for the drain of rain and melt water. Geotextiles, paving stones and paving slabs are laid on top of the trench.
Important! In difficult terrain, paved paths with steps alternate. The geogrid will distribute the load most evenly on the surface.
When there is a choice, different characteristics of the geogrid are applicable, the height of the rib varies. For reinforcement of slopes of different steepness, panels with different cell sizes are used:
- an angle of inclination up to 10 ° is reinforced with a cell edge up to 50 mm;
- up to 30 ° - 100 mm;
- up to 45 ° - 150 mm;
- from 45 ° degrees (and more) - 200 mm.
Literally in a year, road embankments, the edges of orchards and vegetable gardens, natural slopes on the site within 15-35 ° will be under reliable protection. An additional bonus is aesthetic landscaping with rapidly growing wild growth. Moles and rodents leave from under the honeycomb structure, which they could destroy the inclined section with burrows coming out to the surface. These recommendations are relevant for those who are interested in the question of how to strengthen the slope of the ravine at the edge of the summer cottage. A multilayer artificial layer of 30-40 cm will help solve a difficult problem.
Geogrid for slope strengthening: capabilities application
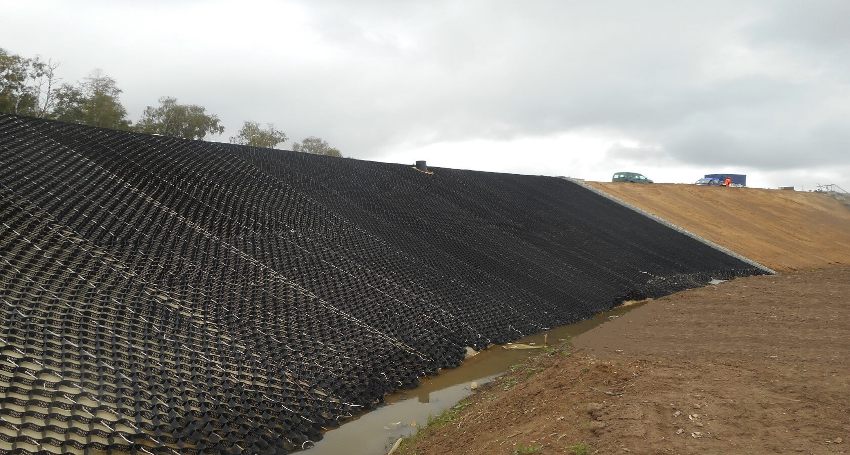
Synthetic honeycomb fabric made of soldered strips 1.5 mm thick is successfully used for full-scale reinforcement of slopes. The cells are filled with natural or artificial aggregates, as well as soil from excavations. Purpose - to counteract the erosion of the surface layer of the soil and improve soil characteristics during the construction of access roads and improvement of sites.
In fact, it is a landscape geogrid that strengthens the slopes. Since the beginning of its production in 2003, the polymer reinforcing structure has been certified, produced in accordance with TU, which vary at specialized enterprises. All tests were successful, after which she was registered in the list of materials for strengthening roads and slopes. It has the same functionality and general characteristics, differs in parameters:
- polymer material;
- width of tapes;
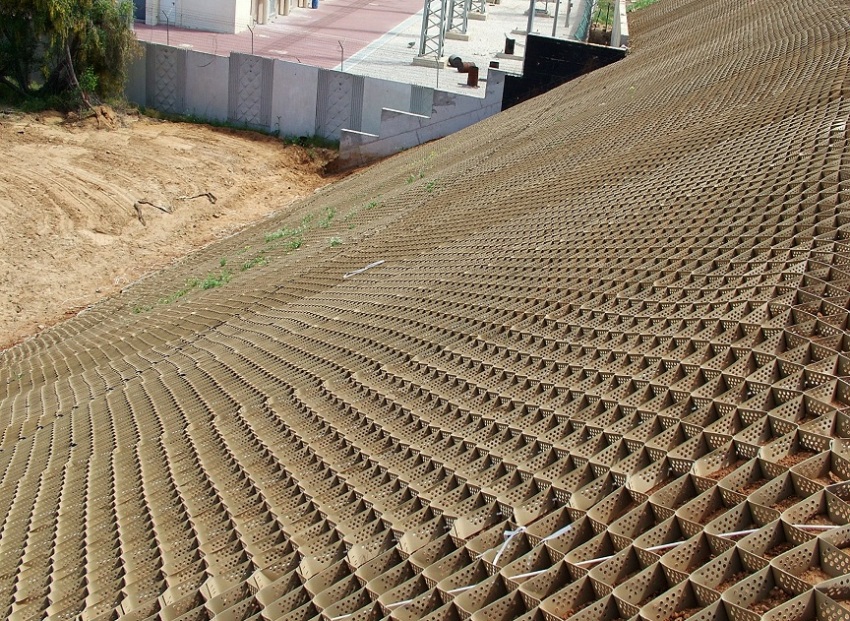

A geogrid installed on slopes strengthens and stabilizes the soil, prevents the soil from moving down
- dimensions of panels;
- there are perforated and voluminous offers.
The polymer material, neutral to the external environment, from which the landscape geogrid is produced, is non-toxic. It is not subject to destruction by ultraviolet light, petrol resistant (important for the construction of gas stations). The polymer material does not decompose under the influence of destructive microflora, which significantly extends the service life of the fortified areas.
What is preferable to choose a geogrid
During the construction of facilities and communications, one often has to deal with difficult terrain. It is necessary to take measures so that part of the infrastructure or object does not slide into the water or ravine. Hilly terrain, construction in the river floodplain, cottages and hotels on the seaside - all this involves geogrid mounting. The crumbling of soils during earthworks is the main obstacle to the construction of buildings and the improvement of the adjacent territory.
A train rushing along an embankment by the sea or a steep slope along mountain cliffs is a spectacular sight. However, engineers worked on the reinforcement of the slopes so that the wagons and trucks did not fall into the sea with all their contents. The observant eye is familiar with the fortified slopes, stone terraces and gabions, road embankments and even artificial slides.
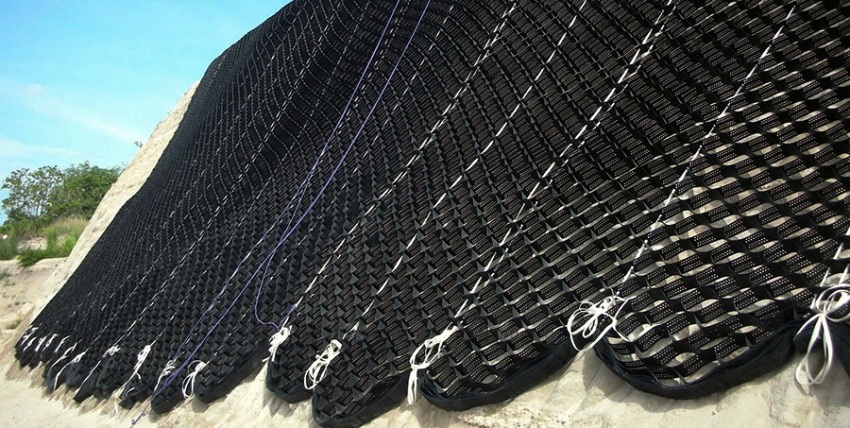
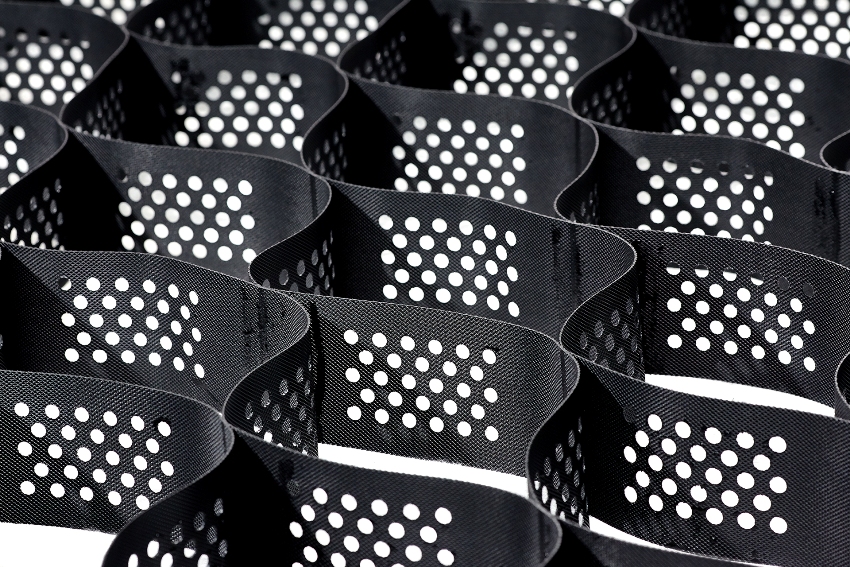
A stable frame formed when the panel is stretched on the soil surface is designed for reliable fixation of loose fillers:
- crushed stone;
- sand;
- priming;
- loam;
- small construction waste.
Today geogrids for road construction with a propylene cell structure are widely used. Volumetric windows made of high ribbons, reminiscent of a honeycomb, are intended for ground fillers, and a conventional geogrid is intended for reinforcing the trench layers.
For crushed stone fractions, lattice windows of different formats are suitable, but they are larger than geogrid holes. Both varieties are used for multi-layer sandwich in road construction. The lattice base is more suitable for forming gentle slopes after excavation.
It is interesting! The geogrid is overgrown with grass or is specially covered with fast-growing plants, which additionally strengthen the slope with roots. This principle is used in landscape design - under green slopes and shore strengthening with a geogrid.
The geogrid is strengthened differently - gravel and sand are mixed, sifting through the "windows", some of them will get tightly stuck or get entangled in the fibers. Small stones will simply press adjacent stones and the base to the ground, eliminating the movement of rubble of different fractions. During compaction, large fragments of stones go deeper into the cells of the geogrid and "fix" them even more to the soil. This stabilizes moving soils, eliminating rock displacement.
Cellular plastic paths for summer cottages are also produced, which are covered with small stones. The difference between geo-grids is significant in window sizes - 35x40 mm, 33x33 and 40x40 mm. If it is difficult to fill the soil into a small grate after excavation, cover the crushed stone with a flat mesh or perforated geotextile, cover it with soil and sow grass.
It is interesting! The construction of many facilities for the Sochi Winter Olympics would have been impossible without reinforcing the slopes with hetextile.
The need for a geogrid is palpable in case of high-quality construction of infrastructure facilities - roads, access roads, parking lots. The inconspicuous base is comparable to the reinforcement of concrete products, although the mesh and cellular base is soft and elastic. At the same time, they significantly save on the amount of crushed stone (other filler), extending the service life of the road surface and sloping lawns.
Double twisting and bonding of fibers provides strength and plasticity of the structure, which is important in climates with seasonal temperature differences. The load is distributed evenly over the entire surface of the artificial turf.
Functionality of universal geotextile reinforcing mesh
The development for reinforcing slopes was appreciated by specialists of various profiles:
- in landscape design;
- when landscaping parks and squares;
- in the construction of artificial embankments and reservoirs;
- when erecting retaining walls.
Many people prefer to buy land plots by the sea or in the floodplains, but do not think about strengthening the soil. A cottage on the coast is great, but no one foresees the threat of soil erosion and erosion of slopes. Housing in a low-lying area under a slope or a summer house on the edge of a cliff is also a risky undertaking.
Important! If the building is already there, but there is a gradual erosion of the soil, you should not wait for a disaster, it is better to start without delay by strengthening the foundation.
The use of a plastic geogrid for reinforcing slopes reduces the cost of preparing sites for buildings, increasing the safety of all communications.
Using the ability of the fortified slope to withstand significant loads, the functionality of the geogrid can be much wider:
- Anti-erosion protection of the relief.
- Fixing cones in railway construction.
- Construction of support fences.
- Reinforcement of road surface cushions.
- Strengthening steep slopes, coastal zones of artificial and natural reservoirs, drainage streams.
Suburban areas allocated for summer cottages are most often not suitable for multi-storey buildings. The reason is unstable ground that requires strengthening, especially in hilly areas. Sandy and loamy soils "creep away" after excavation, especially when it is an inclined area.
Often, developers and landscape designers are in a hurry to complete an object, planting plants on the ground without reinforcement. But it is not known how long young plants will be able to hold unstable soil with their roots without using a geogrid. – it is risky to do it.
Strengthening the slope and embankment geogrid for road construction
For the owners of the plots, settling in the new territory brings joy and the need for improvement, including the construction of access roads from the highway. Often you have to use the existing drainage pipes, but you also need to buy a volumetric geogrid.
The natural slope of the terrain can be an obstacle to the construction of a full-fledged road. It forms grooves from sewage during rainstorms. It is often problematic to build a small embankment and lay a flooring - a natural gutter interferes. A multi-layer geogrid base will solve the problem forever.
Helpful advice! By strengthening the road embankment with a geogrid, the road base is made more durable. An additional pipe along the access road organizes the drainage outflow.
The geogrid is placed on the sand poured to the bottom over about 10 cm of gravel, after which the groove is covered with a sand pillow. A pipe is laid on the base, then everything is filled with the same materials, leveled and tamped under the geogrid.
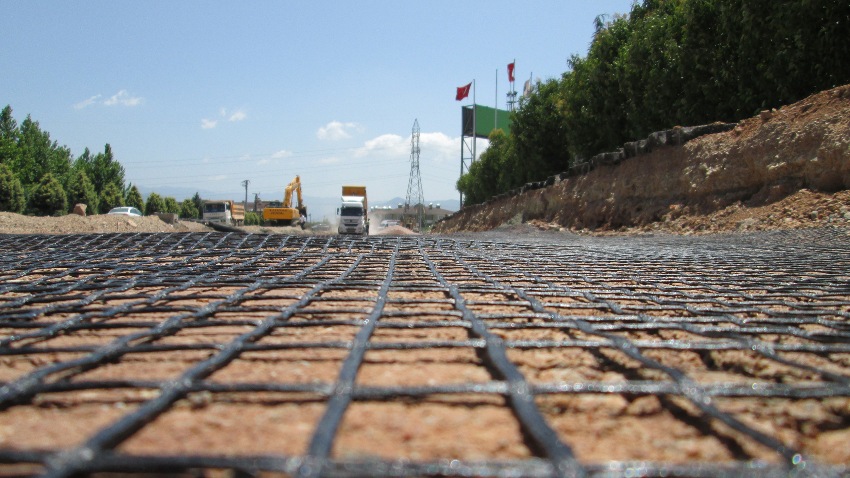

Before laying geomaterial, it is necessary to carry out preparatory work, remove debris, fallen leaves
The resulting pad is able to pass ground and surface water, keeping crushed stone from erosion. If everything is done according to the technology, then the cells of the reinforcing cloth will not let the chipped stone into the sand, the strength of the embankment will increase many times over.
It is better to roll up the road surface with asphalt. It's expensive, but nothing better has been offered yet. Several owners can arrange for a share of the work. If you make an embankment and reinforcement yourself, it will cost much less than a full road construction service. A short turning gap where there is no asphalt can be poured with concrete, but large format paving slabs are better.
It is better to additionally strengthen the steep slopes of the embankment at turning sections with geoplastic or to make a combined flooring. A well-organized congress to a suburban area will serve for more than a dozen years without repair.
Geogrid for slope strengthening parking lots and gas stations
In any area to be improved, it is important to strengthen crumbling earth embankments and slopes in order to prevent destruction. Most often, the washout of heterogeneous loose soil is observed after showers, weathering - after hurricane winds.
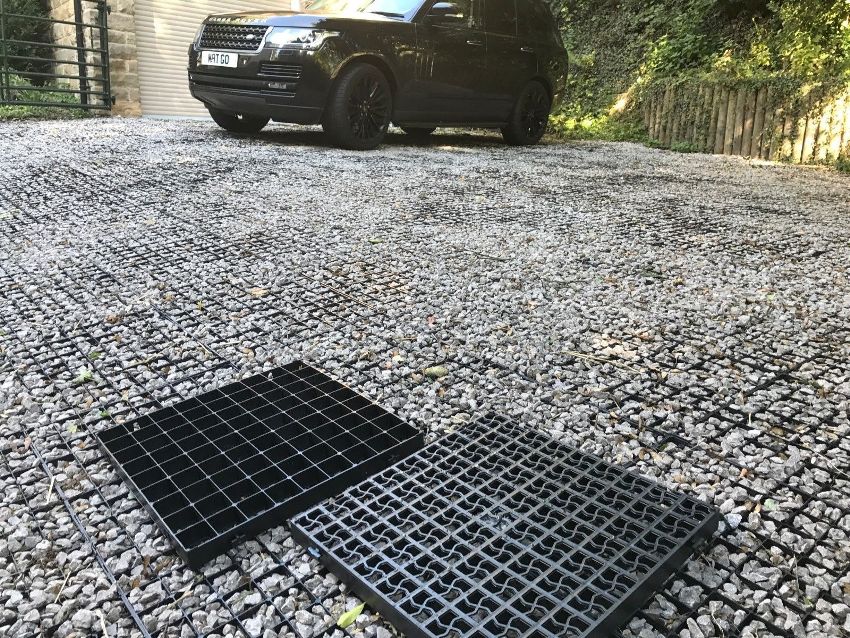

The choice of a geogrid for parking depends on the location and expected loads of the future parking
First, prepare the problem area for reinforcement with geotextile, removing the unstable layer with a bulldozer (excavator, other equipment for earthwork). Although the upper level is usually fertile with organic matter, it will be lost due to erosion. In a small area of gas station or parking, the sod layer can be removed with a shovel before work.
An equal surface before using the geogrid must be covered with a pillow of gravel, slag, sand or gravel. A layer of up to 5 cm is compacted with a vibratory roller (in another way, the method depends on the area of the fortified area).
Further, one cannot do without strengthening the slopes with a geogrid, which serves as the main surface fixture. A dense layer of geotextile will be needed to prevent the germination of weeds if the site is ennobled by landscape design. The framework and roots will reinforce the crumbling surface. For this, a conventional low density geoxytyle is sufficient.
The lawn bed is fixed with special polymer or metal anchors for the geogrid, in extreme cases, with wooden stakes that will reliably serve inside the structure. Anchors with a diameter of 10 mm should be long enough, about 200-500 mm, depending on the density of the soil. Long and sharp stakes are easier to penetrate and are sold in packs of 100 to 250.
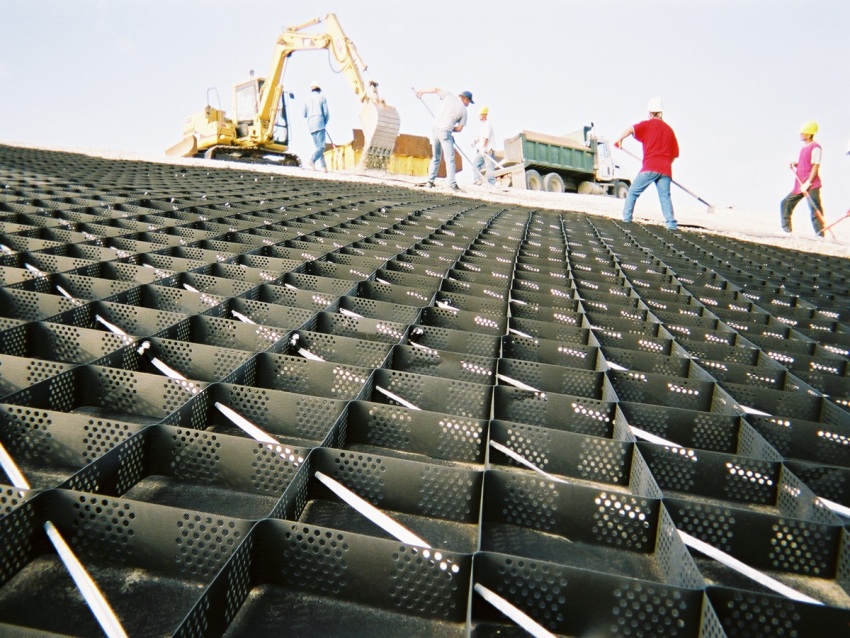

Several types of geogrids can be used to reinforce an asphalt concrete site intended for parking a freight transport
When reinforcing the filling and parking area, the fixing of the unfolded 3D format panels is carried out in stages. Metal anchors are used as reusable, they can be removed after filling the geogrid with filler. But it is important to make sure that they do not go out (they can damage the wheels of the car).
On a steep slope, it is better to leave the stakes for additional reinforcement of a reliable structure. It is enough to leave 2-3 pins at the edges of the canvas - about 10-20 anchors will be involved in securing the fragments of 20-30 cells. When stretched, the geogrid is fixed at a distance of 12-15 cm in width and 10-12 cm in length.
Note! An alternative fixation method is synthetic ropes passed through folded meshes. Stretch the web, as in the case of a conventional installation, securing the beginning of rolling with metal anchors.
The main fixing is in the corners, the anchors for attaching the geogrid can be driven in with any working or universal tool. After filling the cells, remove the anchors in width and length, replacing them with L-shaped fasteners, which securely fix at the edges to the ground.
Cultivation of the hardened surface with geotextile fabrics
The filling of the plastic geogrid windows with filler is carried out to the entire height of the cells, but so that the mounting anchors are visible. At the end of the main work, fertile soil is added along the height of the cells (even a little more to hide the mesh relief).
Lawn grass seeds are sown on the fixed surface. It is not at all necessary to do this in season, it will germinate itself when conditions are favorable. The finished lawn needs regular watering. It is desirable to provide an artificial slope with a lawn with an automatic irrigation system (at a gas station, parking lot, adjacent to the enterprise territory).
Important! With daily watering, at the beginning of plant growth and in the future, it is important to ensure that there is no excess irrigation washing away the fertile layer with seeds.
Along the edges of the lawn, where the mesh ends to strengthen the slope, you can fill the area:
- stone chips;
- crushed stone of fine fraction;
- large expanded clay;
- any other substrate for landscape design.
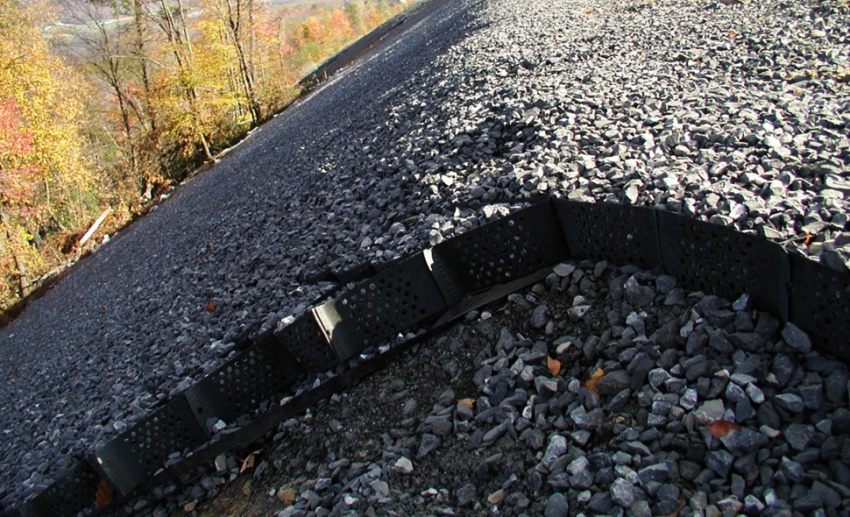

When stretched, the geogrid forms a stable frame, which is fixed on the ground surface with a filler
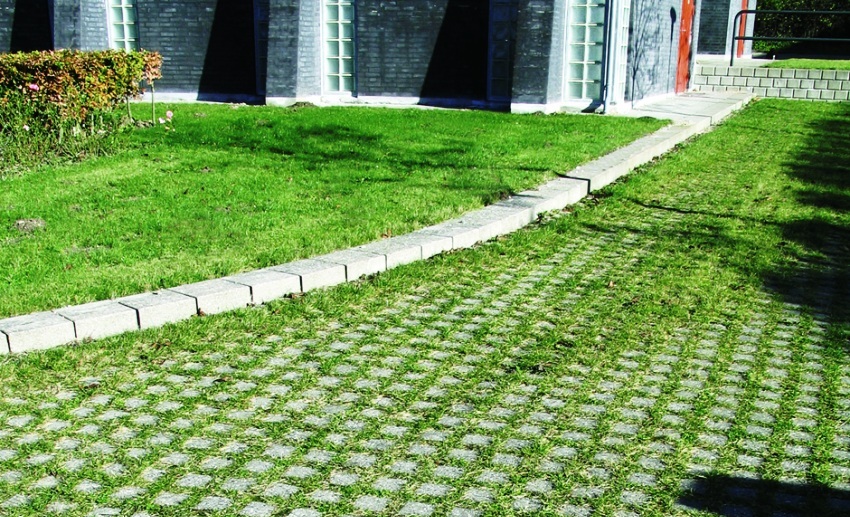
This method of landscaping is also used for eco-parking, when the car is parked on a green lawn. Ecological parking on the site is modern and attractively effective, but the foundation must be well tamped. Only the lawn is not mowed, it is crushed by parked cars - it can withstand small and medium-sized cars.
The lawn grass requires periodic renewal, so it is sown on "bald" tire tracks. Polymer geogrid will give the parking lot ease of maintenance, reliability in strengthening and beauty of the grass cover.
Advice! Natural compaction methods are used after backfilling the cells. The soil will shrink after tamping and watering.
To enhance the drainage of excess moisture in the edges of the walls of the cellular structure of the geogrids, additional perforations can be made on request.
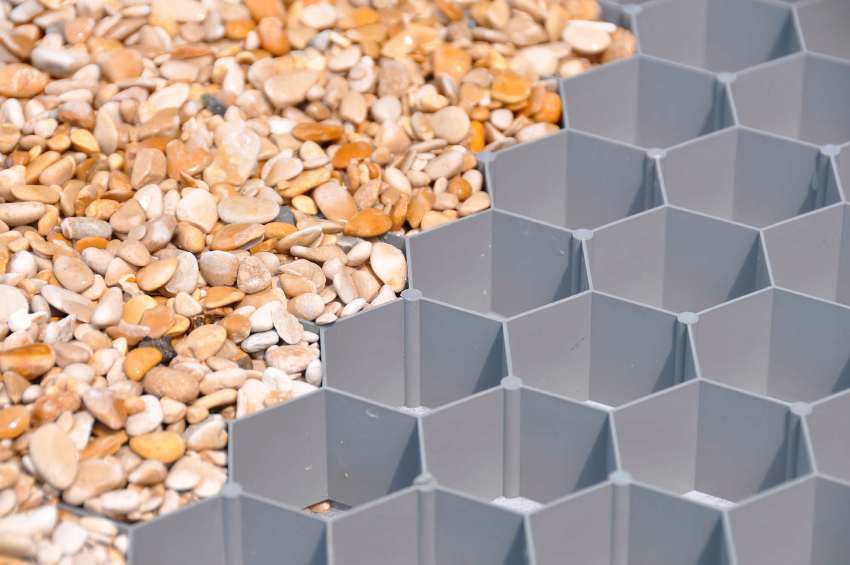

Filling the windows of a plastic geogrid with filler is carried out to the entire height of the cells
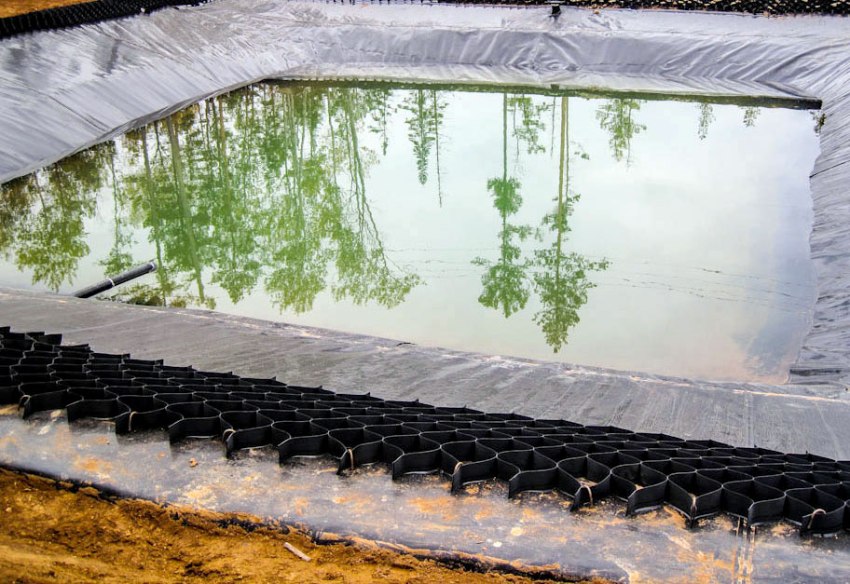
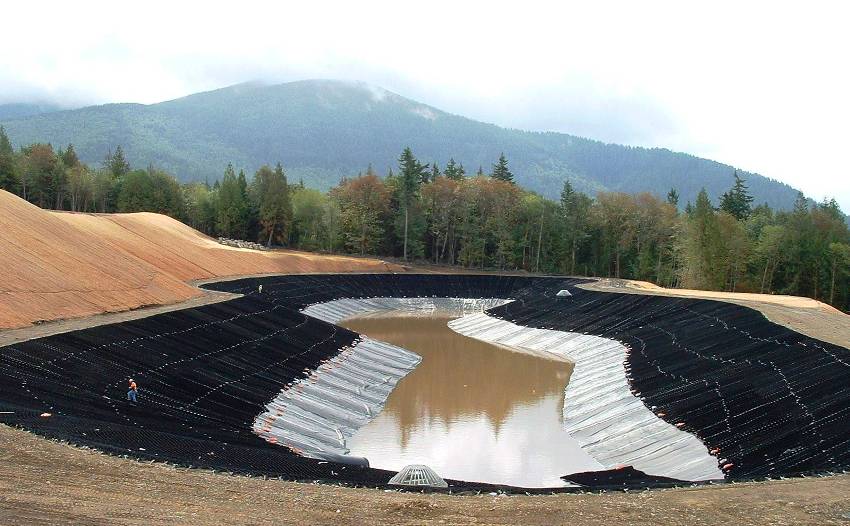
Application of a geogrid for natural and artificial reservoirs
The described type of geosynthetics is widely used to reinforce the coastline. This is true when it is planned to build a country house on the banks of a river or lake, especially with a pier for small yachts or boats.
Artificial reservoirs are often made at their summer cottage, with bridges and islands:
- ponds;
- swimming pools;
- cascading streams;
- decorative mini-lakes.
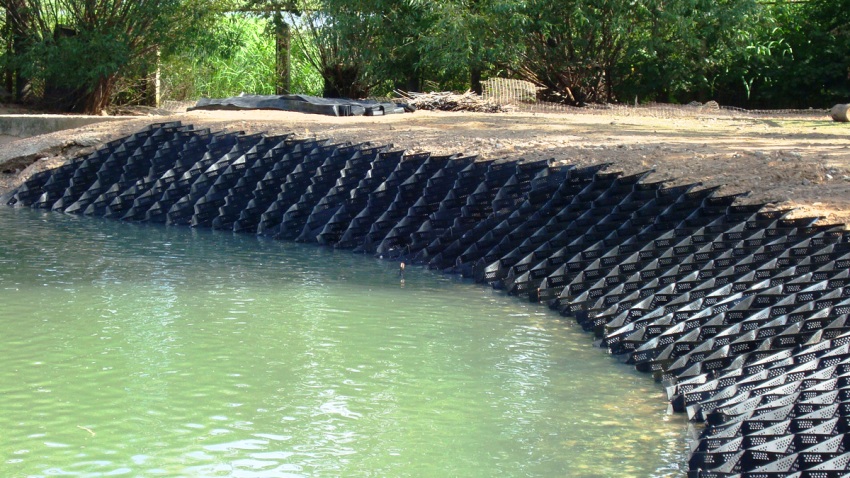
Even the slopes of a canal, a reservoir, and a small river bed are reinforced with polymer nets to resist erosion. In this case, the geotextile, not subject to decomposition and decay, descends from the shore with one edge straight into the water.
Before laying the polymer frame, it is recommended:
- drain water from the pond (at least partially);
- remove construction and household rubbish;
- clean the coastline from plants;
- fix geotextiles on the markings, which provide drainage;
- fix the mesh.
If the banks are reinforced in another way, for example, with a concrete geogrid for reinforcement, the polymer mesh is placed on the bottom.
Often, combined methods of strengthening the slope descending into the water are used, where geogrids Prudon 494 are far from the last place. It not only stops or prevents erosion processes, but also remains a good basis for anchoring vegetation along the entire coastline.
Does the polymer geogrid affect the overall eco-balance of the reservoir?
The plastic grate allows water streams to pass well, but the bottom relief is not destroyed. Polymers are non-toxic, retain their structure for many years, while fish do not get entangled in a large grid, as in a lightweight fishing net. Thanks to these properties and the preservation of the bottom relief, additional protection of the ecosystem with Prudon geogrids is carried out.
Protected in this way, the shoreline of the reservoir does not interfere with the normal functioning of the ecosystem. The net is quickly covered with bottom fouling, where fish spawn safely, and the food base for aquatic fauna multiplies.
Arrangement of the coastline of artificial reservoirs instills confidence that the vegetation planted on the slope will not slide under the water. This provides a beautiful coastal landscape by the artificial pond.
Helpful advice! It is better to distribute plants to distant cells so that the roots do not interfere with the development of neighboring hydrophytes.
Coastal strengthening is carried out not only with the help of geogrids, but also using other methodologies.In each case, it is important to follow the technology in accordance with the selected material. An artificial pond without special means is gradually silting up, like a natural reservoir.
Strengthening road slopes using geogrids
Among the most effective technologies for strengthening crumbling slopes, the method of reinforcement with volumetric synthetic gratings has proven itself best. Great opportunities at a low cost of the geogrid - a guarantee of reliable operation of this material for stabilization:
- highways;
- railway track;
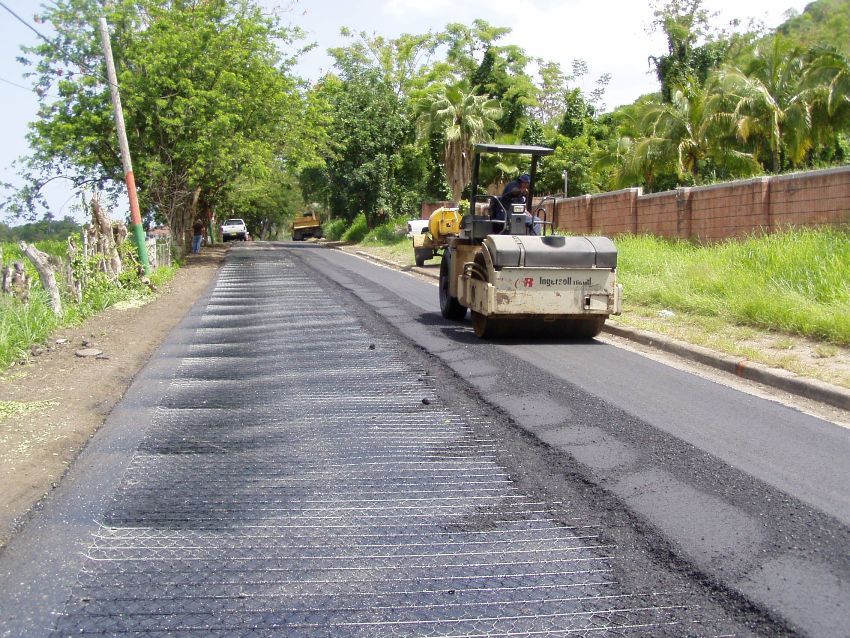

Reliable strengthening of roads can be carried out using a durable stable layer, which consists of a geogrid
- bulk shafts and dams;
- cones of bridge supports;
- retaining walls and fortifications;
- all kinds of earthen structures.
The practice of using a geogrid in road construction has proven a significant increase in the reliability of highway slope coatings. It is the optimal reinforcement method for all types of slopes that need to stabilize cones and embankments at a junction or railroad track.
Among similar proposals, experts recommend the domestic geogrid SLAVROS and the biaxial grid GSST (“Makhina-TST” Belarus) with a minimum relative elongation.
Note! Elongation of the GSS not more than 4% corresponds to the maximum working conditions for reinforcing asphalt concrete layers.
When choosing an elastic fastening of embankments and slopes, they rely on the technical parameters of the geogrid, which remain determining:
- the steepness of the embankment;
- indicator of flowability of the surface layer of the soil;
- the alleged filler;
- planned load on the structure.
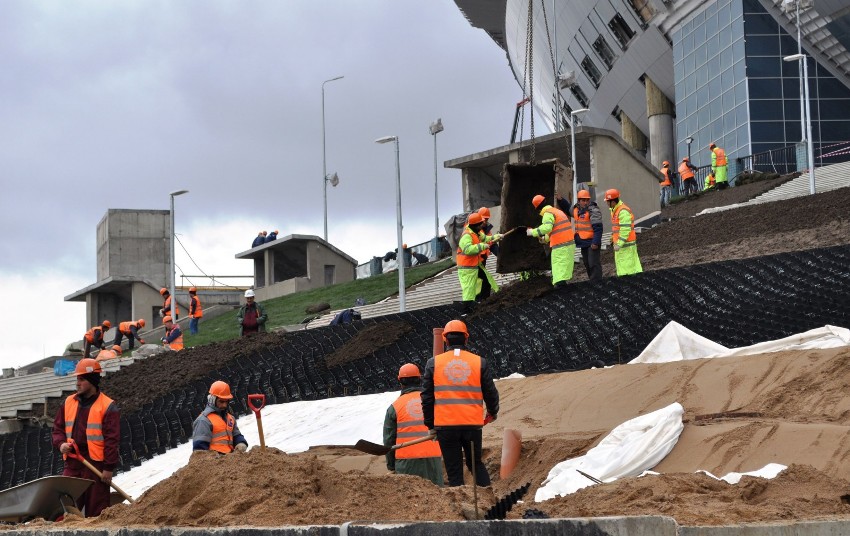
On the prepared base of the cones, embankments and slopes, lawn grass is sown and fast-growing perennials and shrubs are hauled out. The process of strengthening the slopes with a geogrid is carried out in stages. The substrate is filled up manually or mechanically - with an excavator, loader, truck crane.
How to choose a material for road reinforcement
The choice of the best option is carried out by design organizations, based on general technical problems. In places where there is more load from water flows (in mountainous and hilly areas), it is necessary to fill heavy stones into wide cells. The most popular are geogrid panels for strengthening slopes with volume cells 210x210 mm, the height of the tapes is 100 mm.
Important! For road embankments, especially where there is a large traffic load, experts recommend imported geogrids - Armatex RSM, Armatex Zh, TENAX LBO, TENAX 3D Grid.
The format provides a satisfactory level of surface reinforcement against erosion, weathering and other erosion factors. Reinforcement in this way is sufficient to reinforce crumbling slopes:
- slopes of the autobahn roadway;
- hangar areas for wholesale and retail trade;
- parking near the mall or residential complex;
- road parking;
- the foundations of the runway;
- the foundations of the tramway;
- cones of bridges and other objects.
Helpful advice! To reduce the cost of work, according to the technology of laying the geogrid, the cells are covered with soil from the given area. Fertile soil is added under the green growth on top, so it is better to preserve the sod layer in places of erosion.
When laying geosynthetics, the surface layer of embankments and slopes is prepared for anti-erosion work, after removing the sod, marking is applied. If there is a natural storm runoff nearby, gutters are provided. The configuration of embankments, trenches and cones depends on the terrain and the loads on the highway.
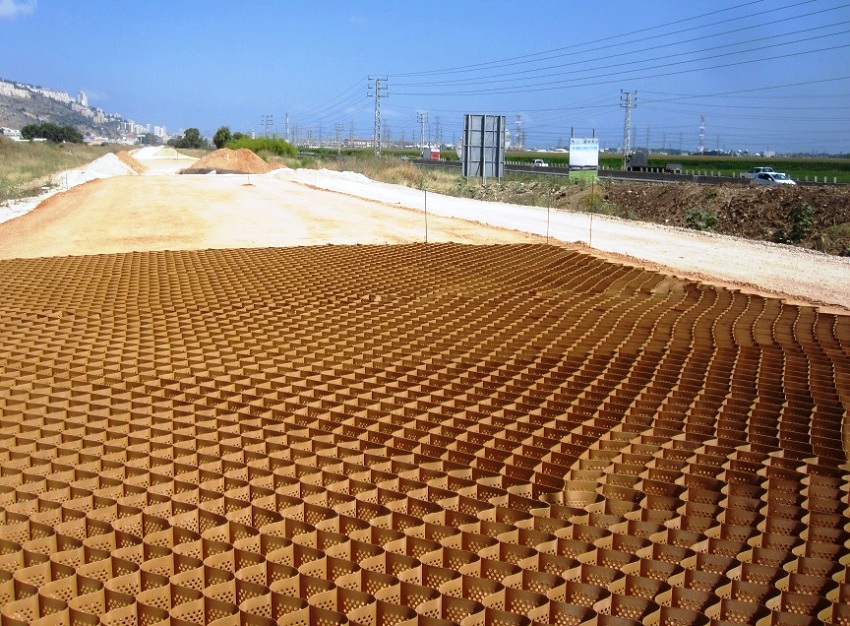

When choosing a geomaterial, several factors must be taken into account: the slope angle of the base, the type of soil, the features of the reinforcement object
The filler is poured into the cells from the top and compacted mechanically, after which the excess is removed above the level of the geoframe.
How geomats and geogrids are applicable for summer cottages
For the improvement of the suburban area, which has a complex relief with a slope, the same technologies and materials are used as at large objects.
The synthetics of the mesh for strengthening the slopes, forming a dense base on the surface, should adhere to the ground as much as possible. It is important to properly prepare the eroded slope itself:
- remove stones, branches, stumps, debris;
- if there is a planting of plants according to all the rules of landscape design, shrubs and wild growth are removed;
- depressions, pits and depressions are filled with soil and tamped, in addition to performing the function of drainage gutters.
Important! When stretching the geogrids work from top to bottom, geomats are laid from bottom to top, slightly pulling the canvas. In difficult places, more frequent fastening with pins or anchors is made.
On top of the geomat, slopes, terraces and slopes are covered with chernozem or other fertile substrate and compacted. Lawn grass seeds are sown layer by layer upon completion of the reinforcement work. This will ensure full fouling of the surface and additional adhesion of synthetics to the soil.
When forming landscape design, a special geogrid is used for paths - narrower canvases are convenient for working in the country. It is applicable both for laying a trench filled with pebbles, and for forming a lawn adjacent to the alley.
As you can see, a polymer mesh or geogrid for strengthening slopes is a simple solution to complex problems of strengthening crumbling surfaces.