The importance of concrete in the construction industry can hardly be overestimated. The basis of the foundations among the indicators of concrete is its strength. Namely, the compressive strength. Consequently, concrete structures are designed so that the concrete can accept compressive loads. The strength of the concrete is determined by the concrete grade and the concrete class. The table of the relationship of grades and classes of concrete allows you to find the right solution in the production of construction work.
Content [Hide]
- 1 Application of concrete in construction
- 2 Influence of the composition of components and technological features on the strength of concrete
- 3 Types of concrete and their classification
- 4 Table of concrete grades and their characteristics
- 5 Concrete grade and concrete class. Dependency table of brands and classes
- 6 Frost resistance of concrete
Application of concrete in construction
The range of modern use of various concrete mixtures in construction is constantly increasing. Concrete of high strength grades is considered promising, as well as special concrete with the following technical parameters: durability, low sediment, frost resistance, heat resistance, low mobility, resistance to cracking.
The main use of concrete is in precast or monolithic concrete and reinforced concrete structures and structures. In each type of construction (foundations, columns, walls, etc.), it is necessary to use concrete of the appropriate class and grade. Their characteristics are provided for by the project of the construction site.
Concrete grades are basic indicators of its compressive strength. The higher their degree, the higher the requirements for concrete strength.
Conformity tables for the class of concrete and its scope:
| Scope of use | Massive foundations in dry soils | Massive foundations in wet soils | Massive foundations in water-saturated soils | Underfloor preparation |
| Mix consistency | Hard | |||
| Class (B) | 7,5 | 10 | 15 | 12,5 |
| Scope of use | Outdoor and basement staircases | Septic tanks, cesspools | Floor slabs, beams with sparse reinforcement | Floor slabs, beams with frequent reinforcement |
| Mix consistency | Plastic | |||
| Class (B) | 7,5 | 15 | 20 | 22,5 |
Influence of the composition of components and technological features on the strength of concrete
The strength of concrete directly depends on the components involved in the preparation of the mixture:
- cement. The amount of cement contained affects the strength of the concrete up to a certain point. After that, the strength indicators become insignificant, while other concrete characteristics (creep, shrinkage), on the contrary, become worse. In this regard, the quantitative composition of cement in a cube of concrete should not exceed 600 kg. The higher the grade of cement contained in concrete, the stronger it is;
Useful advice! When preparing the concrete mixture on your own, you should use cement of a grade that is twice as high as the grade of concrete.
- water-cement module. Hardening of concrete with cement occurs with the participation of water from 15 to 25%.The workability of the mixture is possible, as a rule, at 40 - 70%. Excess water promotes pore formation and, as a result, the compressive strength decreases. Concretes with a low water-cement ratio gain strength much faster;
- placeholders. Small fractions of aggregates, the presence of dust and clay, organic inclusions in their composition negatively affect the strength of concrete. The adhesion of coarse aggregates to cement has a positive effect on strength;
- mixing. Compressive strength also depends on how thoroughly the components of the concrete mix are mixed and on what equipment they are mixed. Compaction plays an important role - by increasing the average density by 1%, the strength indicator will increase to 5% (per 1 cubic meter of the mixture);
- age and temperature conditions of hardening. The increase in compressive strength over time is influenced by the mineral structure of the cement - different cements contribute to a different increase in strength. The optimum temperature for concrete mixture hardening is 15 - 20 ° С, the degree of humidity is from 90 to 100%. To ensure sufficient moisture for hardening, it is recommended to cover the concrete with foil. At temperatures below zero, hardly any hardening occurs. It is possible to achieve a decrease in the freezing point for water with the help of special additives.
Types of concrete and their classification
According to the use of the binder component in the mixture, concrete is divided into cement, lime, gypsum, asphalt, silicate, clay, etc.
The use of certain fillers divides concrete into types:
- heavy (gravel, crushed stone from dense rocks, used in concrete and reinforced concrete structures);
- especially heavy (iron ore, barite, used for the military sphere, nuclear power plants, landfills);
- lightweight (natural slag pumice, found application in coatings and fences);
- especially lightweight (foam concrete or aerated concrete).
According to their properties, concretes are divided into waterproof, frost-resistant and fire-resistant, the degree of density of the concrete mixture divides them into rigid and plastic.
Table of concrete grades and their characteristics
To choose the right concrete mix, you need to know the correspondence of grades and classes of concrete to a specific type of work performed. It will be irrational to use concrete that is more durable than the structure requires. Basically, concrete is used for construction, not exceeding the compressive strength of the 500 grade.
Consider the table "Concrete grade and concrete class depending on the use of the ready-mix":
| Concrete grade and class | Main application |
| M100, (B7.5) | Preparatory works before pouring foundation slabs, curbs, thermal insulation of structures, as an underlying layer before reinforcement |
| M150, (B12.5) | Paths in summer cottages, small areas, pouring monolithic foundation slabs |
| M200, (B15) | The foundation for the foundation of a private house, blind area, strip foundation, cushion for road surface, floor screed |
| M250, (B20) | Installation of a foundation for a private house, stairs, small floors, fences, fences, outbuildings |
| M300 | Capital construction of a private house: walls, floors, foundations |
| M350 | Foundations of multi-storey buildings, beams, floors, columns |
| M400 | Hydraulic structures, bridges, storage facilities, military facilities |
From the table we learn which brand of concrete for the foundation can be used to build a house in the private sector.
If you are planning a small outbuilding, you can use a mixture with a low indicator (M200) of the concrete grade. For the foundation of a private house with more than one floor, a higher grade is used (M250, M300).
Useful advice! When installing a strip foundation, in addition to the grade of concrete, it is necessary to take into account the characteristics of the soil in which it will be located.
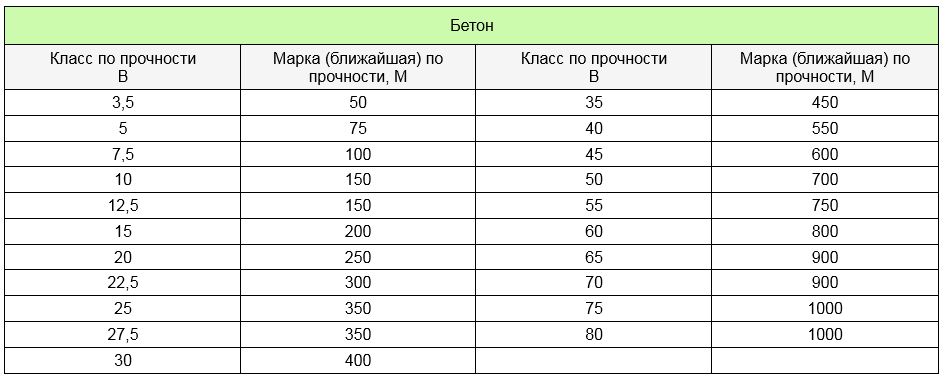
Concrete grade and concrete class. Dependency table of brands and classes
The concrete grade is determined based on the characteristics of the binder component, the water-cement ratio and the density of the filler. Concrete is classified into ordinary and lightweight.
Related article:
Table "Proportions of concrete per 1m³". Quality concrete mixes.
The composition of the concrete solution. Strength indicators. Compliance of grades with the use of concrete. Calculation of the ingredients of the mixture. Solution preparation.
Correspondence table of grades and classes of concrete:Consider the relationship between the brand and the class of concrete. The correspondence table of the brand and class of concrete will help to transfer the brand to the class and vice versa.
According to the compressive strength, measured in MPa, the concrete class is assigned. So, the definition of B20 shows: the letter B is the designation of the class, the number 20 is the pressure of 20 MPa maintained by the test cube.
The conformity of the compressive strength of concrete by classes in MPa to concrete grades is assigned by the conditions of the technical documentation.
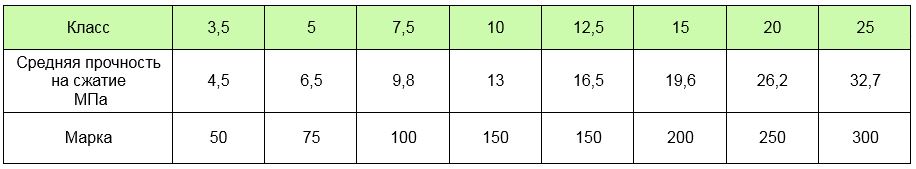
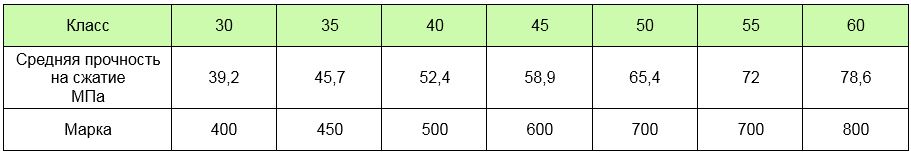
Below are two tables "Concrete compressive strength class in MPa".
Table No. 1 - from 4.5 (MPa) to 32.7 (MPa):
Frost resistance of concrete
Frost resistance of concrete is understood as the ability of the material to undergo repeated freezing and thawing without collapsing and without losing its compressive strength.
The ability of water to expand at low temperatures, filling the voids of the material, leads to its destruction. The higher the porosity in concrete, the more water will fill the voids. This means that the frost resistance indicator directly depends on the density and structure of the material.
Frost resistance of concrete is an indicator that is especially taken into account in climatic zones where concrete structures are repeatedly frozen and thawed. Then there is a risk of loss of their bearing qualities and damage.
The reason for the destruction of concrete products is a brand that does not meet frost resistance standards. If the grade of concrete for frost resistance is selected correctly, the concrete structure will last more than a century. For concrete with high frost resistance, the main indicators, in addition to the presence of cement, are the cement grade, the water-cement factor, the setting conditions of the mixture and other criteria.
Useful advice! Obtaining a higher grade of concrete for frost resistancecontributes to the addition of antifreeze additives (PMD) to the mixture. Their function consists in reducing the required amount of water and compacting the concrete.
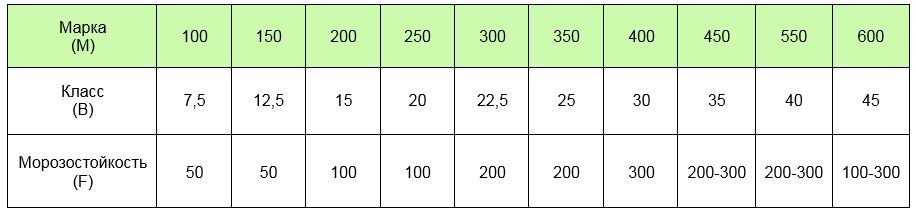
Frost resistance is indicated by the letter F and a digital designation (from 50 to 100), where the numbers correspond to the number of periods of freezing and thawing of concrete structures in which their properties do not deteriorate.
A high strength grade corresponds to a higher frost resistance grade of concrete.
Table of the ratio of the brand, class and frost resistance of concrete: