Today communications made of polymeric materials have replaced most of their metal counterparts. However, steel still remains a common alloy used in pipelines. One of the main characteristics of steel pipes that affects the accessibility is the diameter. This indicator is mandatory when drawing up construction schemes. The diameters of steel pipes are regulated by the relevant GOSTs.

The diameter of a steel pipe is one of the most important parameters affecting the serviceability of a product
Content [Hide]
- 1 Types of steel pipes by the method of their production
- 2 Diameters of steel pipes: what are these indicators for and how they are determined
- 3 Pipe diameter measuring systems: table (inches and millimeters)
- 4 Outside diameter of pipes (Dн): classification of steel products
- 5 Steel pipe table: diameters, price per rolled meter
Types of steel pipes by the method of their production
Steel pipes are used in the laying of water supply systems and gas transmission lines. Such products have many positive qualities, among which are high strength, resistance to linear expansion. A significant disadvantage of such products is that they have poor resistance to corrosive effects. All steel pipes are classified according to the method of manufacture and purpose.
One of the most common types of steel pipes are electrowelded products. They are also called longitudinal seam. They are made of sheet steel. The use of electric welding equipment allows you to get a small, even seam. Such pipes are used for laying water supply lines and gas transmission systems. The diameters of pipelines of this type are quite easy to determine using regulatory documents (GOST 10704-91). The range of section sizes in this case is 10-1420 mm.
The next type of steel pipes is spiral seam. Such products are made from steel, which is produced in rolls. Like the previous type, these parts have a seam, however, it does not differ in the minimum width. Thus, spiral pipes are not able to withstand high pressure indicators (unlike electric welded ones). Because of this, they are not used for laying gas transmission systems. These products are regulated by GOST 8696-74.
Modern industry allows the production of structures that do not have a seam at all. Seamless pipes are made from special blanks. It should be noted that such products are made in two ways: hot and cold.In GOSTs, the diameters of steel pipes are prescribed in special tables containing other geometric characteristics of products, which simplifies the search. Seamless parts are governed by GOST 8732-78 and GOST 8734-75.
The range of diameters of products that do not have a seam ranges from 10 to 550 mm. The absence of a seam significantly increases the strength characteristics of these pipes, which allows them to be used in critical communications.
Note! Normative documentation controls seamless products, however, it applies only to parts with a diameter of less than 250 mm.
Diameters of steel pipes: what are these indicators for and how they are determined
Knowing the exact value of the diameter that a water or gas pipe has, it becomes possible to calculate the volume of a substance transported through communications. The use of such pipes in construction requires a clear definition of the dimensional characteristics necessary for the calculation of economic systems.
An example is the heating system. The diameter of pipes in such communications must be clearly calculated so that in the winter period the system provides uniform heating of living quarters.
Today, there are several common methods for calculating the diameter of steel pipes. The size chart that can be found in the regulatory documents is the simplest one. You can also determine this parameter using online calculators. Such programs are located on specialized sites on the network, so it is not difficult to find them.
An independent calculation of the diameter of the communication is carried out using mathematical expressions. The type of formula depends on the operational purpose of the communication. For example, the following equation is used to determine the diameter of the heating pipe:
D = sqrt ((3.14 x Q) / (V x DT)), where:
D - diameter (internal);
Q is the heat flow rate, calculated in kW;
V is the velocity of the substance transported through the pipeline (measured in m / s);
DT is the temperature difference at the starting and ending point of the system (input / output);
sqrt - square root.
This formula allows you to fairly accurately determine the diameter of the pipe. The designation of this indicator in the diagrams makes it possible to correctly calculate the required pressure and the amount of transported substance per unit of time.
What pipe diameters exist: their varieties
Today, diameters are divided into several types, depending on what exactly this value characterizes. To use this parameter in calculations, it is recommended to study the types of diameters.
Nominal size of pipes (DN). Indicator of the inner space of the pipe. This parameter is calculated in mm or inches. In the second case, the value is rounded. Knowledge of this parameter allows you to select accessories (fittings) of the required size for pipes.
Nominal diameter. This indicator is very similar to the previous type, but it has some differences. For example, the main characteristic of the nominal parameter is its high accuracy, which does not tolerate rounding.
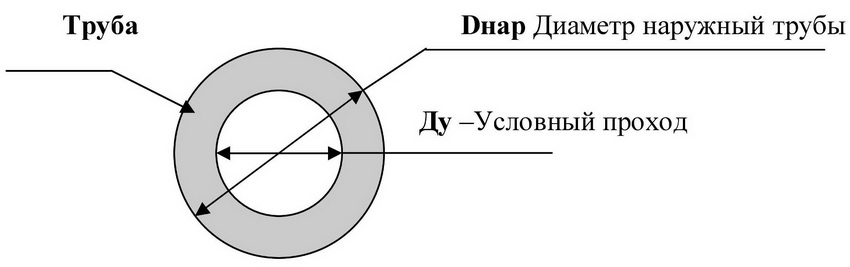
Inner diameter (Du). This indicator is a physical quantity that is measured in mm. The inner diameter is used when calculating the permeability of a piping structure. This value should not be confused with the nominal pipe diameter.
Note! To calculate this parameter, there is a special formula: Dy = Dн - 2S.
Outside diameter (Dн).According to this parameter, all pipes made of steel are divided into 3 main groups: small, medium and large. Each group has its own size range and purpose. The easiest way to determine this indicator is from the table of steel pipes. GOSTs regulating such products can be easily found on the Internet using the search box of your browser.
It is necessary to note such a parameter as wall thickness. This value is physical and affects the quality characteristics of the part. For example, the volume of the product and its mass depend on the thickness of the walls. The wall thickness is calculated in mm. To determine it, the following simple formula is often used:
t = Dн - Dу
Pipe diameter measuring systems: table (inches and millimeters)
Products, the diameter of which is calculated in inches (for example, 5 ″), are used when laying water pipelines and gas transmission structures. On the Internet, you can find tables containing this value in both millimeters and inches. Some of the schemes combine both measurement systems, which is very convenient. A five-inch pipe corresponds to a standard 125 mm bore.
The measurement of the diameter of pipes in inches is used during the installation of water and gas transmission lines, as this simplifies the overall calculation. One inch equals 25.4 mm. It is important to remember that when measuring a pipe, 1 inch has a different size, namely 33.5 mm. This is explained quite simply: the dimensions of the pipes are calculated by the inner diameter, and not by the outer one. When drawing up the installation plan and the diagram, this discrepancy must be taken into account. This information allows you to answer the question of how to measure the diameter of the pipe and avoid mistakes.
Table 1. DN in millimeters and inch size designation system for steel pipes:
| DN, mm | Thread diameter, inches |
| 150 | 6″ |
| 40 | 1 1/2″ |
| 80 | 3″ |
| 15 | 1/2″ |
| 100 | 4″ |
| 32 | 1 1/4″ |
| 50 | 2″ |
| 125 | 5″ |
| 25 | 1″ |
Helpful information! As a rule, no problems arise when installing only steel products, since they are measured in inches. However, when it becomes necessary to replace the old communication from steel with plastic, confusion can occur. Therefore, it is worth remembering that the actual and metric inch sizes differ.
In most cases, laying inch pipes does not cause any difficulties. The nature of the discrepancy lies in the designation of steel products (water and gas), which are sold and marked with a nominal diameter, while their real cross-section has other dimensions. An example is a simple calculation of the dimensions of a pipe, the outer diameter of which is 140 mm, and the wall thickness is 5.5 mm.

To avoid mistakes when planning communications, it is necessary to take into account both the outer and inner pipe diameters.
A simple equation is used to determine the actual diameter:
D = Dн - t x 2
After introducing the required values, this formula takes the following form: D = 140 - 5.5 x 2 = 129 mm. This indicator corresponds to the real diameter of the pipe, in which the section of the outer wall is 140 mm. However, the nominal bore or inner diameter of an inch pipe (or millimeter) is the dominant value. In this case, this value is 125 mm, it is for it that most construction calculations are made.
For joining steel and plastic pipes, special transition elements are used - fittings. These adapters allow you to connect two pipes with different cross-sectional parameters, made of different materials. In order not to make a mistake when installing a communication or replacing it, it is recommended to take into account both the outer and inner diameters of steel pipes.
Outside diameter of pipes (Dн): classification of steel products
As mentioned above, the inner and outer diameters differ from each other.The first of them is used to designate individual elements of pipeline structures. Steel products are also sold by the inner diameter. This indicator is important in the event that it is necessary to carry out installation calculations of a water supply or gas line. In turn, the outer diameter is used to determine the strength characteristics of the pipeline and its resistance to mechanical stress.
The outer diameter of steel pipes is a characteristic by which all products made of this material are classified. Depending on this parameter, there are three main types of pipelines:
- small;
- medium;
- big.
Pipes that belong to the small group have a diameter range from 10 to 102 mm. Medium-sized products can have a cross section from 102 to 426 mm. The diameter range of large steel pipes starts from 426 mm. In turn, it is recommended to determine the inner diameter according to the table.
Small pipes are used in the installation of communications in residential buildings. City water transport lines are laid by means of medium-sized products, and they are also actively exploited by companies that are engaged in the extraction of oil (crude). The main areas in which large steel products have found application are oil and gas transportation. Trunk lines are assembled from large parts. The diameter of gas pipes can be up to 1220 mm.

The range of steel pipes is quite wide, since these products are used in all areas where the laying of communications is required
Standard diameters of steel pipes: table and description
When finding the inner diameter, the indicator corresponding to the size of the nominal bore is rounded to 0 or 5. Thus, when determining this characteristic, the size is standardized to the nearest parameter of the metric system.
Related article:
GOSTs of steel pipes: basic standards for quality products
Different types of metal products. Varieties of pipes. Manufacturing methods. Technical characteristics of steel pipes according to the standard.
Knowing this information, it is easier to calculate the pipe diameter. How this parameter is measured in millimeters and inches has already been said above.
Note! The most widespread, due to serviceability, are products with a diameter of 426 to 1220 mm. These steel pipes are used as trunk lines for gas and oil pipelines, sewers, as well as structures used for irrigating fields.
In residential buildings, steel water pipes are used, the diameter of which is 15 or 20 mm (sometimes 32). For sewage, larger products are used, which is due to the need for drainage. Heating systems are made up of small pipes.
Table 2. Effect of diameter on the operational area:
| Operational scope | Diameter, mm |
| Plumbing in residential buildings | 15-32 |
| Gas pipelines in residential buildings | |
| Sewerage systems | 50-100 |
| Gas and oil transportation lines | 426-1220 |
Normative documents contain more detailed tables, which contain information not only about the section, but also about other geometric characteristics. They are the easiest way to determine the pipe diameter (in millimeters and inches). It is important to remember that by using special tables, you can calculate the required cross-sectional indicator (internal or external) of both steel and other types of pipes.
Finding the diameter of steel pipes: GOST table with thicknesses
The use of special tables located in the regulatory documentation allows you to very quickly determine the required parameter. This can be an inner or outer diameter, and auxiliary geometric characteristics such as wall thickness, mass, etc. are indicated.
It should be noted that the difference between the outer diameter of metal pipes and Dу can reach 7 mm (depending on the type of rolled metal). For example, steel electrowelded parts used in the installation of utility lines may differ in these indicators by 5-10 mm.
Table 3. Diameters and thickness of steel electrowelded pipes:
| Inner diameter (Dу), mm | Outside diameter, (Dн) mm | Wall thickness, mm |
| 80 | 89 | 3 |
| 15 | 20-22 | 1,5 |
| 50 | 57 | 3 |
| 100 | 108 | 3,5 |
| 32 | 42 | 2 |
| 20 | 25-28 | 1,5-2 |
| 40 | 48 | 3 |
| 25 | 30-32 | 2 |
The main indicator indicating the accessory of the product is undoubtedly the inner diameter. Pipes are also designated by the external size of the section, which is a prerequisite for calculating the mechanical resistance.
Note! The sizes of products with inch markings are most easily determined using a tabular method. It is important to remember that when joining steel lines with pipelines made of another material (for example, plastic), it is necessary to take into account not only Du, but also Dn.
The popularity of the tabular method is due to the fact that combined pipeline structures are common in the modern world. Such systems contain steel pipes and polymer elements (fittings).
Steel pipe table: diameters, price per meter of rolled steel
The cost of one meter of these products is determined by their mass. In this case, a certain relationship can be traced: the thicker the product made of steel, the greater its weight. On the Internet, you can find many tables that contain information about the prices of various parts, classified by the inner diameter. Steel pipes belong to the middle price segment. They are more expensive than polymeric ones, but surpass them in strength and pressure resistance.
It should be noted that various alloys and protective additives can be used for the production of steel pipes. It also affects the final cost of the products. For example, galvanized parts or stainless steel pipes have a higher price than elements made from conventional steel.
Table 4. Cost of the most popular water and gas pipes made of steel:
| Du, mm | price, rub. (for 1 m) |
| 50 | 80-170 |
| 15 | 32-70 |
| 40 | 80-108 |
| 32 | 53-95 |
| 20 | 40-50 |
Thus, the diameter of water pipes and gas transportation products affects their cost. Parts that have a cross section of over 100 mm are practically not used in everyday life. The cost of such pipes is quite high, since 1 m of a part can weigh more than 10 kg. The heaviest pipe has a diameter of 1220 mm and a wall thickness of 16 mm. The weight of a meter of such a part is approximately 475 kg.
Diameter is a necessary characteristic, without which the laying of a pipeline structure is impossible. When determining this parameter, it is necessary to clearly understand that there are several of its varieties. In the tables that can be found in the relevant regulatory documents, the inner diameter of steel products is most often indicated. If you decide to use a special formula to determine the cross section, it is recommended that you pay attention to the examples containing the solution.