To create a favorable environment, optimal temperature and humidity, ventilation systems are used in all residential and industrial premises. Depending on the method of air circulation, purpose, design and application, ventilation systems are divided into types. To be sure of the advisability of using a particular system for a particular room, you need to familiarize yourself with the main types, functions and purpose of ventilation systems.
Content [Hide]
Classification of ventilation systems
The following types of ventilation systems are distinguished:
Depending on the way the air flows move:
- with natural urge (natural ventilation);
- with mechanical induction (forced ventilation).
Depending on the purpose:
- forced ventilation;
- exhaust ventilation;
- combined ventilation.
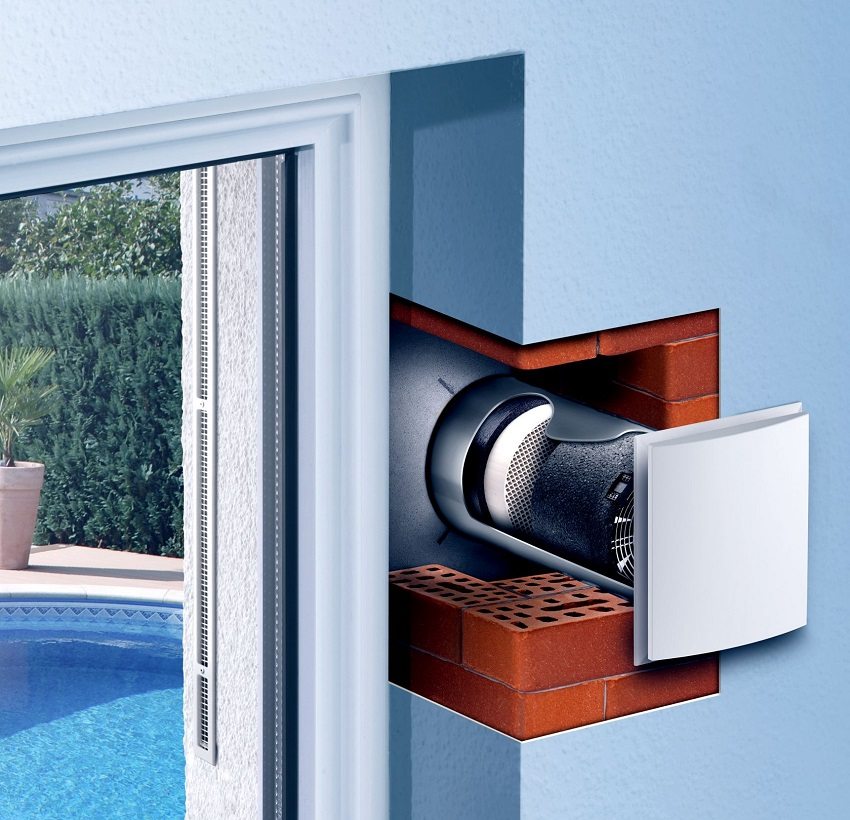

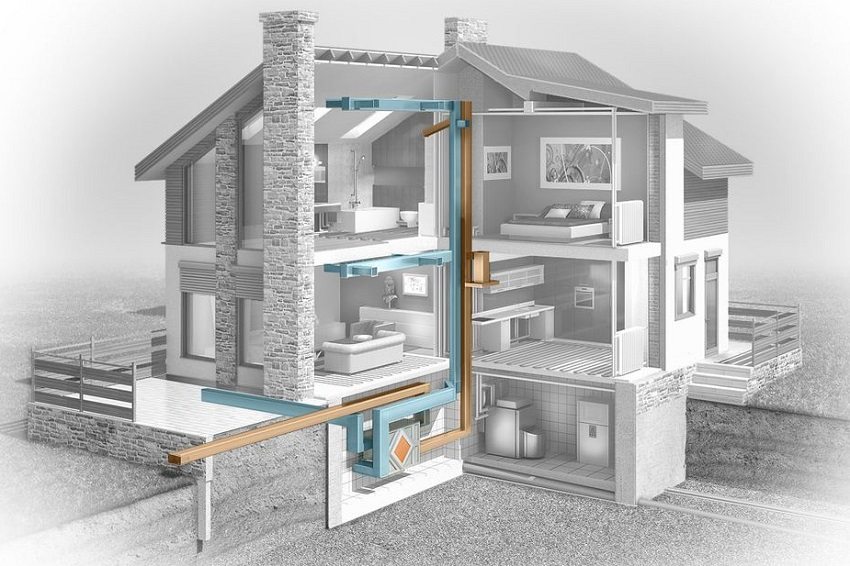
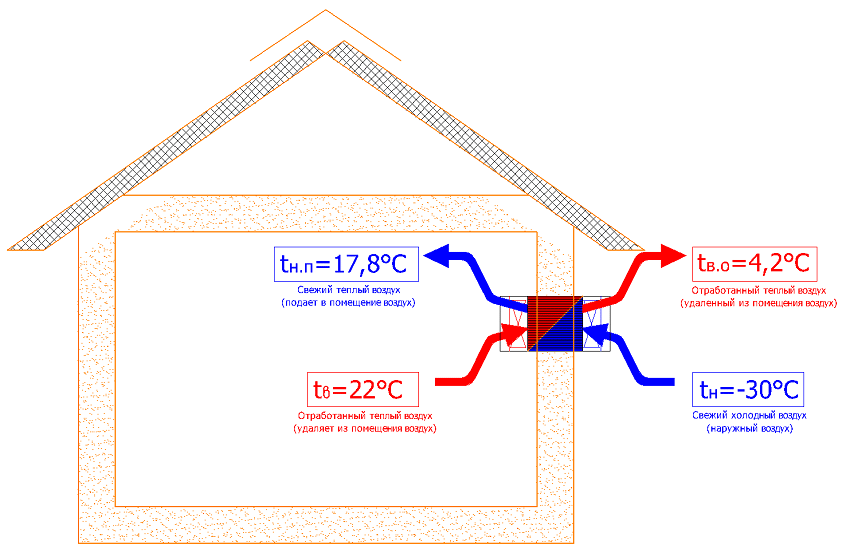
Recuperator built into the outer wall of the house - a simple solution for the supply of clean air to the room
Natural ventilation systems
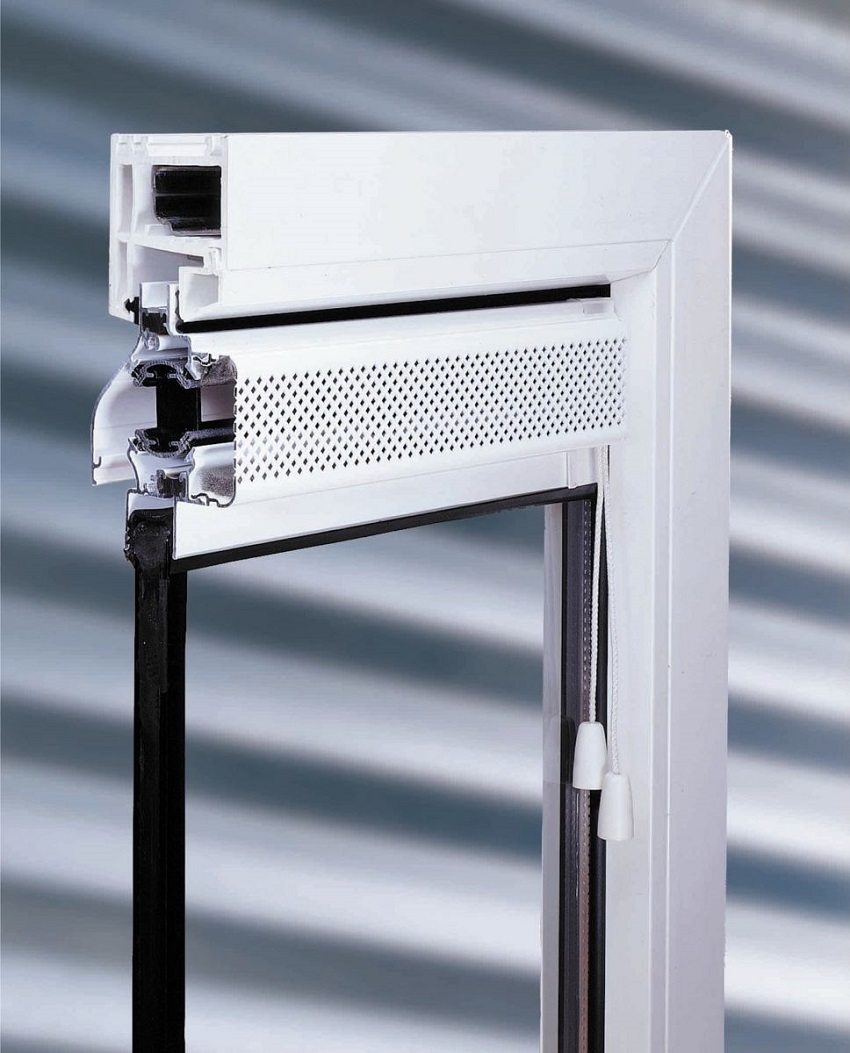
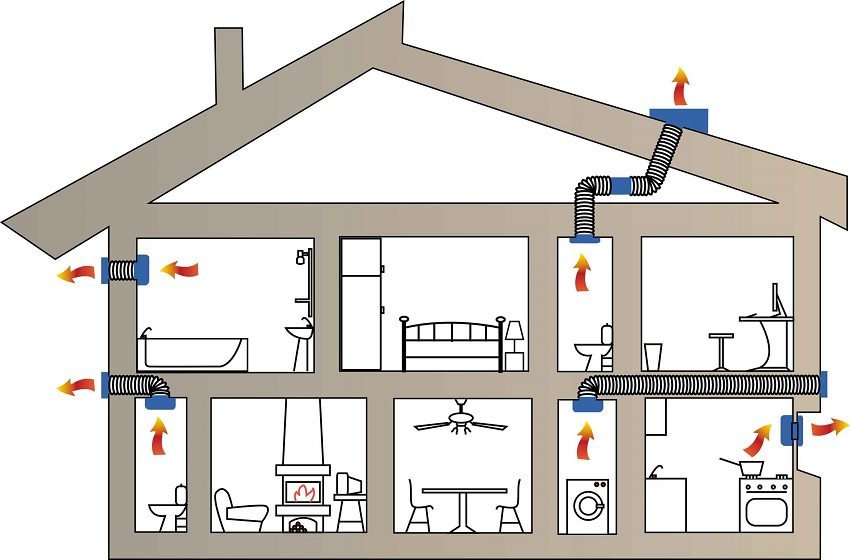
The natural air ventilation system is not equipped with electrical equipment. Air circulation in such a system is carried out due to the difference in pressure and temperature of the outside air and indoor air, as well as wind pressure. For multi-storey construction, vertical ventilation ducts are arranged, which are closed with ventilation grilles at the exit point in the premises (kitchen, bathroom). The ventilation channels are led out of the roof and deflectors (aerodynamic devices) are installed on them, which help to enhance the air outlet by means of wind force. The intake of a fresh air flow is ensured by leaks of doors and windows, as well as their open position. The movement of air flows in the scheme of a natural ventilation system occurs from the bottom up.
The natural ventilation system of the room, on the one hand, is reliable and durable, since it does not have mechanisms and automation, on the other hand, the system is highly dependent on natural factors (air temperature, external air flow rate), there is a risk of clogging the air ducts. In addition, with the widespread use of sealed structures in rooms plastic windows, the volume of the supply flow has decreased.
Forced ventilation systems
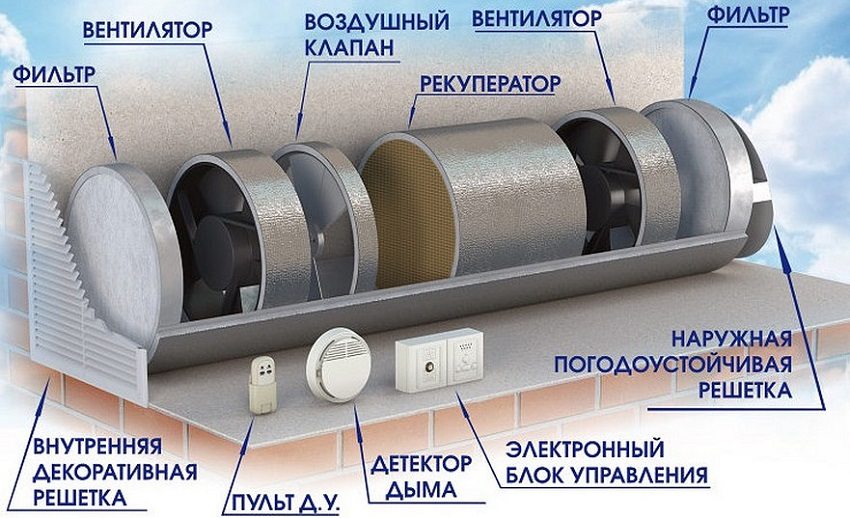
In the case when natural ventilation is unable to provide the required air exchange, ventilation systems with mechanical induction are used. Due to the use in the circuits of such installations of various devices as a fan, recuperator, filter, etc., the movement of the air flow occurs regardless of weather conditions. In addition, forced systems are capable of cleaning, heating or cooling the supplied air, and regulating the flow rate. Artificial air exchange systems are quite effective, but more expensive to operate and depend on the supply of electricity. Forced installations are equipped with automatic control.
The combined system may include exhaust fans to be built into the kitchen and / or bathroom ducts. Moreover, the fans can be endowed with artificial intelligence (timer, hydrostat, motion sensor), which will also help to avoid unnecessary energy consumption. While the device is automatically turned off, the air flow is natural. Sometimes window or wall inlets are used to increase the air flow.
Useful advice! Combined systems reduce energy costs and ensure the required level of air exchange.
A competent calculation of the efficiency of a particular ventilation system is carried out by a specialist.
Supply and exhaust ventilation systems
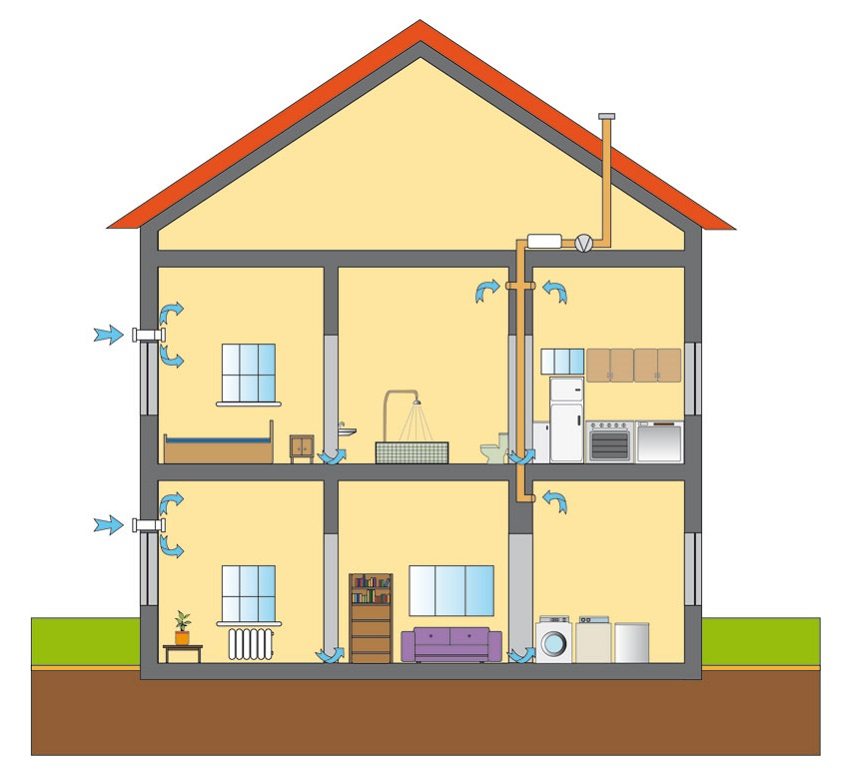
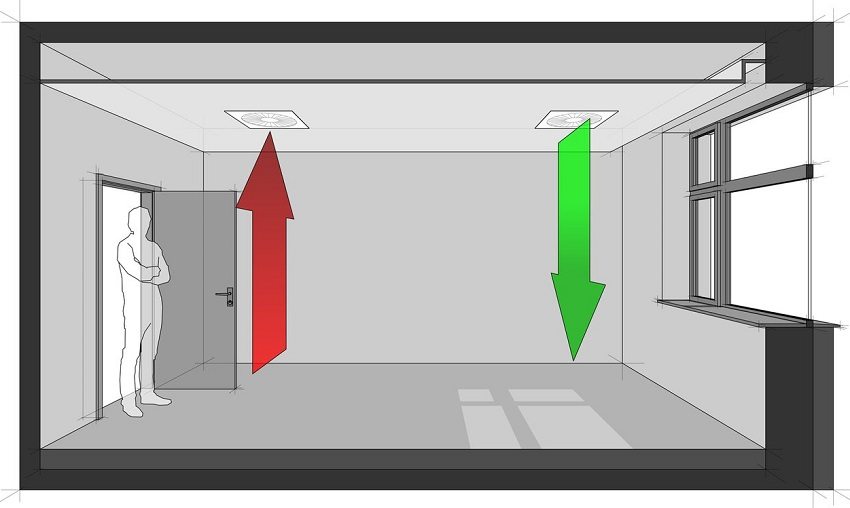
The supply ventilation system ensures the flow of outside air into the room. With the help of various devices, the incoming air is purified, humidified, heated or cooled. Exhaust of polluted air is carried out using exhaust ventilation systems. The operation of the supply and exhaust unit should be based on the calculation of the balance of air exchange.
Related article:
|
There is only supply ventilation or, conversely, only exhaust ventilation. Depending on the ventilation zone in the room, supply and exhaust ventilation can be local (concentrated in a specific place) or general exchange (serve the entire room).
Ventilation of local and general exchange type
The ventilation system serving a specific area in the room is local ventilation. Local supply ventilation provides fresh air to a certain place in the room, for example, a work area, while local exhaust ventilation works to remove polluted air in places of its concentration. The use of local ventilation systems is mainly industrial, as an option for domestic use of local exhaust ventilation - extractor hood over the stove.
The general ventilation system carries out the air exchange of the entire room. As well as local, general exchange ventilation system can be in two versions - supply and exhaust. The supply general exchange system is performed mechanically, since there is almost always a need to clean and heat the supply air.Exhaust general ventilation can be naturally induced (unless otherwise required by the norm) or be equipped with simple devices for removing polluted air.
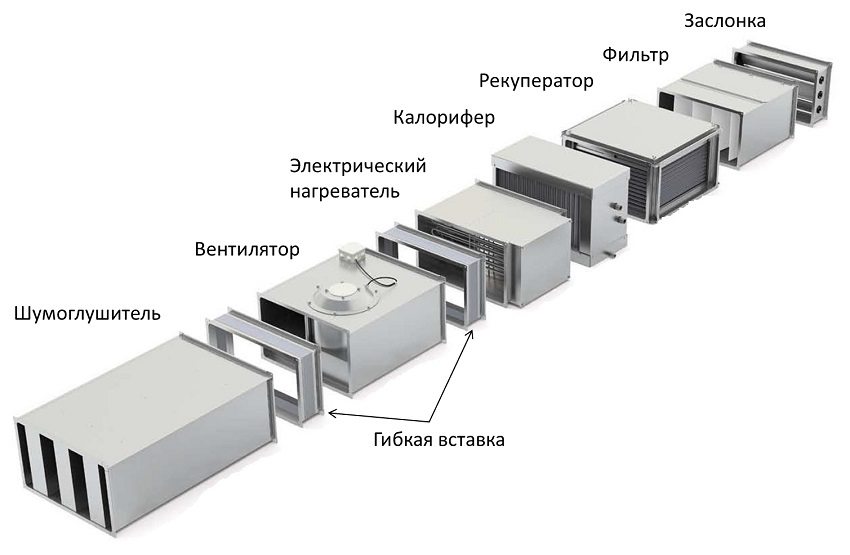
Type-setting and monoblock ventilation systems
Type-setting ventilation system - these are separate elements and devices for ventilation, assembled according to the scheme into one system. The advantage of such a ventilation system is that it can be assembled in blocks and devices according to individual choice and for rooms of different purpose and area. It is mandatory that the scheme and calculation of ventilation systems in the typesetting version must be performed by a professional.
With a monoblock ventilation system, all devices and process elements are concentrated in one housing (monoblock), equipped with noise insulation. The set of devices in a monoblock installation may be different, but often a heat recuperator is included. Among the advantages are the ease and speed of installation of the ventilation system, a minimum of consumables, and a low noise level. All devices are assembled and tested at the stage of their production, so monoblock systems are quite effective.
Air heating and ventilation system
Air heating is one of the most promising modern types of space heating. The scheme of such a heating system has several advantages:
- combining heating and ventilation functions;
- safe mode of operation;
- high sanitary and hygienic indicators;
- use of different heat carriers in work.
Air heating systems perform both heating and ventilation work. During the heating period, they operate using air recirculation. Taking into account the heat sources available in the room, air heating units can be equipped with an electric or water heater. Air heating works thanks to a supply ventilation system with an air heater heated from a central heating system. The presence of automatic control allows you to select the required operating mode and regulate the temperature of the heated room. Air heating systems combined with ventilation are quite capable of providing heat to the entire serviced room.
Calculation of ventilation systems
The ventilation calculation should result in a reliable and easy-to-use ventilation system that provides the required air exchange with a low noise level. When calculating, many use prepared calculators to automatically select the parameters of the ventilation unit.
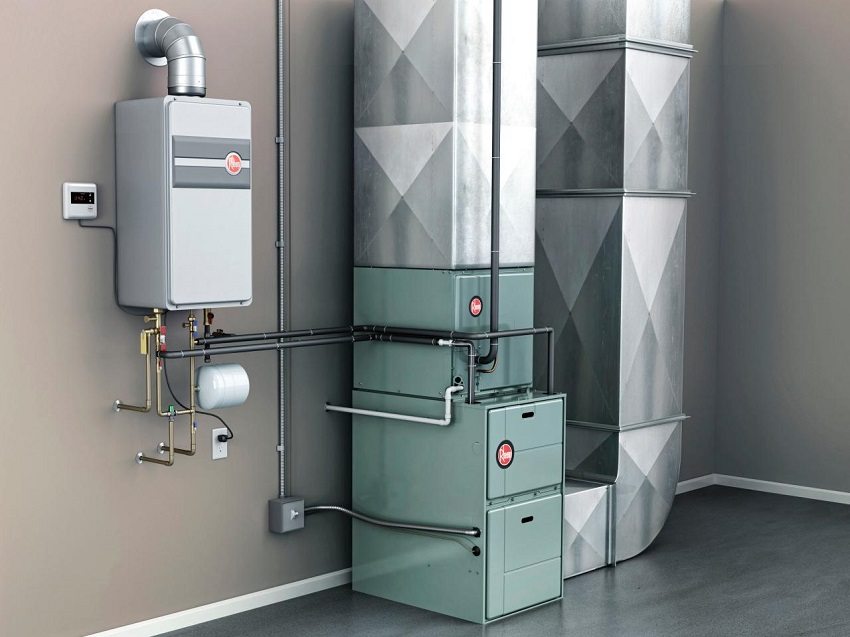

Air heating systems, combined with ventilation, are able to provide heat to the whole house
Useful advice! When calculating ventilation, obligatory guidance is required by state standards and rules expressed in SNiP 41-01-2003, as well as the corresponding sanitary and hygienic requirements.
The calculation of the ventilation system combines several stages. Air exchange is calculated (air capacity), determined in cubic meters per unit of time (hour). For the calculation, a diagram of the entire object is drawn up, indicating the size and purpose of each room. Air exchange is calculated according to two indicators: the number of people and the frequency.
- Calculation of performance by the number of people:
L (required air exchange) = Lnorm x N, where
Lnorm - standard consumption for 1 person;
N is the number of people.
- Frequency calculation:
L (required air exchange) = n x H x S, where
n - frequency (standard) air exchange;
H - room height, m;
S is the area of the room, m².
The value of n for residential buildings is 1-2, for office buildings 2-3.
From the obtained values of air exchange for ventilation, the larger is taken.
The calculation of the air ducts is performed after the diagram of the air duct network has been drawn up. Such a scheme should take into account the length of the network and the calculated air exchange in all rooms. According to the duct diagram, the parameters of the air ducts and air distributors are calculated.

The calculation of air ducts is performed after ventilation system diagram created
- The formula for calculating the cross-sectional area (calculated) of the duct:
Sc = L x 2.778 / V, where
Sс - area (calculated) section, cm²;
2.778 - proportionality coefficient (hours / seconds, meters / centimeters);
L is the flow rate of air passing through the duct, m³ / h;
V - air speed, m / s.
- The formula for calculating the cross-sectional area (actual):
for a circular section:
S = π x D² / 400
for a rectangular section:
S = A x B / 100, where
S - cross-sectional area, cm²;
D is the diameter of the circular section, mm;
A, B - the height and width of the rectangular section, mm.

When calculating ventilation, specialists are guided by state standards and the corresponding sanitary and hygienic requirements
The next step is to calculate the resistance of the air distribution network. The calculation must take into account each element of the network. Performed by specialists using a specific program or calculator for ventilation parameters.
Next, the power of the heating element is calculated (air heater).
- The formula for calculating the power of the heater (P, kW):
P = ΔT x L x Cy / 1000, where
ΔT - temperature difference at the inlet and outlet of the air heater, ºС;
Cу - heat capacity of air (taken equal to 0.336 W · h / m³ / ºС);
L - air capacity, m³.
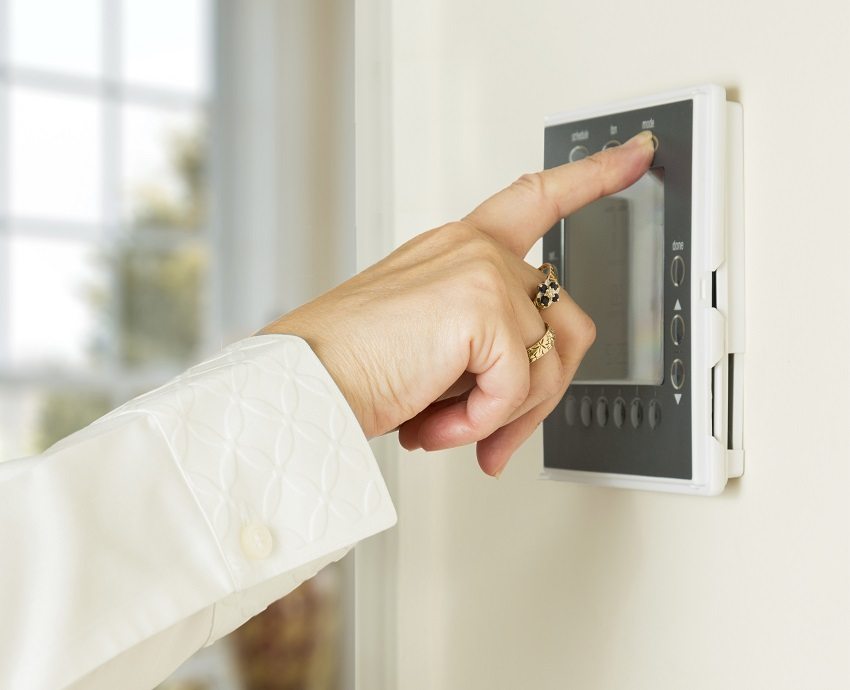
By adhering to the SNiP requirements in the calculations, it is possible to minimize the costs of all elements of the ventilation unit and its operation. Modern ventilation supply systems are equipped with a remote automatic control panel, which allows you to regulate air exchange and select the optimal operating mode. Automatic control regulates the air temperature in the room, the fan speed, and also monitors the operation of the air heater.
Useful advice! When choosing a ventilation system, give preference to installations with a digital automation system. The display of the control panel of such a control shows information about the operation of the entire ventilation system.
More modern automatic control systems allow you to control filter contamination, operate on a timer, and control the air humidifier.
Testing of ventilation systems, their operation and maintenance
As soon as the installation work is completed, ventilation systems are tested. The tests are documented by the Certificate of Completion.
Individual equipment testing includes the following activities:
- control of the conformity of the installed equipment to the SNiP requirements;
- tests of mounted installations in idle mode for four hours of continuous operation. This stage includes testing of starting devices, the level of heating of electric motors, the quality of oil seals, assembly and installation control.
Tests of ventilation units are carried out when the facility has not yet been put into operation. Since the air distributors are installed very recently, tests are carried out without them. If the system is working properly, then when they are connected, the operation will be normal. The act reflects that the tests of the system were carried out without connecting the air distributors. Control measurements during testing are carried out by an independent laboratory that has the appropriate accreditation.
Correct operation of ventilation systems requires the following measures:
- planned inspection and troubleshooting of the ventilation unit;
- timely replacement of broken exhaust grille mountings;
- filter replacement:
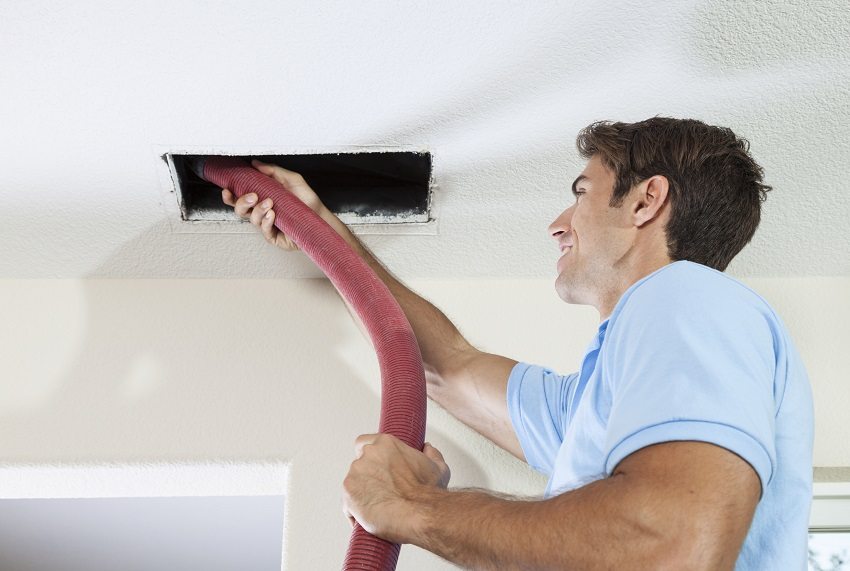
- cleaning ventilation systems from blockages;
- disinfection of air ducts.
The necessary information on the types of ventilation systems, their operation and maintenance will help in choosing the optimal equipment for the required air exchange in the room.