Modern building materials are notable for their low cost and manufacturability. Therefore, there is a huge difference between buildings built 50-70 years ago and new buildings of the present time. The multi-layer structure of modern materials allows you to minimize the cost of additional insulation, nevertheless, insulation for the walls of the house inside and outside is widely used in construction today.
Content [Hide]
- 1 Which insulation is best for the wall of a brick house: internal or front?
- 2 The choice of wall insulation from the inside: materials, their classification and characteristics
- 3 Types of insulation for indoor walls: expanded polystyrene materials
- 3.1 Expanded polystyrene: advantages and disadvantages of the material
- 3.2 Extruded polystyrene foam: the advantages of insulation
- 3.3 Extruded polystyrene foam: insulation disadvantages
- 3.4 Penoplex is one of the varieties of expanded polystyrene
- 3.5 Advantages and disadvantages of Penoplex wall insulation
- 3.6 Types of insulation for walls from the inside based on cotton wool
- 3.7 Features of foil and liquid insulation for building walls
- 3.8 Average prices for various types of insulation materials
Which insulation is best for the wall of a brick house: internal or front?
The opinions of experts on which material is considered the best insulation for the walls of a house made of bricks or panels differ. However, professionals agree on which side is best to insulate the room. The facade insulation procedure is considered to be more effective and of high quality than during internal work. But there are a number of cases that do not allow facade work.
As a rule, problems with freezing of premises affect apartments in panel and brick houses built more than 30 years ago.
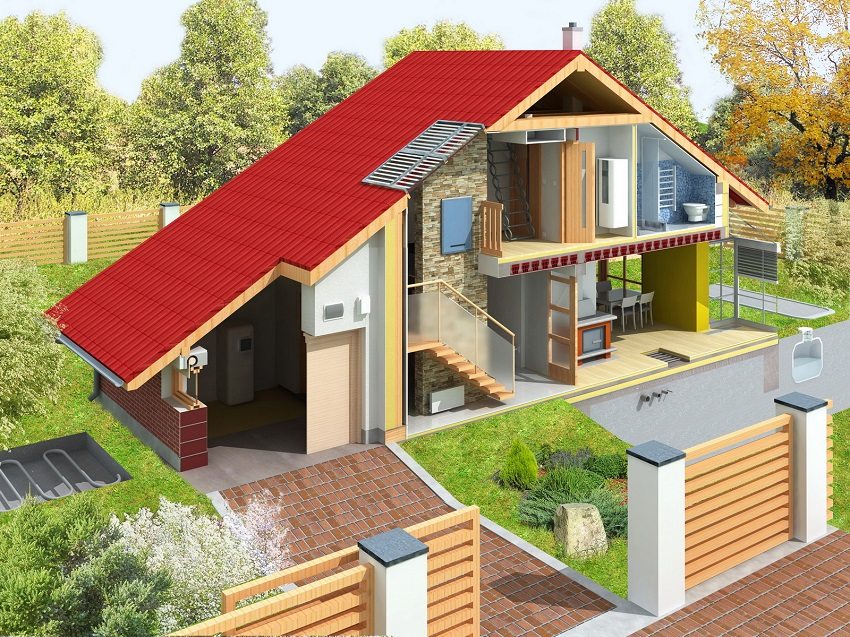

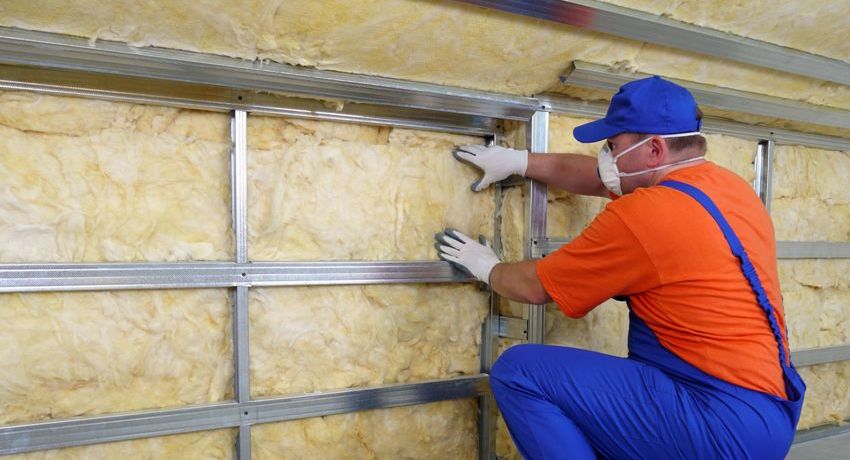
Thermal insulation of a house from the inside is a procedure containing a lot of tasks, one of which is the choice of material
If we talk about facade insulation, then the owners of such housing face certain difficulties:
- high costs of paying for the services of specialists (external insulation of a house, due to its complexity, is difficult to do with your own hands, so you have to hire specialists to perform high-rise work);
- with an inconvenient location of the apartment, it is impossible to perform the external insulation procedure (such structural elements of the building as a staircase or an elevator shaft create serious obstacles to external work);
- restrictions on the architectural appearance of the building (most of the old buildings are finished with expensive materials, some of them belong to architectural monuments, as well as monuments of history and culture, so the city authorities veto any changes in the facade of such structures).
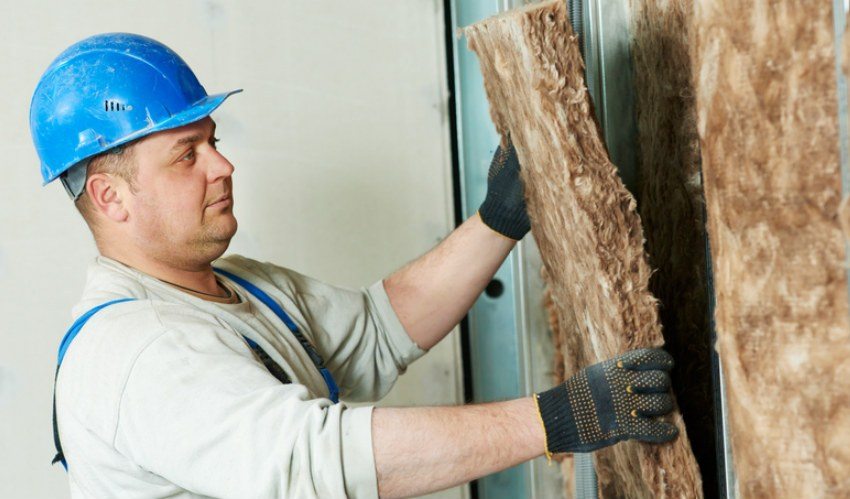

It should be remembered that mounting a sufficiently thick layer of insulation on walls will reduce the area of the room
Note! Over the past decades, some amendments have been made to GOSTs and SNiPs, therefore the possibility of carrying out front or internal insulation of each individual house should be considered individually.
What are the disadvantages of attaching insulation to the wall from the inside
If, for some reason, you decide to perform the insulation procedure from the inside of the building, it is worth analyzing in advance all the disadvantages of this event. This will allow you to avoid mistakes and choose the right material.

Insulation of walls from the inside will be most effective if it is included in the construction project
Disadvantages of interior work:
- Installation of insulation for walls inside the premises significantly reduces the usable area. A room with an area of 20 m² can lose about 0.5-2 m² after internal insulation.
- To carry out work, you will need to move away from the walls or take out all things from the room. During this entire time, you will not be able to operate the room.
- Installation of heat-insulating materials will require additional work: expanding the ventilation system, taking protective measures to prevent the formation of condensate, which has a detrimental effect on the insulation. Otherwise, thermal insulation materials will quickly lose their useful properties.
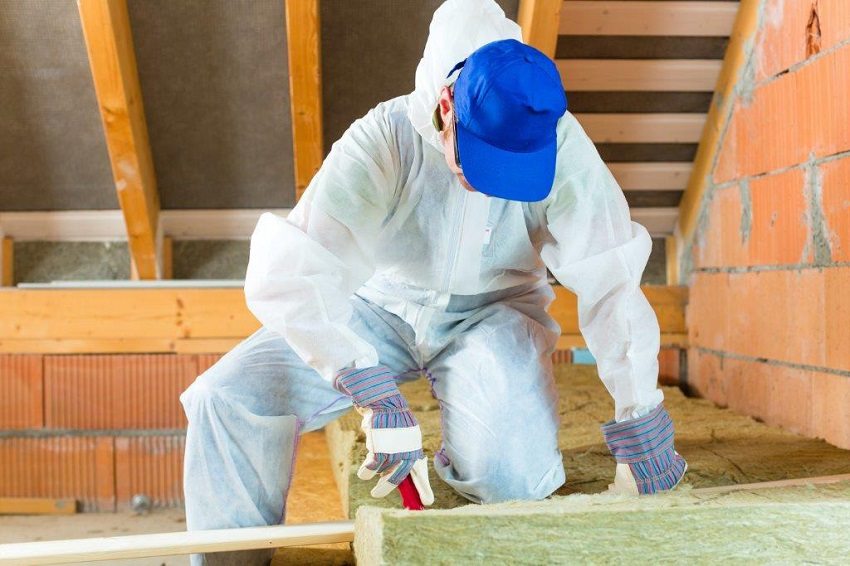

The insulation material must be harmless to health, resistant to high temperatures, durable and durable
Compliance with all technology requirements increases the total cost of the work, and if the rules are violated, there is a risk of failure.
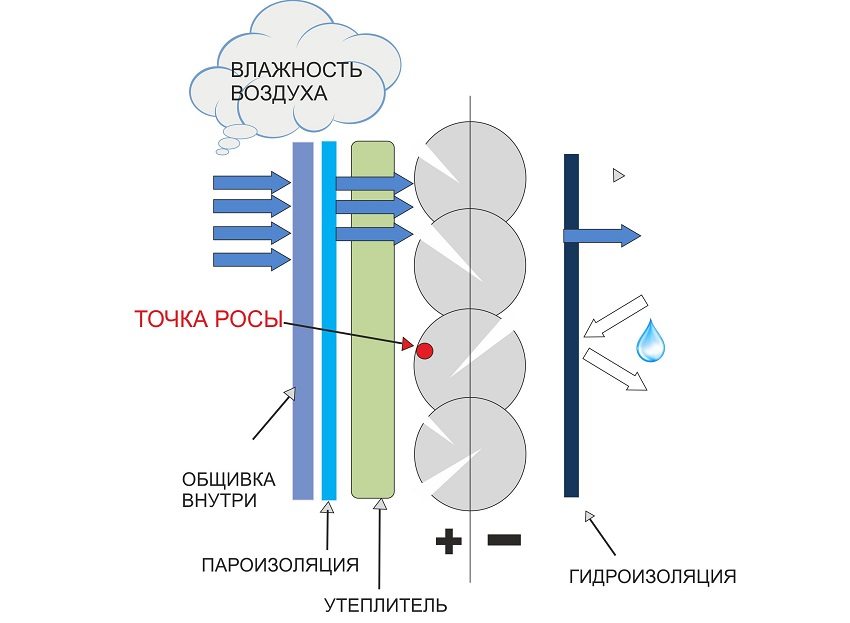
Insulation for the walls of the house inside: dew point and its effect
In construction terminology, there is such a thing as "dew point". It is an indicator responsible for the formation of condensation inside the walls of a building. Regardless of the density of the wall insulation, any of the materials causes condensation. By itself, this process is natural and is provoked by the effect of temperature changes on humidity.
Note! Internal insulation is more conducive to the formation of condensation not only on the walls, but also inside them. This disadvantage is especially relevant for wooden houses, since wood is highly susceptible to the harmful effects of moisture.
According to the laws of physics, condensation falls out inside structures when the temperature reaches 10.7 ° C.
In a building with facade insulation, the walls are warmed up by the internal temperature of the room. On the outside, protection from cold is provided by a layer of heat-insulating material. Due to the unique properties of thermal insulators, which can be estimated from the thermal conductivity table of heaters, the temperature of these materials is practically unchanged. Therefore, when a dew point occurs, its influence will be superficial or even be in plasterthat dries on its own.
With internal insulation from the outside of the building, nothing protects the walls from the cold, therefore, the dew point will be located inside the structure. Every year the amount of moisture will increase, and due to the constant freezing and thawing of water, the enclosing structures will be destroyed.
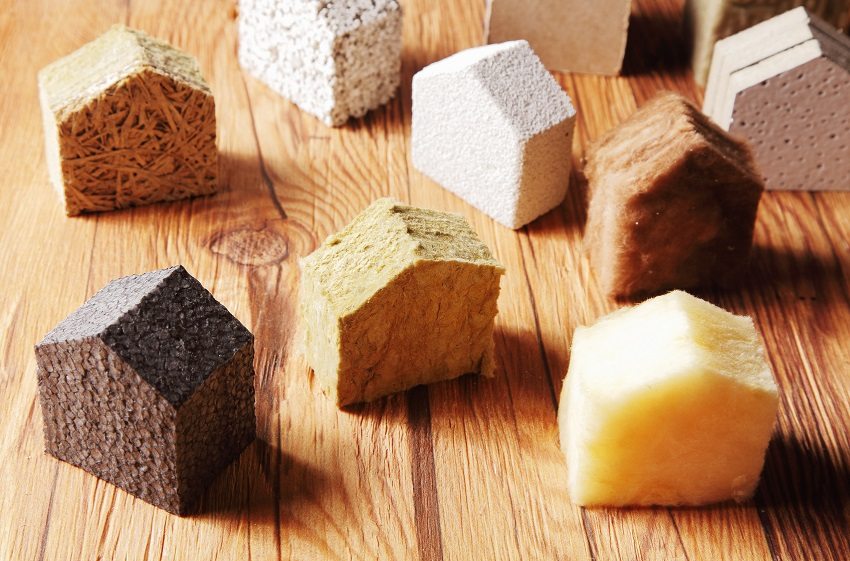

A wide range of heat-insulating materials for walls will allow everyone to choose the most suitable insulation
The choice of wall insulation from the inside: materials, their classification and characteristics
To determine which is the best insulation for the walls of a frame house or a wooden one, it is necessary to compare the characteristics of each of the materials, the advantages and disadvantages. This will allow you to create a complete picture and make the right choice.
Note! Insulation materials are used on all planes of structures. This is the only way you can eliminate heat loss and create optimal indoor climatic conditions for living. Thermal insulation can be installed even on external walls, attic and basement floors.
Which insulation for walls is better to buy: factors affecting the choice of insulation
The formula for calculating the thickness of the insulation for the walls is based on the level of thermal conductivity of the enclosing structures that have already been installed, as well as the characteristics of the climatic zone. Calculation manipulations can be performed by a designer with the appropriate profile, or a highly qualified heating engineer.
The specialist will need several parameters to perform calculations:
- The thickness of the walls in the room.
- The material from which the walls of the building are made.
- The type of insulation material you have chosen for your insulation work.
- The lowest temperature that was observed in a room with heating.
A professional will need about 20-30 minutes to make calculations. time. It is not possible to visually determine the required thickness of the insulating material as there is a high probability of error.
To calculate the thickness, you will need to calculate the heat transfer resistance (R):
D / L = Rwhere
L - coefficient of thermal conductivity of the material,
D - wall thickness.
The thickness of the insulation is determined by the inverse formula:
LxR = D.
The key point in choosing a material for thermal insulation is the physical parameters of the walls, namely vapor permeability and thermal conductivity. It is recommended to take the thickness of the material with a small margin.
Table for calculating the thickness of the insulation for the walls:
| Insulation type | Density (kg / m³) | Temperature for calculations | |
| -25 ° C | -35 ° C | ||
| Perlite, glass wool, mineral wool | 200 | 10 cm | 15 cm |
| Expanded clay | 500 | 20 cm | 30 cm |
| Slag | 1000 | 30 cm | 40 cm |
Properties of insulation for walls from the inside: main characteristics
When choosing materials, first of all, you should rely on the properties and characteristics of insulation.
The most important characteristics to determine which insulation is best for the walls of a wooden house inside are:
- thermal conductivity is the most important indicator for the selection of insulation materials. The less insulation is able to keep heat in the room, the more insulation material will need to be installed. This indicator is in direct proportion to the level of hygroscopicity;
- density is another indicator that affects the level of thermal conductivity. It largely determines the characteristics of surfaces with different types of placement. The higher the density, the greater the level of thermal conductivity;
- hygroscopicity - materials with a low index are characterized by poor absorbent properties, which reduces the level of thermal conductivity. The durability of insulation and the choice of the material itself for carrying out these works depend on hygroscopicity.
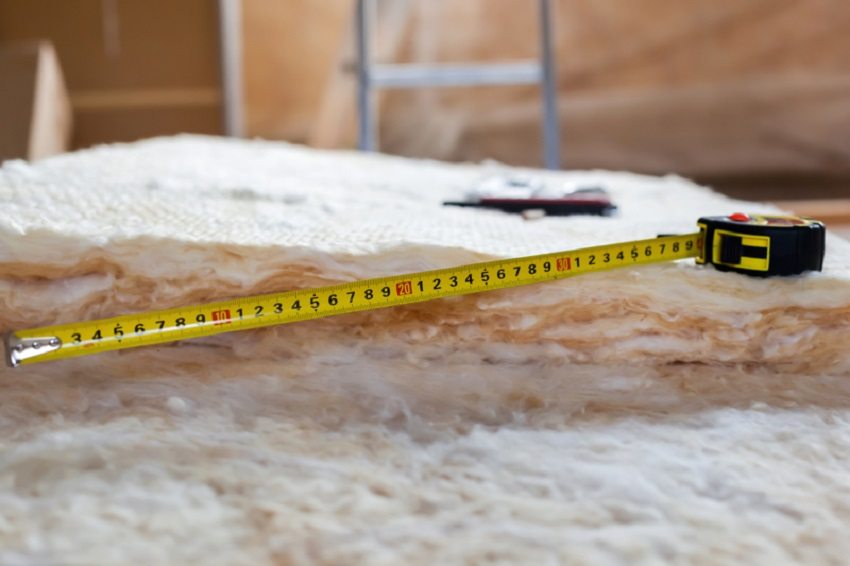

Before installing the insulation, it is important to correctly calculate the required amount of material
Helpful advice! Wall insulation is recommended in the warm season. The walls must be well dried.
In addition to physical properties, insulation materials also have mechanical characteristics. Within the framework of this feature, 4 classes of materials are distinguished:
- Cotton wool is a roll-type insulation and other products that are made using it.
- Bulk - granular foam substances or materials in the form of crumbs with different sizes of fractions.
- Foam blocks - glass, foamed concrete and other materials with suitable properties are used as raw materials.
- Plates - products in the form of plates obtained by pressing and gluing (may have different dimensional parameters).
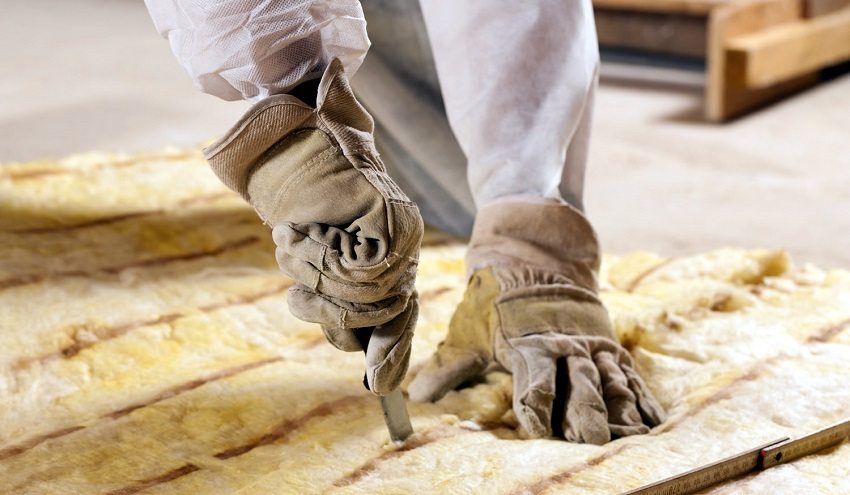

When working with mineral wool, respirators are used to protect the respiratory system, and special clothing and gloves are used to protect the skin.
Thermal insulation properties of wall materials
Despite the wide range of wall insulation materials available on the construction market, there is no insulation that could offer universal characteristics and properties.
Helpful advice! If you are thinking how to insulate the walls in a corner apartment from the inside, or premises in a wooden house, in each case the choice of material will be different. It is worth dwelling on the most important characteristics.
Comparative table of material properties:
| Material class | Material name | Minimum layer, cm | Density (kg / m³) | Hygroscopicity | Thermal conductivity |
| Bulk | Slag | 30 | 1000 | B | AND |
| Expanded clay | 20 | 500 | D | B | |
| Glass pore | 10 | 15-120 | AND | D | |
| Vermiculite, perlite | 10 | 40-100 | AND | D | |
| Basalt fiber | 15 | 130 | B | D | |
| Roll | Glass wool | 10-15 | 75-175 | B | D |
| Minvata | 10-15 | 35-125 | B | D | |
| Wired mats | 10-15 | 75-150 | B | D | |
| Plastiform | 2 | 50-60 | D | D | |
| Isover, URSA | 10-15 | 35-125 | B | D | |
| Penofol | 5 | 60-70 | IN | D | |
| Expanded polystyrene | 10 | 30-40 | IN | D | |
| Polyurethane foam | 10 | 30-60 | IN | D | |
| Plate-sheet | Styrofoam | 10 | 35-50 | IN | D |
| Mipora | 10 | 25-40 | IN | D | |
| Minvata + glass wool | 10-15 | 75-250 | B | D | |
| Wood fiber | 1,5-3 | 250 | AND | B | |
| Foam blocks | Expanded clay concrete | 40 | 1000 | IN | AND |
| Foam concrete | 25 | 600 | B | B | |
| Aerated concrete | 20-40 | 400-800 | B | B | |
| Aerated concrete | 20-40 | 400-800 | B | B | |
| Gas silicate blocks | 20-40 | 400-800 | B | B |
Hygroscopicity and thermal conductivity parameters:
- A - very high;
- B - high;
- B - medium;
- G - low;
- D - very low.
Related article:
Installation of insulation for walls inside the house in the country. Types and installation of insulation for walls inside the house. Detailed characteristics of materials for insulation. Installation of various insulation materials on internal walls.
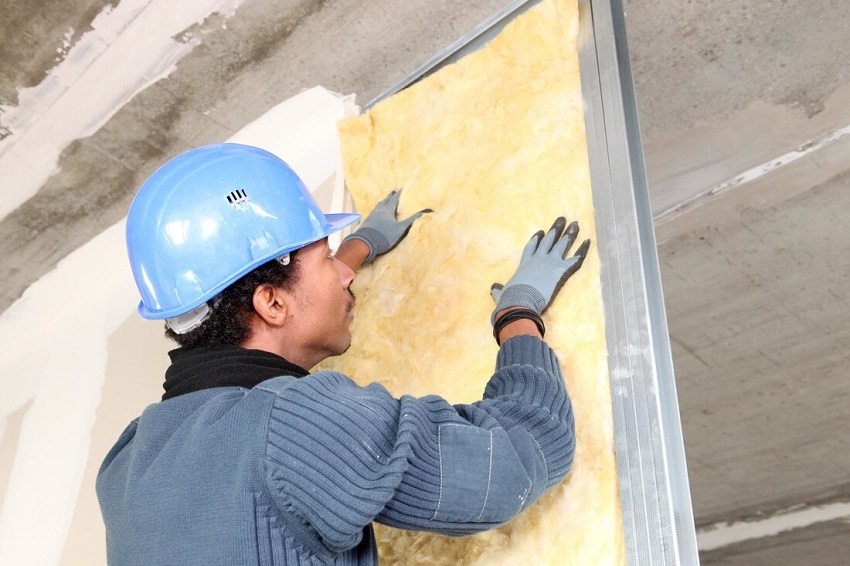
Types of insulation for indoor walls: expanded polystyrene materials
The most common material is polystyrene foam, which has excellent thermal performance and relatively low cost. In addition to an affordable price and a small indicator of thermal conductivity, this material has a lot of other qualities, both positive and negative.
Expanded polystyrene: the advantages and disadvantages of the material
Advantages of insulation with expanded polystyrene:
- Low purchase price - the cost of the material is directly affected by its density, but when compared with other types of insulation, these products are much cheaper.
- Low level of thermal conductivity - due to the poor permeability of the plates, you can save on their thickness, as a result, you get a saving of useful space in the room.
- Simple installation system - the products are lightweight, therefore they do not cause difficulties during the installation process.
- Durability.
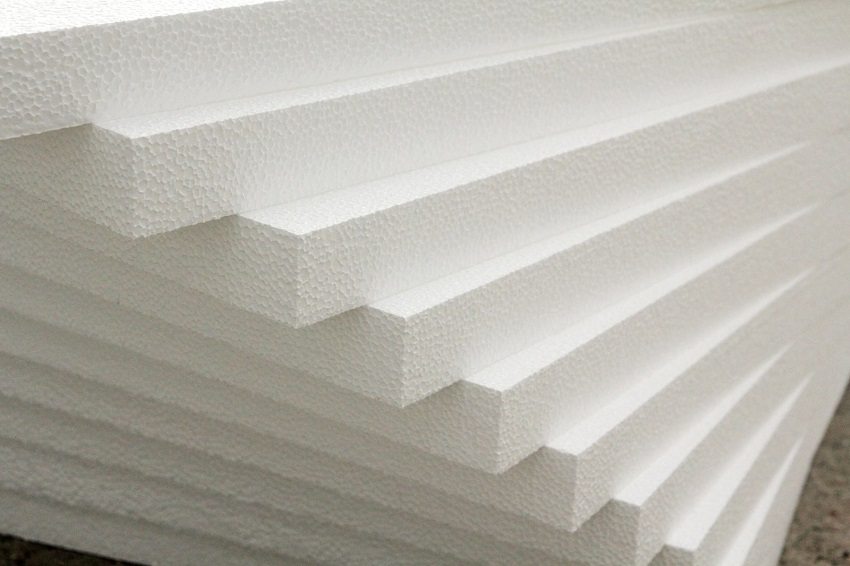

The popularity of expanded polystyrene has grown due to the fact that its sheets have a low specific gravity and, unlike cotton wool, have greater moisture resistance
Helpful advice! Despite the fact that polystyrene is widely used for insulation, it cannot be called the best environmentally friendly insulation for walls of the house or the most suitable because of its flammability. Moreover, in the process of combustion, the material releases toxic substances.
Disadvantages of insulation with expanded polystyrene:
- The material burns well enough - this process is accompanied by the release of hazardous and toxic substances. Especially serious consequences arise if the insulation is done from the inside.
- Due to the fragility of the slabs, which can break during the installation process, costs and the amount of construction waste increase.
- Rodents can damage the insulation by gnawing their moves in it.
- Low level of vapor permeability - it will be necessary to improve the ventilation system, otherwise condensation may form on the walls.
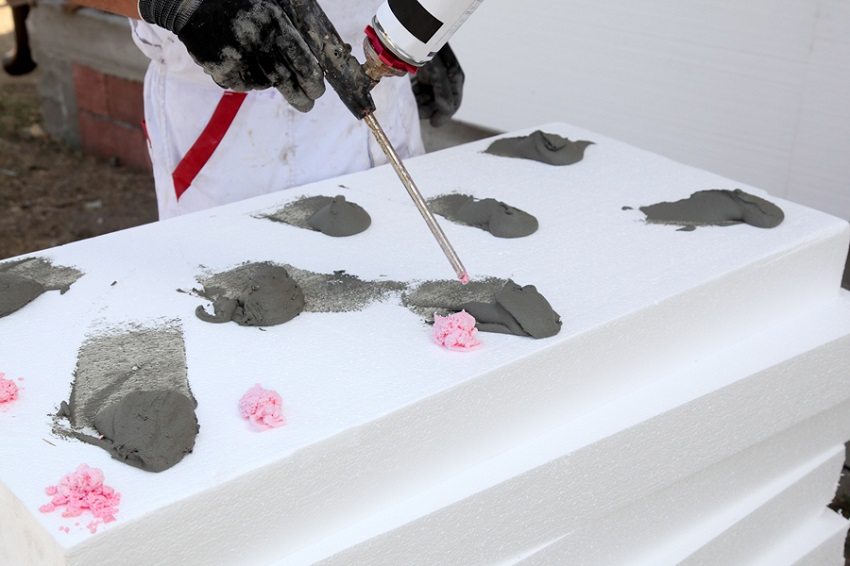
Extruded polystyrene foam: the advantages of insulation
An extruded version of this material - EPS is used as an alternative replacement for expanded polystyrene. Thanks to its improved characteristics, its scope of application is much wider than that of conventional foam.
Strengths of the material:
- Very low thermal conductivity, due to which the material is widely used in construction (insulation of almost all structural elements of a building, including the floor and roof).
- The flammability index has been significantly improved, but this only applies to high-quality material, which is made in compliance with all technological subtleties in production.
- High strength - installation of EPS is possible in areas where other types of materials cannot cope with the task of insulation, for example, under the floor screed.
- Low level of water absorption - in some situations there is no need to use additional hydro and vapor barrier layers.
- Durability - compliance with the installation technology allows us to make the service life of the material long enough.
- Simple installation system - regardless of whether internal or facade insulation is performed, the installation of the material is quick and easy.
Helpful advice! Use EPPS to insulate the foundation of the house, as well as the basement and basement.
Extruded polystyrene foam: insulation disadvantages
In comparison with foam plastic, the disadvantages of EPS are much less, but they do exist.
Disadvantages of EPSP insulation:
- Poor vapor permeability - installation of a good ventilation system is required, since the walls of the room after insulation practically do not "breathe".
- Despite the fact that the flammability index has significantly decreased, there are a large number of products on the market that are manufactured in violation of production technology.
- Due to the unfair attitude of some manufacturers to comply with the requirements for the production process and raw materials, the issue of the release of toxic substances remains unclear. When choosing a material, you should carefully study the information about the manufacturer and its products.
- Higher price compared to Styrofoam.
If it is not possible to carry out facade insulation, the use of EPS as a heat-insulating material is much safer than in the case of foam. The main thing is to install a high-quality and efficient ventilation system.
Penoplex is one of the varieties of expanded polystyrene
Penoplex is produced in the form of expanded polystyrene plates, manufactured using a special extrusion technology. The material is obtained by forcing a plastic mass that has been foamed and heated. The extrusion is done through forming nozzles called nozzles.
Due to the interaction of high temperatures and high pressure, when solidifying, the penoplex becomes finely porous. Its structure consists of small air cells 100-200 microns in size, isolated from each other.
Note! Due to its unusual structure, polystyrene foam provides excellent insulation properties and high strength (especially in front of mechanical factors).
The modern assortment offers several varieties of this material, designed for different purposes:
- Dense products marked -45 for pavement decking.
- "Penoplex Foundation" for warming the basement elements of the building (protects the foundation part of the structure from freezing, prevents the formation of cold bridges, which usually arise between the ground and the premises).
- "Penoplex-wall" for facade insulation works with heat-insulating and sound-insulating properties.
- "Penoplex-roof" for processing roof slopes and thermal insulation of attic floors.
- "Penoplex-comfort" for internal insulation works.
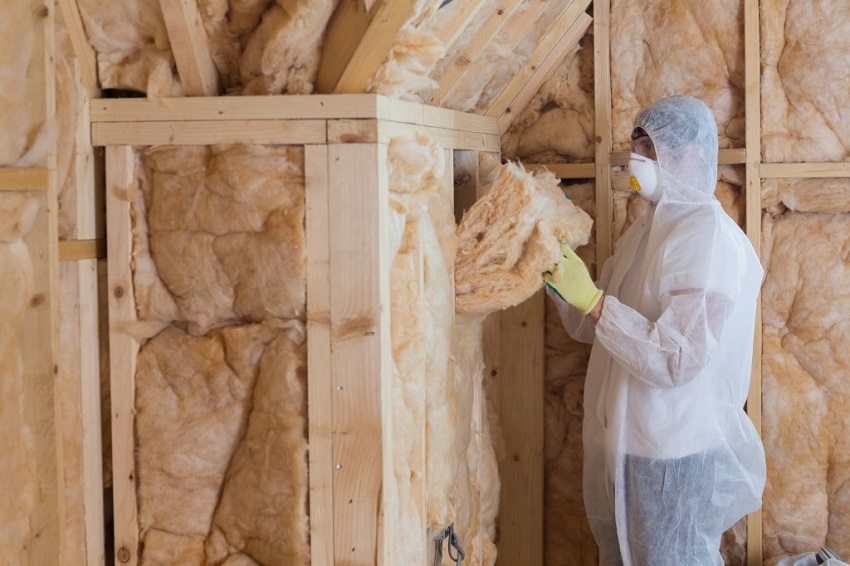

It is better to carry out insulation work in the warm season, during the period without precipitation and high humidity
Advantages and disadvantages of Penoplex wall insulation
Penoplex advantages:
- low level of water absorption (0.6% per month);
- small coefficient of thermal conductivity (0.03 W / mx ° C);
- resistance to the effects of mechanical properties (no punching or any other structural changes from pressing, provided that it is laid on a flat surface);
- low level of vapor permeability (physical and technical characteristics do not allow the material to absorb fumes, therefore, penoplex can be used to insulate rooms with a high level of humidity, for example, a sauna or a bath);
- light weight;
- simple installation and processing system;
- long service life (up to 50 years);
- resistance to chemical factors (salt solutions, alcoholic compounds, alkalis, water-based coloring compounds, carbon dioxide, etc.).
There are a number of substances that can damage penoplex or deprive it of its useful properties. These substances include:
- diesel fuel;
- oil-based coloring compositions;
- petrol;
- enamel dyes;
- ethyl acetate or methyl acetate based solvents;
- acetone and formaldehyde;
- other active substances.

Installation of each type of insulation is carried out in accordance with certain requirements and norms
Types of insulation for walls from the inside based on cotton wool
Mineral wool is commercially available in the form of slabs with different density levels, as well as roll products. It is used to insulate wall surfaces, roof and attic floors. It is allowed to use the material for interior work on warming rooms.
Note! For mineral wool insulation for walls inside the house, the price depends on the density (as well as for other types of thermal insulation materials). The higher this indicator, the higher the cost of products.
Advantages of mineral wool insulation:
- low flammability index (when burning, the material is accompanied by smoldering with gradual attenuation without the release of smoke and harmful substances);
- excellent air and vapor permeability;
- advantageous heat engineering characteristics;
- resistance to insects and rodents;
- sound insulating properties.
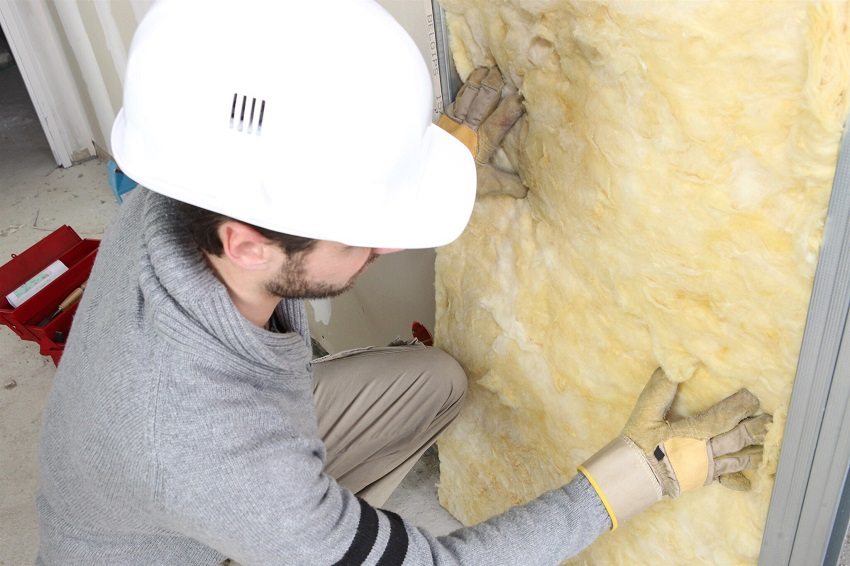

Glass wool is used for heat and sound insulation of ceilings, basements, facades, internal and external walls
Disadvantages of the material:
- vulnerability to moisture and high absorbency with the loss of beneficial properties;
- installation work requires the use of overalls, which complicates the process of installing a heater;
- the cost of purchasing protective materials (waterproofing and vapor barrier);
- over time, mineral wool shrinks.
There are two more types of wool-based heaters on the market: glass wool and ecowool.
Glass wool has almost the same properties as mineral wool insulation, but it is more elastic and resistant to vibration. Its main drawback is its dangerous effect on the human body, which complicates the installation process.
Ecowool, on the contrary, is considered one of the most environmentally friendly heaters, but the cost of this material is appropriate.
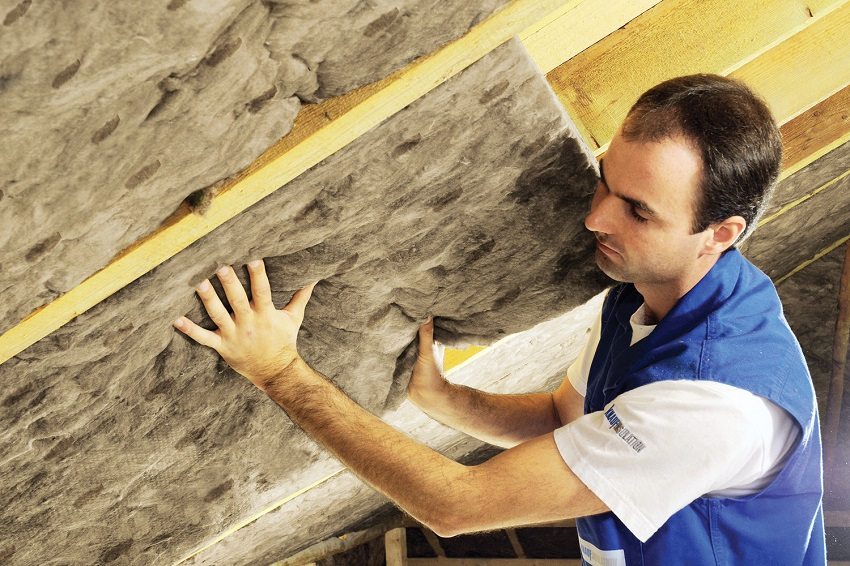

Ecowool is not recommended for use when insulating the basement and ceilings above basements, in which the humidity level is consistently high
Features of foil and liquid insulation for building walls
Insulation for liquid wall insulation is considered the thinnest. In terms of external characteristics, it is similar to a conventional dye composition. The only thing that distinguishes it is the structure, consisting of microscopic vacuum spheres that form an insulating effect.
This type of material appeared on the market relatively recently, and due to its high cost it is not yet as popular among consumers as other types of insulation that were considered earlier.
Note! According to information from manufacturers, 1 mm layer of liquid-ceramic thermal insulation material has the same capabilities as mineral wool, the layer thickness of which does not exceed 5 cm. This advantage largely justifies the high cost of the material in comparison with others.
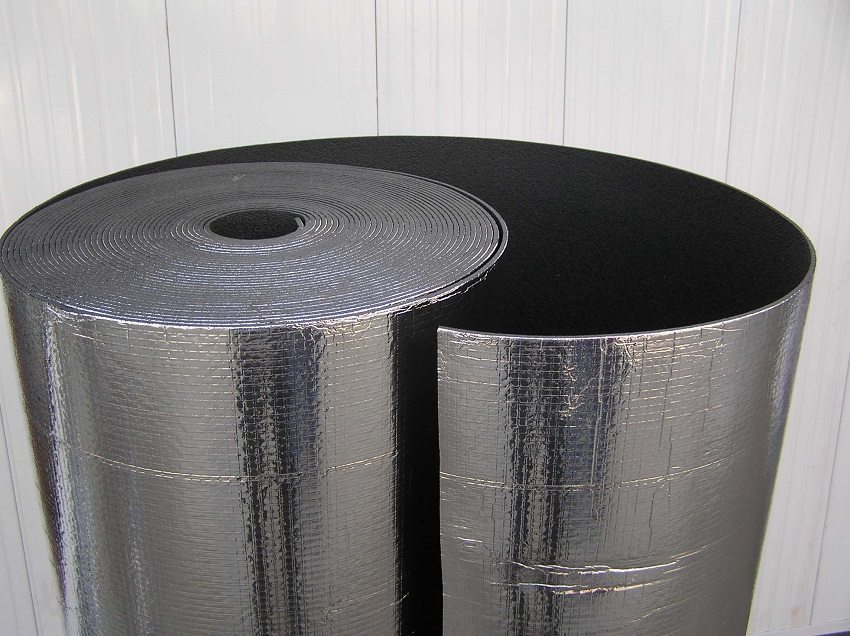

Foil insulation is a multilayer material consisting of closed-cell polyethylene foam of various thicknesses and aluminum foil
Insulation with foil for walls inside the house in the country is often used. Due to the reflective coating, this material prevents heat from escaping from the room. As a rule, manufacturers supplement mineral wool or foamed products in plates and rolls with foil backing.
Average prices for various types of insulation materials
Comparative table of the cost of organic, reflective and inorganic insulation:
| Material type | Name | Cost, rubles / m² |
| Organic | Arbolite thermopanel | 520 (2 pcs. = 1 m²) |
| Penoizol (sheet) | from 1200 (m³) | |
| DVIP Steiko Standard | 173-1713 | |
| Polyurethane foam | 400-850 | |
| Ecowool | 1700-5000 (m³) | |
| Penoplex (Comfort) | 1197-1447 | |
| Reflective | Armofol (Extra) | 70-165 |
| Porileks (NPE) | 650-1450 | |
| Ecofol (unilateral) | 1440-1656 | |
| Penofol 2000 | 51-355 | |
| Inorganic | Mineral wool | 310-820 |
| Glass wool | 400-1350 | |
| Akterm (liquid ceramic thermal insulation) | 3200-7200 (10-20 L) | |
| Stone wool | 335-1320 (m³) | |
| Liquid rubber | 750-850 |
Foil insulation for walls is a reflective type of insulation material. They are also called reflex, since they slow down the movement of heat flows, namely infrared radiation.
Reflective materials include polished aluminum, which can be single-layer and double-layer. To improve the effect, the metallized layer is supplemented with foamed polyethylene. Such materials include: Porileks, Ekofol, Penofol, Armofol.
To make the right choice of insulation, it is enough to study well all the advantages and disadvantages of each of the materials and, by comparing them with your budgetary capabilities, as well as the operating conditions of the room, you can choose the right products.