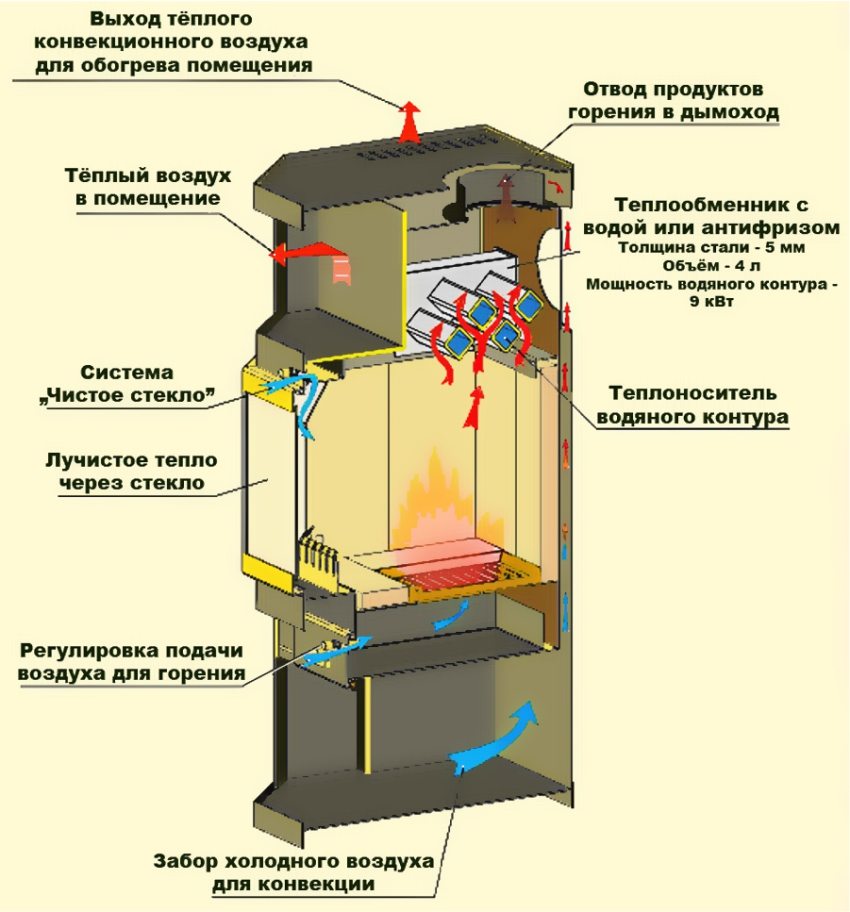
Stove heating is a classic for cold Russia, but for some reason it is often considered only as an alternative to central, electric or gas heating. Meanwhile, a stove with a water circuit for heating a house can provide its inhabitants not only with the desired watts of thermal energy, but also with hot water for domestic and sanitary needs.
Content [Hide]
- 1 Advantages and disadvantages of stove heating
- 2 A stove with a water circuit for heating a house: advantages
- 3 The principle of operation of stove heating with a water circuit
- 4 Construction of furnaces with water heating
- 5 Operation of a fireplace stove with a water heating circuit
- 6 The main disadvantages of a home stove with water heating
Advantages and disadvantages of stove heating
Regular wood burning stove or fireplace heat the room due to a combination of radiation and convection heat exchange. The heated massive walls of the oven emit thermal energy, transferring it to the air and furnishings of the room. Cold air is gradually replaced by heated air.
Furnace heating has a number of undoubted advantages:
- does not require connection to electrical and gas communications. Fuel: firewood, coal, peat briquettes - as a rule, cheap and environmentally friendly, its combustion does not harm the environment;
- radiation heat exchange is the most comfortable;
Interesting! Radiation (aka radiant) heat transfer is the only type of heat transfer that occurs without the participation of a coolant.
- most home stoves (long burning or conventional) multifunctional, can be used not only for heating, but also for heating water and cooking (both inside the oven and on the hob);
- in the hot season, a massive brick oven for a house contributes to the air conditioning of the room: due to the fact that it is always built on a separate foundation, excess heat is discharged into the ground;
- a stove or fireplace creates a special atmosphere in the home and in many cases is an element that defines the style of the interior.
However, along with the advantages of stove heating, there are also inherent disadvantages:
- dimensions - the power of heating stoves for a house depends on their dimensions;
- inertia - a traditional brick house oven takes a very long time to warm up and go into operation. True, modern cast-iron stoves for the house, fireplace stoves, potbelly stoves and buleryans are practically free from this drawback;
- high heat loss due to low efficiency (efficiency) - a large amount of heat energy goes through the chimney into the atmosphere;
- the inability to ensure uniform heating of the house. Hot air gradually displaces cold air, but this happens unevenly - the temperature may be too high near the stove and too low at a distance from it;
Fact! The stove can only heat those rooms that are directly adjacent to it. Therefore, in parts of the building remote from it, it was often necessary to arrange an additional stove.
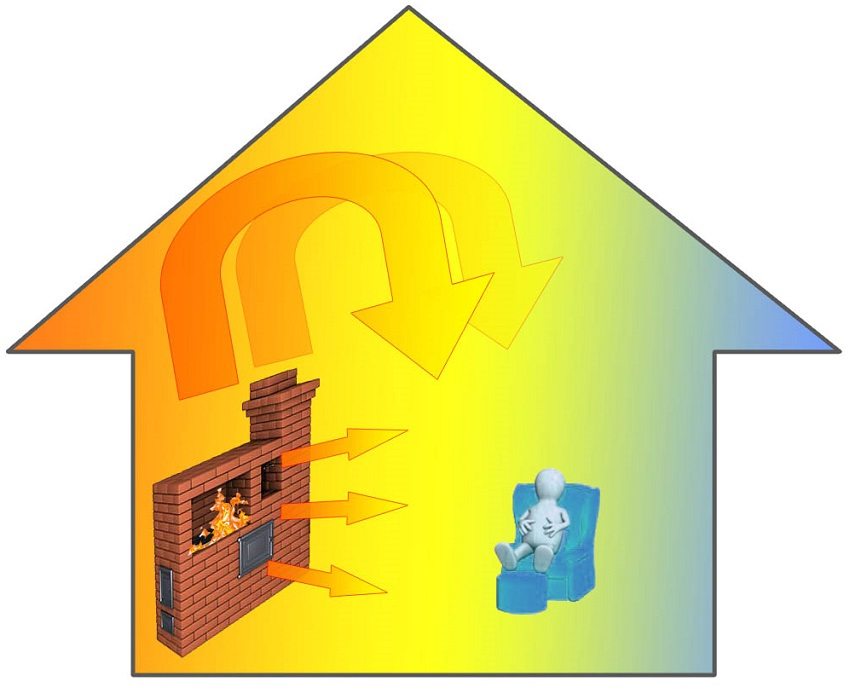
The principle of stove heating - a hot stove emits heat energy into the surrounding space (radiant heat exchange), then cold air is replaced by heated air (convection heat exchange)
- the need for constant maintenance - the stove requires laying firewood, cleaning ash pits from slag and chimneys from soot and debris, maintaining the combustion process, regulating draft;
- complexity of control - it is more difficult to control the process of fuel combustion in a furnace than in boilers;
- the need for good traction - traction is needed for intense combustion, as well as for the removal of carbon monoxide;
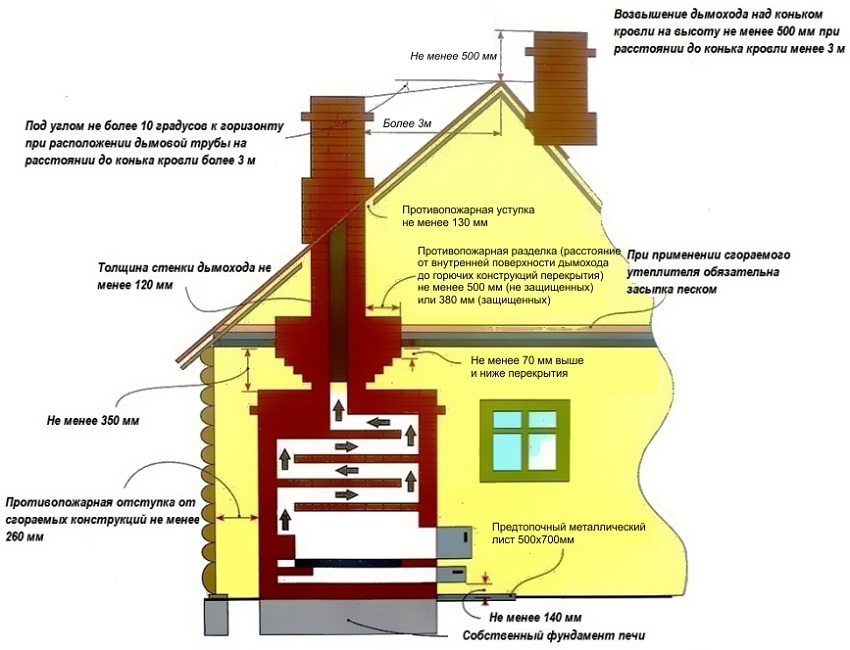
- fire hazard - to ensure fire safety, insulation of chimneys is necessary, especially for a stove in a wooden house. An additional fire hazard factor is created by the fact that instant stopping of the combustion process in the furnace is impossible;
- the need for constant replenishment and storage of the fuel stock, as well as the disposal of waste: slag and ash.

To ensure the operation of the furnace, its constant maintenance is required: laying firewood, cleaning ash pits and chimneys, monitoring the combustion process, adjusting the draft
A stove with a water circuit for heating a house: advantages
As already mentioned, an ordinary stove is not able to provide uniform heating of all rooms in the house. In modern stoves and fireplaces, this problem is partially solved by installing a convection chamber to which the air duct system is connected. As a result, the flow of warm air from the stove is not left to itself, but moves in the limited space of pipes and is regulated by latches, dampers, grates and other additional devices.
However, the air ducts are bulky, eat up useful space, and heat loss increases with the increase in their length and the number of turns. They need supervision and maintenance: periodic cleaning of dust, soot and soot. The air itself has a low specific heat capacity; to transfer heat to a room remote from the furnace, forced pumping of heated air masses by a fan is required. Therefore, water, as a heat transfer medium, is in many respects preferable to air.
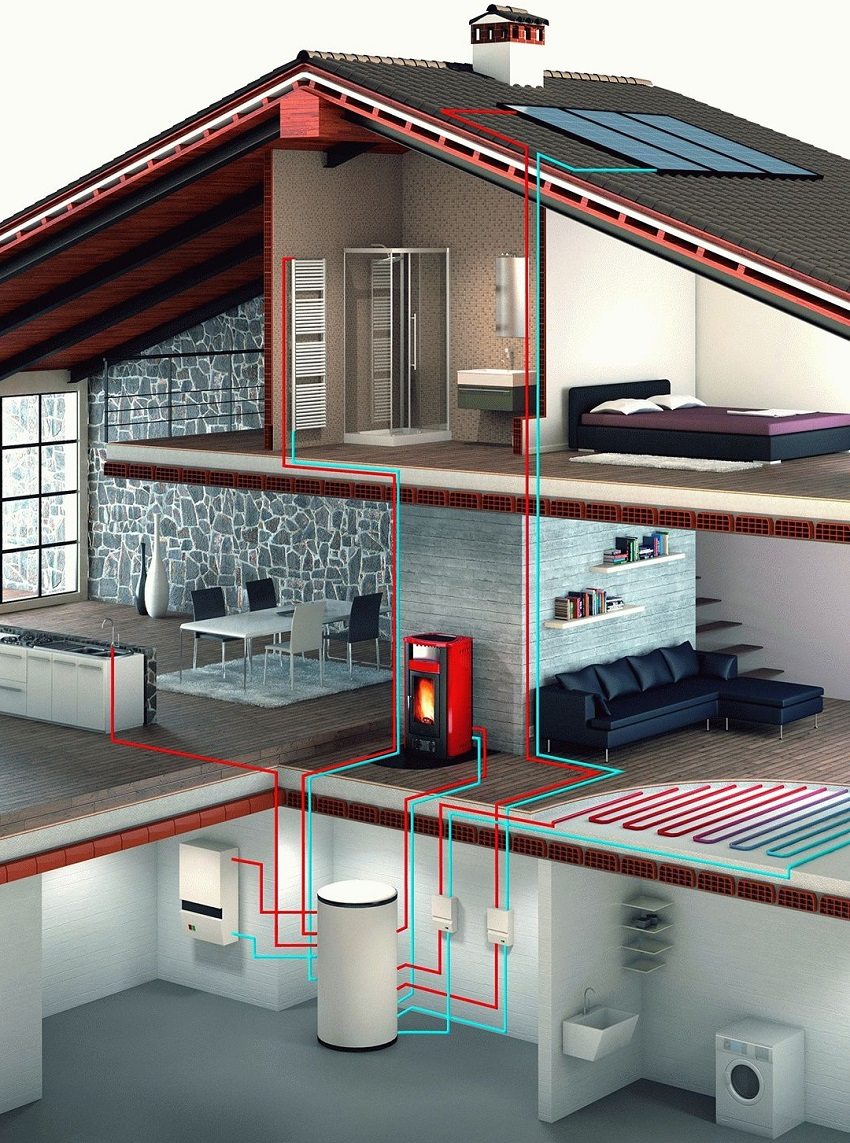
Combined heating system of a cottage using a fireplace stove with a water circuit and solar collectors
Fact! The specific heat capacity of water is almost 4 times higher than the specific heat capacity of air. It is enough to compare 4.187 kJ / (kg × K) and 1.055 kJ / (kg × K).
Hot water can be easily transported through small-diameter pipelines, while transferring heat energy over long distances. In addition, water is a harmless, non-flammable, non-toxic, chemically neutral and readily available substance.
The principle of operation of stove heating with a water circuit
The principle of operation of the heating circuit is simple - the coolant (in this case, water) heats up during the combustion of the fuel, then spreads through the pipes, while giving off heat to the surrounding space.
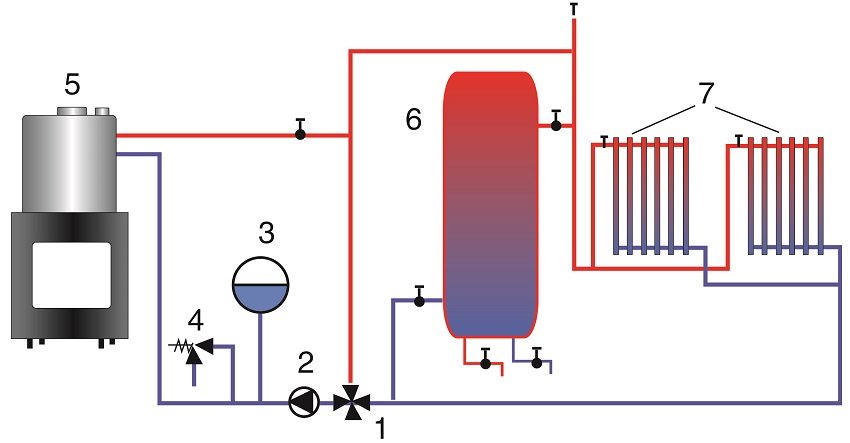
Diagram of connecting a fireplace with a water heat exchanger to a closed heating system with a storage boiler: 1 - mixing valve; 2 - circulation pump; 3 - expansion tank; 4 - emergency valve; 5 - firebox with heat exchanger; 6 - storage boiler; 7 - heating radiators
The prototype of modern solid fuel boilers and long-burning wood-burning stoves for the home are familiar to many - this is "Swede". The Swedish stove has a built-in metal reservoir, which is filled with cold water before laying firewood and kindling.And, although the water heats up for a long time during the furnace, it gives off heat just as long - long after the flame goes out.
Gradually, the water tank was transformed into a heat exchanger, as a result of which it became possible to connect a system of lines for home heating and hot water supply.
Construction of furnaces with water heating
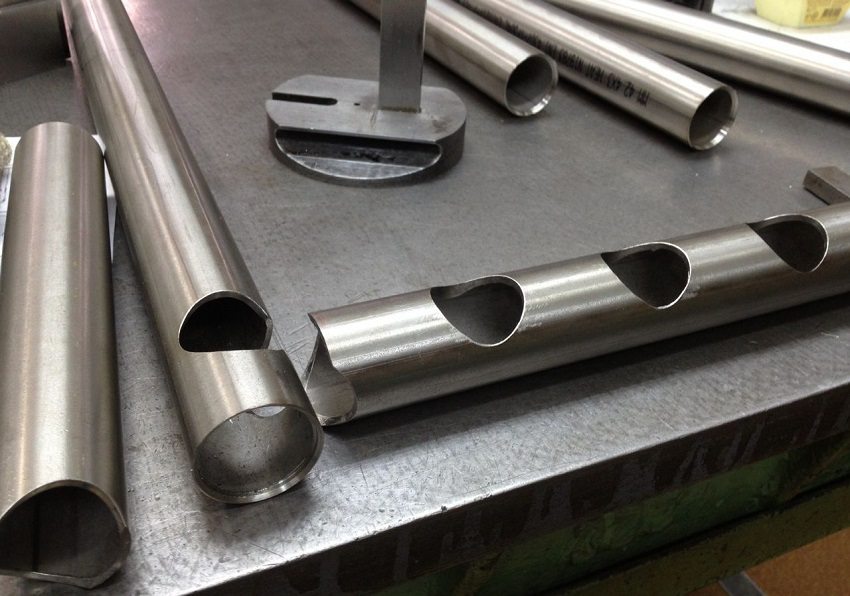
A distinctive feature of any stove for heating a house, equipped with a water circuit, is a heat exchanger, otherwise called a coil, radiator or boiler. This device is able to provide heating of an unlimited amount of water. The dimensions and shape of the tank depend on the volume of the combustion chamber and can vary over the widest range.
Heat exchanger
In some modifications of stoves for heating a house, the heat exchanger is installed directly into the firebox, but with this method there is a danger of a coolant leakage (that is, water) or even an explosion when it overheats and boils. In addition, in this case, the capacity of the combustion chamber inevitably decreases. A safer option is to integrate the heat exchanger into the chimney hood. In this case, most of the hot air rising from the firebox will heat the coolant, and not escape through the pipe to the street.
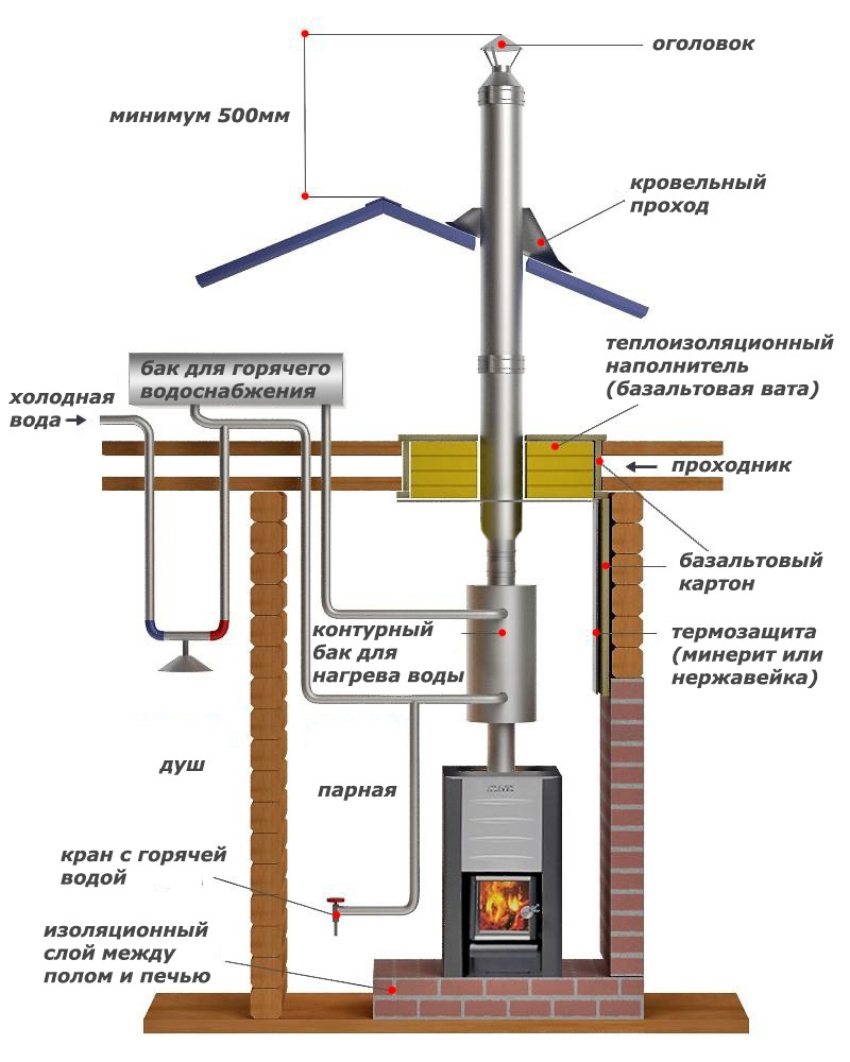
Installation diagram fireplace stove with a water circuit for hot water supply
Calculation of the power and dimensions of the heat exchanger
Self-calculation of the power and size of a heat exchanger is a rather difficult task for someone who is not a heating engineer, but in most cases it is possible to make a rough estimate.
Useful advice! Practice has proven that with a ceiling height of 2.5 to 2.7 m per 10 m2 the area of the house requires from 1 to 1.2 kW of heating system power.
A conventional wood-fired home stove releases about 6.5 thousand kcal within an hour, which is enough to warm up a small country house. The presence of a water circuit will double the level of comfort. After calculating the heat loss, you can calculate the power of the heat exchanger itself. Heat removal from each square meter of its area varies from 5 to 10 kW. This fact is the basis for determining the required power.

When choosing a heat exchanger for a stove or fireplace, it is necessary to take into account the parameters of the structure and the heating system in it.
In fact, there is no need to dive into complex formulas. It is enough to contact the specialists, who, guided by ready-made tables, will select a heat exchanger for the furnace of a private house, corresponding to the given parameters of the structure and the heating system in it.
Material
Before deciding on the design of the register (aka the heat exchanger) of the furnace for the house, you should decide what material it will be made of. There are several options:
- copper - on the one hand, the copper coil is very effective, since the thermal conductivity of this material is one of the best. On the other hand, its melting point is 1083 ° C, and in the firebox - in case of emergency situations, the occurrence of which can never be completely ruled out - it can rise to 1200 ° C. Therefore, the use of copper in the firebox of a brick oven is strictly prohibited. Additionally, you need to pay attention to the fact that the condensate formed during the cooling of the circuit contains aggressive chemical compounds that cause corrosion;
- cast iron - cast iron radiators are very resistant to corrosion, but they are fragile, and thermal deformations that occur during cooling and heating can lead to cracks and damage to the heat exchanger. In addition, a cast iron register - due to the fact that this metal is difficult to process - is assembled from cast parts using threads and seals, which leads to a decrease in the reliability of the unit as a whole;
- steel - the most accessible and easily processed material. Heat exchangers are recommended to be made of heat-resistant steel with a thickness of 3 to 5 mm, using seamless pipes. At the same time, you should maintain such a heating mode in which as little condensate as possible forms, and never drain the coolant, because steel products are subject to corrosion;
- heat-resistant stainless steel- the best, but also the most expensive material for a stove radiator for a private house.
Useful advice! The most suitable steel for the heat exchanger is AISI 304. When manufacturing parts, it is advisable to use laser cutting and welding in argon atmosphere.
Design
The heat exchanger - depending on its material - can be made of round or shaped rectangular pipes, sheet metal, or a combination of these parts. The location and installation method is determined by its shape:
- sheet steel heat exchanger - can be placed in the hottest place, that is, in the combustion chamber. For production, steel sheet 3 ÷ 4 mm thick is used in combination with pipes with a diameter of 40 ÷ 50 mm for connecting the supply and return lines. To avoid the formation of steam plugs, the upper water supply pipe must be at the highest point of the heat exchanger, because if a steam lock enters the heating system, there is a risk of water hammer. Which in turn will lead to the destruction of pipes or radiators. To prevent the water in the heat exchanger from boiling, its internal gap must be at least 30 mm;
- pipe heat exchanger - is made of pipes: round with a diameter of 40 ÷ 50 mm or rectangular profile sections of 40 × 60 or 60 × 60 mm. It can also be located in the firebox (provided that it is not made of copper), the spatial solution depends on the specific furnace. The main thing is that the device should not block the door for filling fuel, grates and smoke ducts. If the stove is a heating-cooking stove, then the heat exchanger pipes are laid only along the side planes of the combustion chamber;
- tubular flat register - most often they are located in the chimney ducts or the hood of the furnace, where the conditions are more gentle, therefore they can last longer than radiators in the firebox. Their dimensions are very impressive, since they are located in places where the heat output is low, and must be calculated in advance, because there should be no obstacles to the exit of flue gases.
Mounting
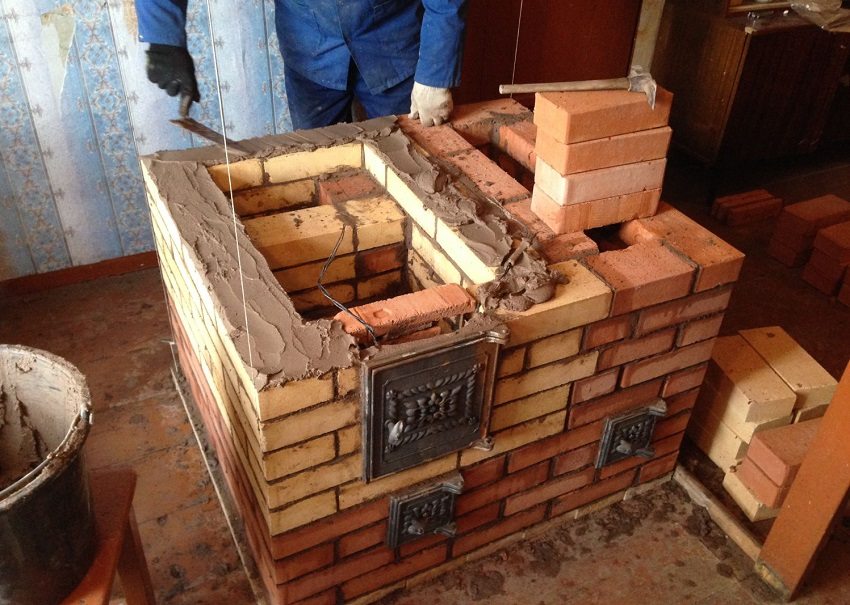
The heat exchanger should only be installed in a dedicated home oven. Video and photo instructions clearly confirm the need to attract a specialist stove maker and follow a number of rules:
- After manufacturing, the heat exchanger must be pressurized twice with a pressure of 6 bar: before and after installation in the furnace;
- the heat exchanger is mounted immediately after the foundation for the furnace is installed, after which it is laid;
- It is absolutely not recommended to wedge the heat exchanger into the oven masonry! There must be a gap of 10 ÷ 15 mm between it and the walls to compensate for thermal expansion;
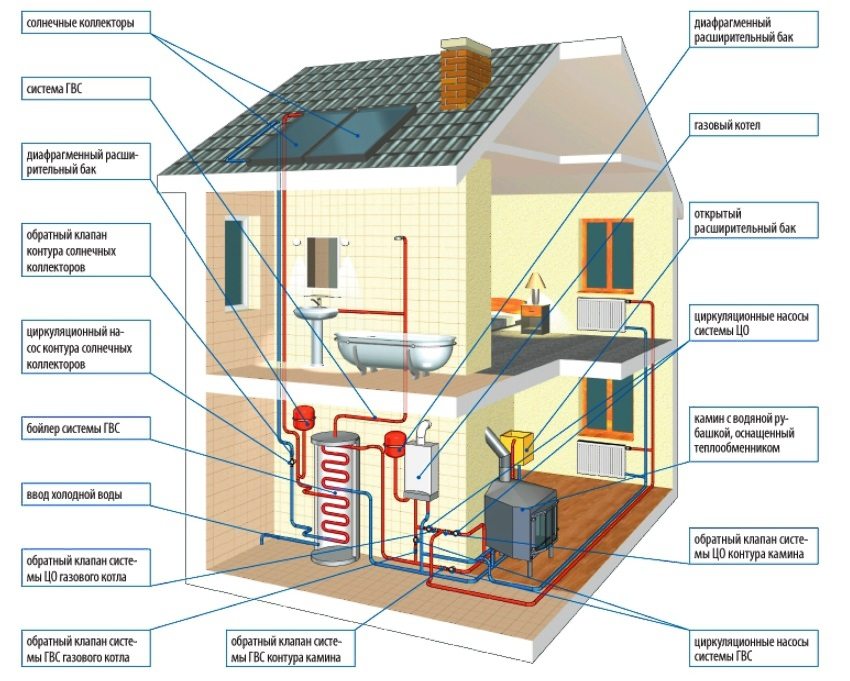
Elements of a combined heating system of a cottage with a fireplace and solar collectors
- when installing pipes, leave a gap of 5 mm and fill it with an asbestos cord or other heat-resistant sealant;
- the pipe section at the outlet must have a length of at least 10 ÷ 15 cm. This will allow cutting a new thread in case of damage;
- heating pipes are connected to the heat exchanger only using a heat-resistant seal;
- reconstruction of the finished furnace in order to install a water circuit in it should be done only by a specialist.
Operation of a fireplace stove with a water heating circuit
For trouble-free operation of the heating system, you must also follow the operating rules:
- Do not use the oven with an unfilled heat exchanger: it will quickly burn out.
- Do not disconnect the heat exchanger from the heating system while the oven is operating. Water expands when heated, and the increased pressure can cause an explosion.
- Do not supply cold water to a heated heat exchanger. Thermal deformation can damage it.
- A circulation pump can be used to increase the efficiency of the heating system.
- If necessary, use antifreeze in the water heater circuit.
- At the lowest point of the heating system, a water drainage tap must be provided.
The main disadvantages of a home stove with water heating
Main disadvantages water heating system associated with the physical properties of the coolant, that is, water. Freezing at 0 ° С, water (more precisely, already ice) reaches its maximum volume at -4 ° С. Expansion of the water frozen in the pipes can lead to their rupture. To avoid this, it is necessary to drain the water from the heating system, if it is not used in the cold season, or to replace it with a special antifreeze.
Related article:
|
Compliance with the rules for operating the stove in the house, photo and video instructions will help to avoid mistakes and suggest the best ways to neutralize deficiencies.

It is better to think about installing a modern brick oven at the design stage of the house, since it involves the arrangement of a chimney and air ducts
A modern brick oven with a water circuit for heating a house is a complex engineering heat engineering structure. Its installation requires the development of a separate project at the design stage of the entire structure as a whole and, most likely, will not do without the involvement of specialists.