The most comfortable for residential premises are temperatures in the range of 20-25 ° C and humidity from 50 to 60%. To provide such a microclimate in the house, you need to take care of the thermal insulation of the walls. The optimal insulation for the outside walls of the house is selected taking into account the material of construction and must meet a number of requirements.

To ensure comfortable conditions in the house, you need to take care of the thermal insulation of the walls.
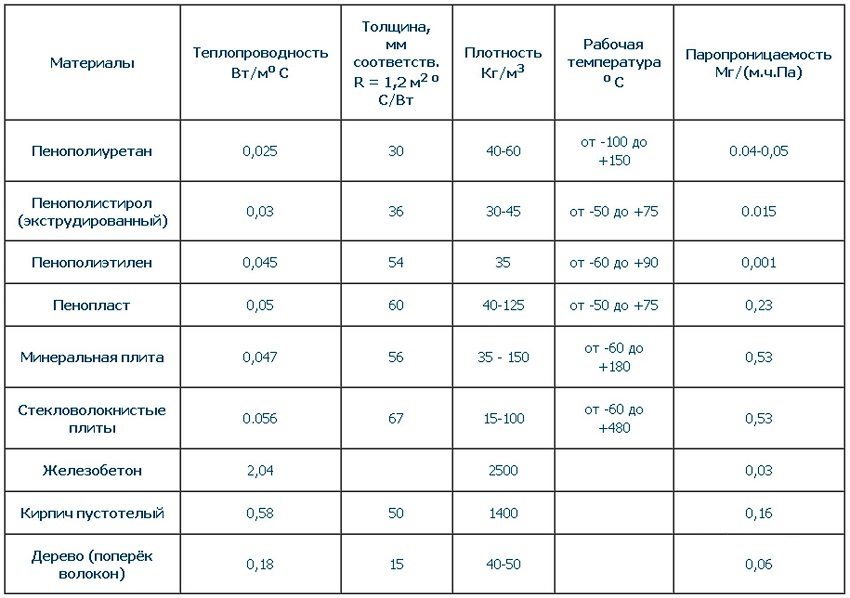
The main criterion for any thermal insulation material is its thermal conductivity coefficient. The lower this value, the better the material prevents heat leakage into the environment.
Fact! The dwelling loses up to 30% of its heat through the walls.
Content [Hide]
How best to insulate the walls of the house
There are two ways to insulate a building - apply internal insulation of premises or make insulation for the walls of the house outside. What kind of insulation is better to use? The answer is hidden in a short expression - "dew point".
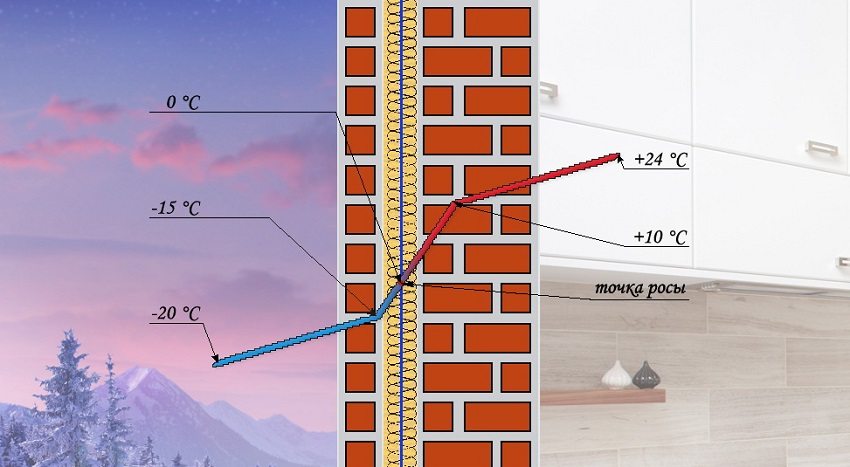
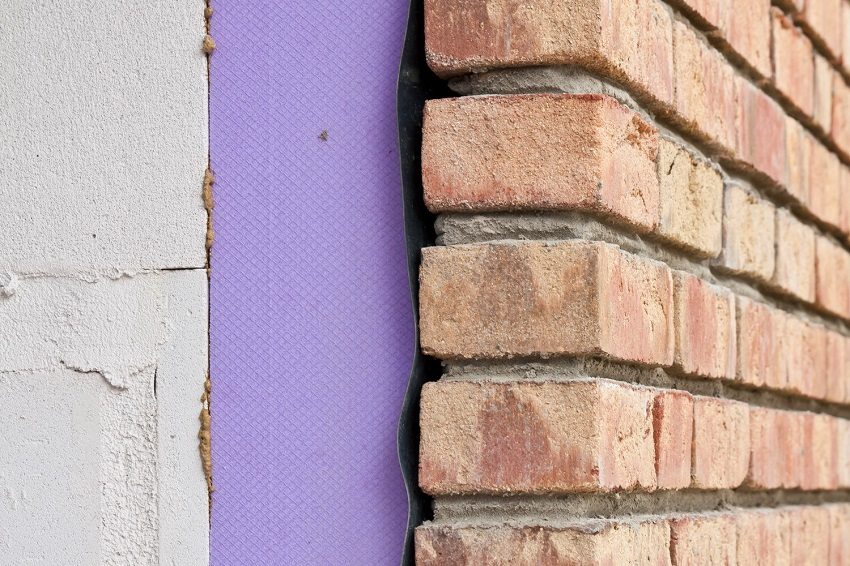
Thermal insulation of the room outside will ensure the correct location of the dew point
The dew point is the temperature at which condensation occurs. A point with this temperature can be located in the thickness of the wall, inside it or outside. Its coordinates depend on the physical properties of the wall materials, the thickness of their layers, as well as the external and internal temperature and humidity.
Important! The position of the dew point will be more optimal even in a completely insulated wall than in one that is only insulated from the inside.
The correct location of the dew point (outside the wall) can only be obtained by installing the insulation of the walls of the house outside, selected taking into account the properties of the material and the thermal calculation in terms of thickness.
The better to insulate the walls outside
Each of the types of modern insulation for the outside walls of the house has its own characteristics and price range. But their main differences are:
- low thermal conductivity;
- minimum values of water absorption and vapor permeability;
- the ability to regulate the indoor climate;
- high rates of sound absorption;
- ecological cleanliness;
- fire resistance and fire safety;
- resistance to chemical attack;
- resistance to biological and mechanical influences (molds, insects, rodents);
- strength and durability;
- elasticity and lack of shrinkage;
- low weight;
- the possibility of installation without seams, joints, voids;
- the ability to fill difficult and hard-to-reach areas;
- ease of installation.
It is also important to take into account the way in which the consumer prefers to mount the insulation outside for the walls of the house. Videos showing the possibility of independent work (like other manuals) can be found in our time enough.
Water absorption and vapor permeability are taken into account to ensure maximum protection of the room from moisture and are selected taking into account the characteristics of the climate and depending on the installation method. Thermal conductivity is used to calculate the required thickness of the thermal insulation material.
The following types of insulation are most often used:
- expanded polystyrene (foam);
- extruded polystyrene foam (eps, penoplex);
- polyurethane foam;
- mineral wool;
- basalt heaters;
- liquid thermal insulation.
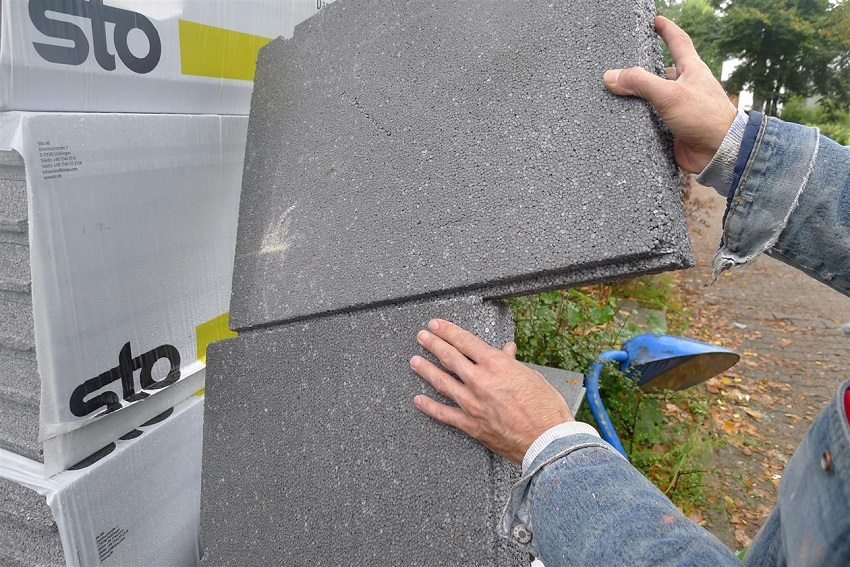
Expanded polystyrene (foam)
Polyfoam (expanded polystyrene) is one of the modern polymer insulation materials for the walls of houses and is used as such in almost all areas of the construction industry: civil and industrial.
First of all, this material is distinguished by low thermal conductivity (from 0.037 to 0.052 W / m * K, depending on density) and water absorption, resistance to biological and chemical influences, and high sound insulation and windproof properties. It belongs to the group of environmentally friendly substances and is quite durable: its operational life exceeds 50 years.
Fact! A 50 mm thick foam layer is equivalent to one and a half bricks in terms of heat retention.
Among its other advantages are flexibility and light weight. This helps to reduce the cost of delivery and installation, ease of work, reduce the load on the walls, which, in turn, eliminates the need for additional strengthening of the foundation.
The disadvantage of expanded polystyrene is its flammability, but the low price makes it possible to insulate all the walls of the house with foam from the outside.
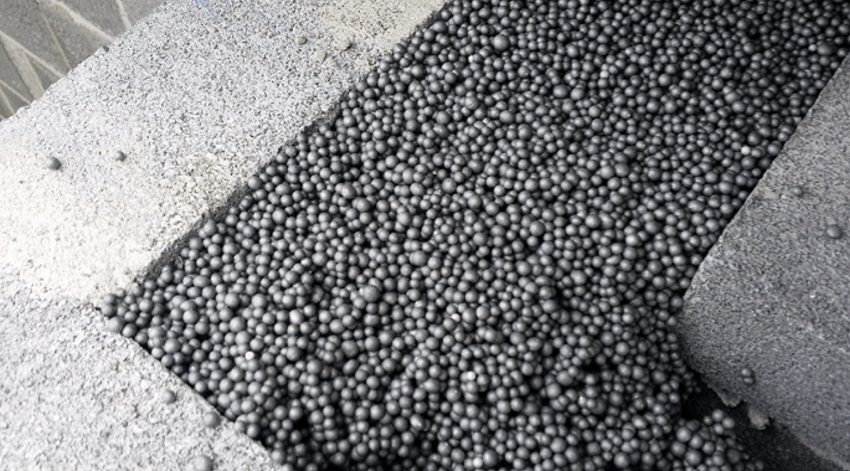
Extruded polystyrene foam (eps, penoplex)
Extruded polystyrene foam (penoplex) is one of the latest generation of thermal insulation materials. In its manufacture, graphite is used in the form of nanoparticles, which increases the strength and energy saving of the product.
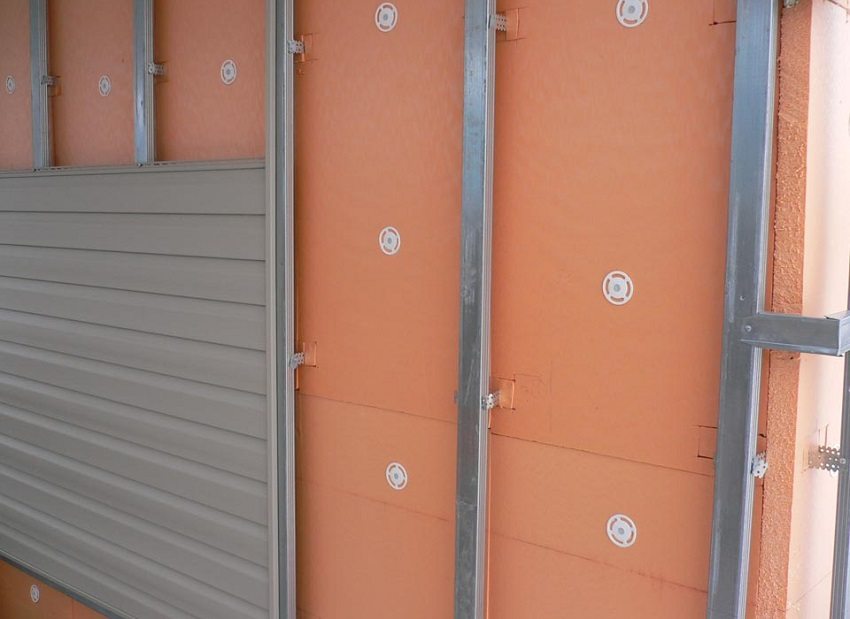

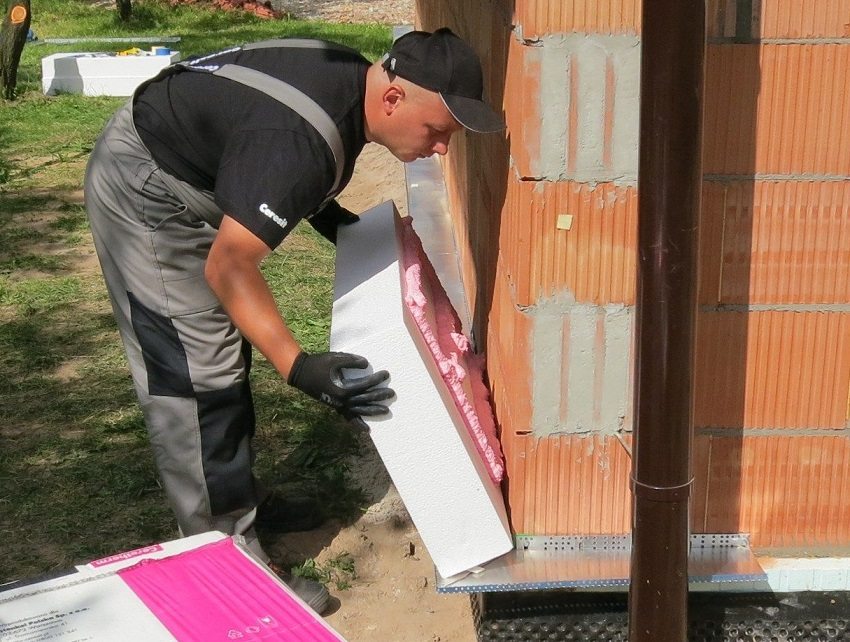
Insulation of walls with penoplex followed by siding cladding
The thermal conductivity coefficient of Penoplex insulation ranges from 0.029 to 0.031 W / m * K. It is resistant to mold, chemicals, insects and rodents and is an excellent sound insulator.
Thanks to this, it is possible to use foam as insulation outside: for walls of wooden houses and other buildings, and inside: floor insulation (especially when installing "warm" floors), basements, balconies and loggias.
Polyurethane foam
Polyurethane foam is a type of plastic with a cellular-foam structure. The mass of the air-filled cells is 90% of the total product weight. Due to this, the value of the thermal conductivity coefficient of polyurethane foam is one of the lowest - from 0.023 to 0.041 W / m * K.
Polyurethane foam is characterized by a high level of adhesion to all types of surfaces: concrete, brick, wood, metal - due to which an airtight coating is created with a guarantee of excellent vapor and waterproofing.
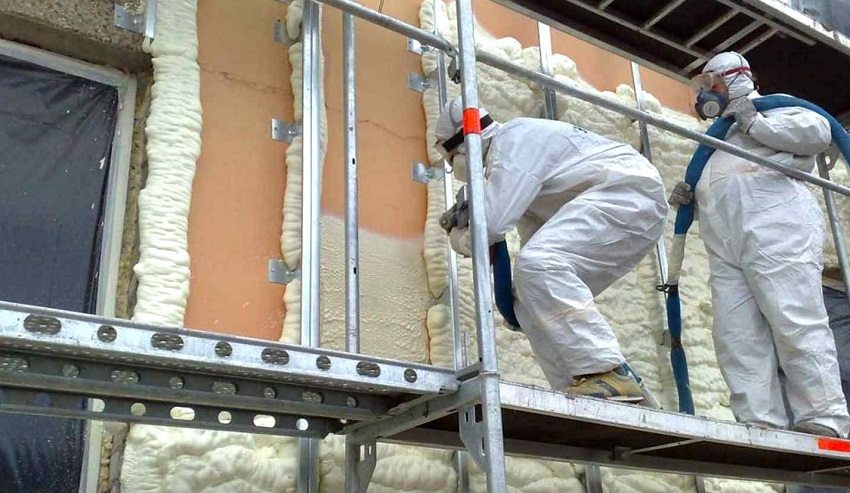
The seamless method of application (using a compressor and a hose) and high elasticity make polyurethane foam an indispensable material for blown thermal insulation when insulating walls outside buildings of complex shapes and frame houses. Insulation for walls outside by blowing can be applied at temperatures up to 100 ° C, the operational period is up to 30 years.
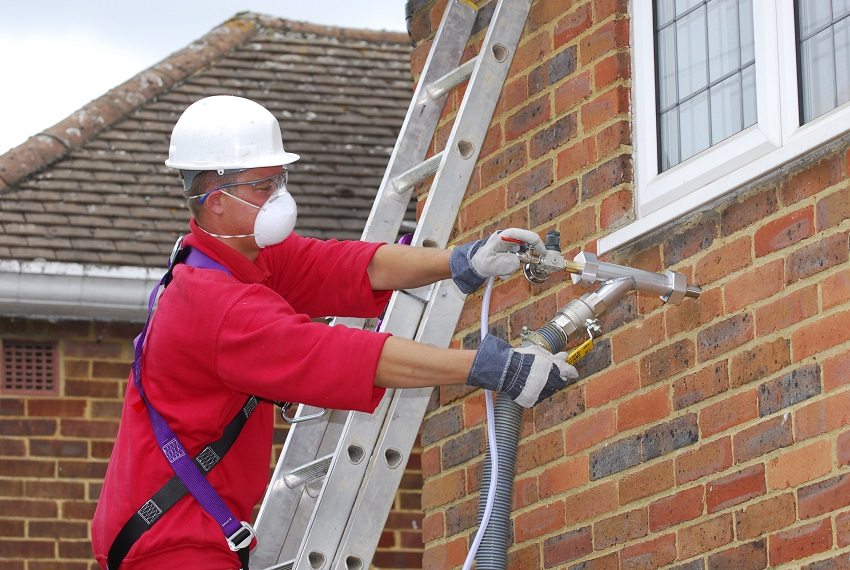

Liquid polyurethane foam can be used as a blown insulation between the building wall and the cladding
The only drawback of the material is its high cost and the need to use expensive equipment for installation.
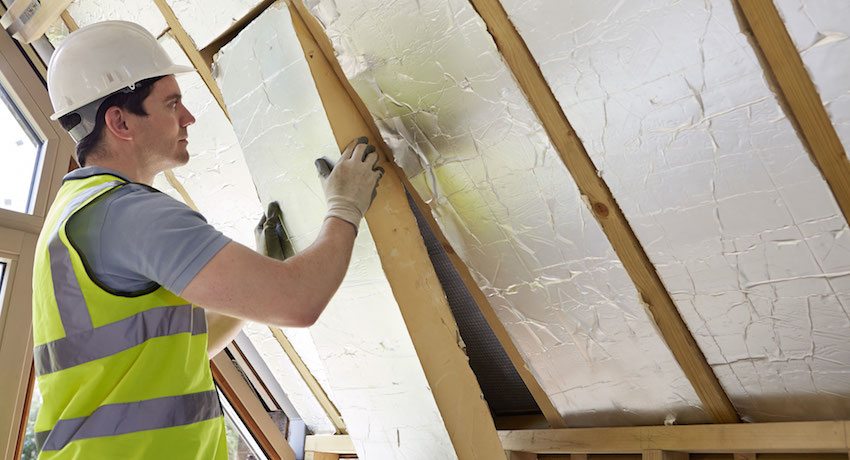
Mineral wool (basalt insulation, stone wool, glass wool)
Mineral wool is a product of slag processing (waste from the metallurgical industry) or rocks: basalt and dolomite. Differs in strength, non-combustibility, durability, environmental friendliness, elasticity, high degree of sound absorption, ease of installation and low cost. The thermal conductivity of this material is in the range of 0.034 - 0.037 W / m * K.
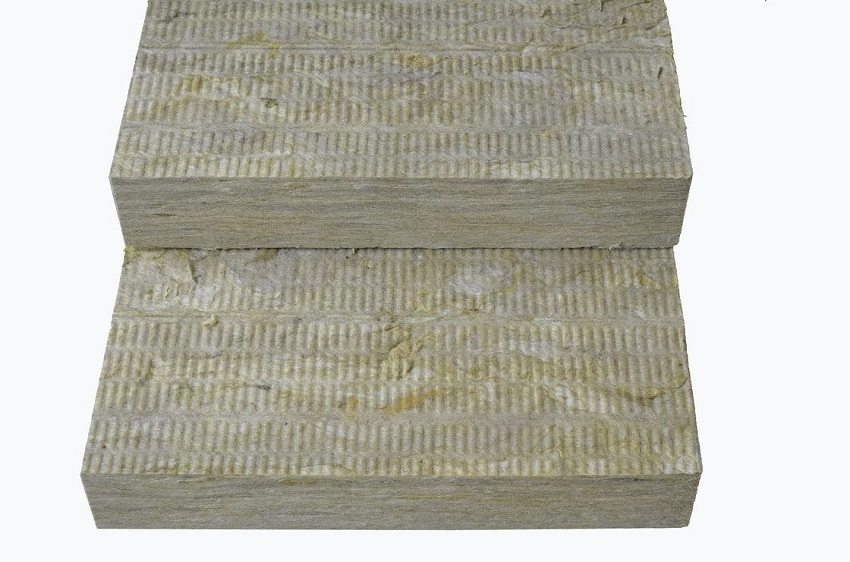

Mineral wool is distinguished by its fire resistance, environmental friendliness, high sound absorption and low cost.
For insulation works, mineral wool is used in the form of basalt slabs or in rolls with a wide range of sizes. Mineral wool is used as insulation for the outside walls of the house. The dimensions of the slabs produced can be as follows:
- 1000 x 600 x 50 mm;
- 7000 x 1200 x 50 mm;
- 9000 x 1200 x 50 mm;
- 10000 x 1200 x 50 mm;
- 10000 x 1200 x 100 mm.
Basalt insulation is used in buildings of any purpose, in particular - for insulation in the country, wooden houses and timber structures, bricks or foam blocks. It is possible to work with this material at temperatures ranging from -60 ° C to + 220 ° C, which is definitely convenient when mounting on walls outside. Insulation in the country, houses made of wood, bricks or foam blocks, garages, warehouses and other buildings - this is an incomplete list of possibilities for using mineral thermal insulation.
Related article:
|
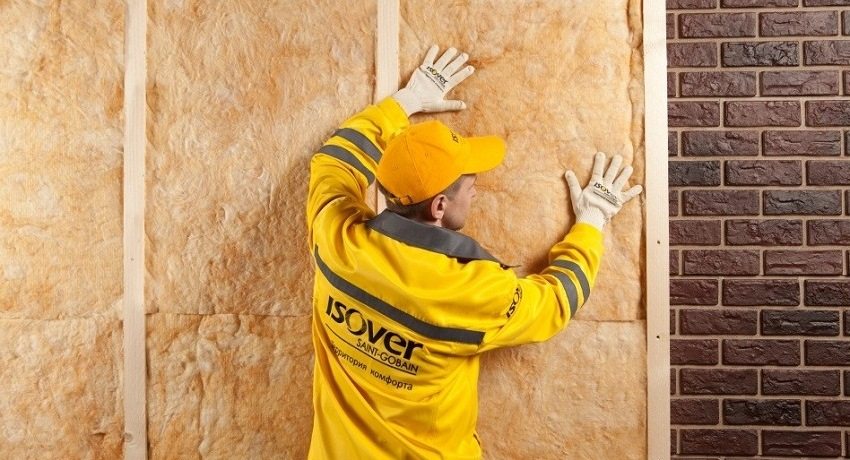
It is most preferable to use mineral wool or basalt slabs during installation insulation for the walls of the house outside under siding.
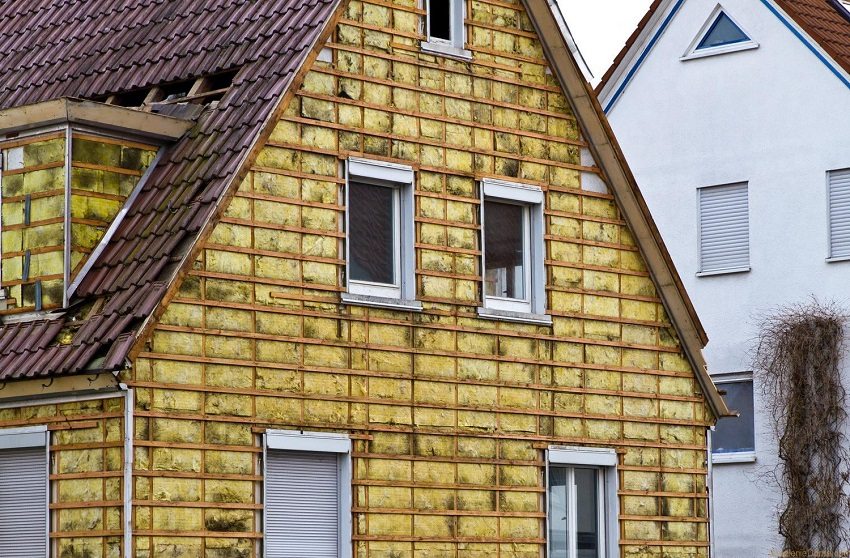

It is most preferable to use mineral wool to insulate the house from the outside, followed by siding.
The use of mineral wool (along with polyurethane foam) is also popular to create a blown insulation. With this method, using a compressor unit, the material is blown between the wall of the house and the finish facade, which also serves as a formwork.
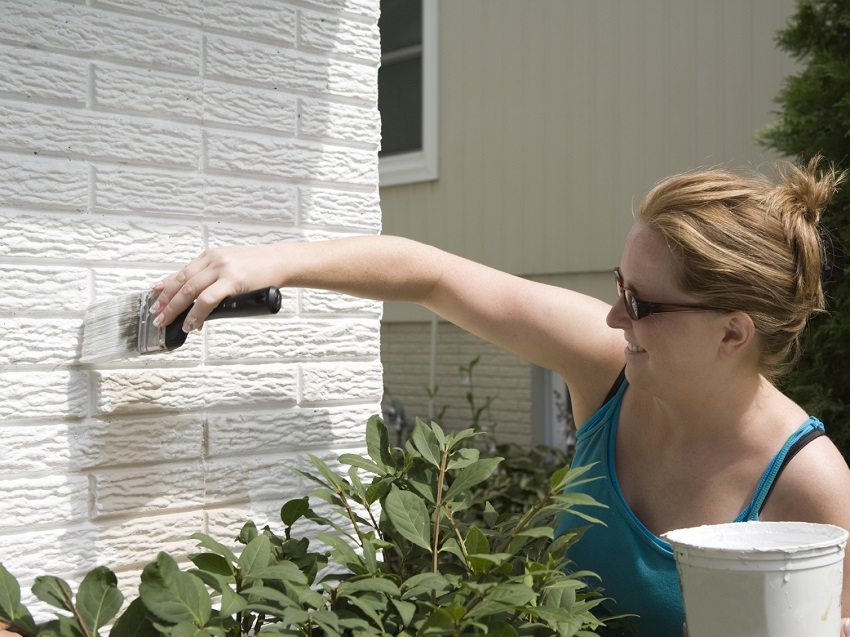
Liquid insulation
Liquid insulation materials can be called new generation heaters. They can be used both for thermal insulation of metal parts (pipes or frames), and as a heater for houses from foam blocks. From the outside, on the walls, these multicomponent ceramic substances look like acrylic paint.
However, they differ from paint in the content of vacuumized voids (up to 80%), due to which they acquire the properties of a heat insulator.
Interesting! Liquid heaters have a record low thermal conductivity coefficient (from 0.0011 to 0.0015 W / m * K). For comparison - the coefficient of thermal conductivity of vacuum is 0.
With a liquid consistency, these materials do not require professional skills and sophisticated equipment for application to any surface: concrete, brick, metal, wood. They are applied using paint tools - brushes, rollers, airless spray guns - and fill all voids and crevices.
After 6 hours of drying, a solid, highly resistant to mechanical stress coating is formed.

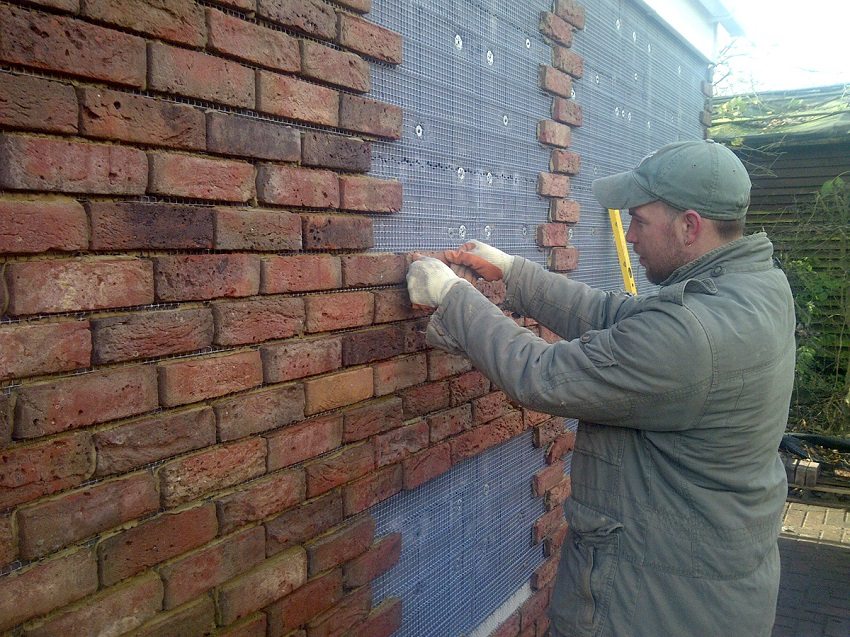
Fixation of sheets of polystyrene or expanded polystyrene is carried out with special fasteners of the "fungus" type
Due to their low thermal conductivity, liquid insulation for walls of the house helps to reduce heat losses, even if applied from the outside in a thin layer.They protect the surface from weather effects (operating temperature range - from -60 to + 260 ° С), solar radiation and precipitation, and metal parts from corrosion.
Interesting! The water absorption of most liquid heaters within 24 hours does not exceed 0.4% by weight.
Coating with a liquid insulation is one of the most effective ways to prevent the formation of condensation and to protect an industrial or residential building from freezing, the development of all types of mold fungi.
Ways to insulate the walls of the house outside
Most modern heaters are universal and can be mounted outside the house on any walls: wood, timber, foam blocks, red or white brick; as well as for various types of exterior finishing of buildings: plaster, vinyl siding, decorative bricks, stone facade slabs. Having familiarized yourself with all the characteristics, you can choose the appropriate type of wall insulation. Outside, houses from a bar are insulated in the same way as buildings from other materials.
Based on the variety of existing thermal insulation materials, for each type of wall, in combination with its decoration, the best installation option for insulation is selected:
- Installation of insulation under plaster.
- Three-layer non-ventilated wall.
- Ventilated facade.
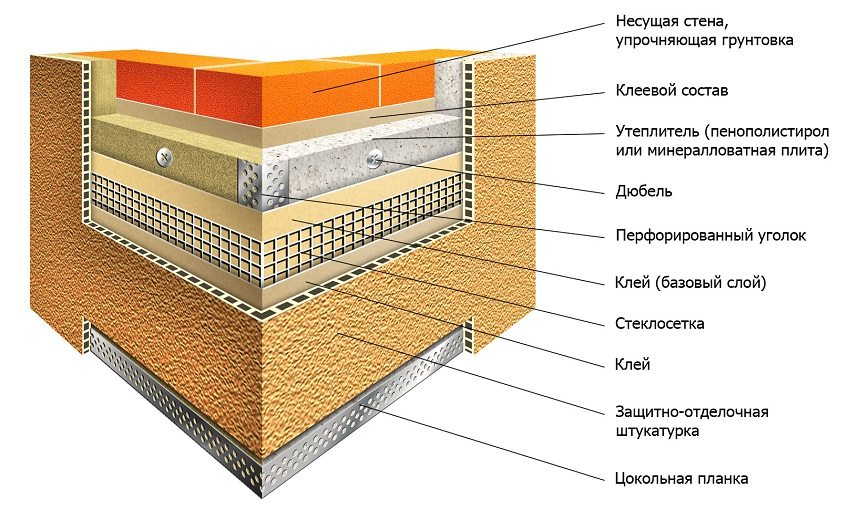
Installation of insulation under plaster
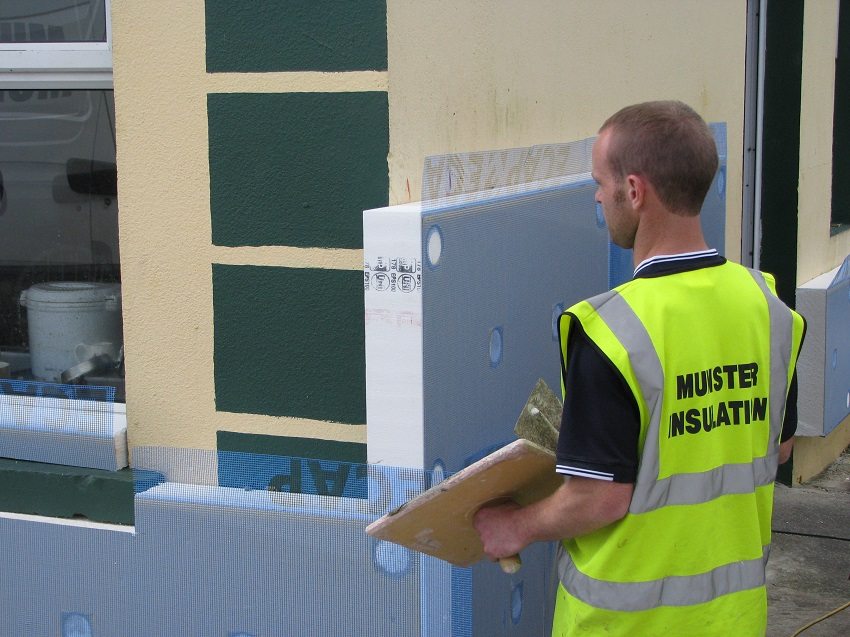
When installing insulation under plaster, for the walls of houses outside, expanded polystyrene, plates of basalt insulation, sheets of mineral wool or insulation foam are most often used as a heat insulator.
The insulation is fixed on the walls of the house from the outside with an adhesive solution and strengthened fiberglass reinforcing mesh... Special fasteners of the "mushroom" type perform additional fixation of foam sheets or basalt insulation plates. For the walls of the house outside, plaster ("wet facade" method) or cladding materials are used as a finish.
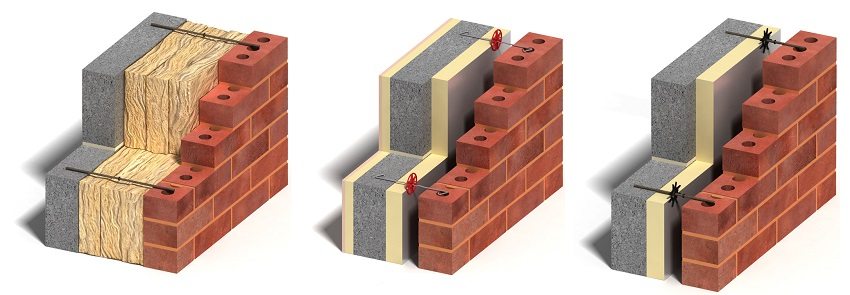
Three-layer non-ventilated wall
A three-layer non-ventilated wall is formed by the walls of the house from the outside, insulation and facade decoration, laid out taking into account the air gap. This method is used for installation with decoration for the walls of the house outside under a brick. Heaters of various types are used with this option, including thermal insulation materials for blown installation.
This method is used to insulate various buildings, both brick or foam concrete, and wood or timber.
Facade finishing is performed with facing slabs, decorative or building bricks.
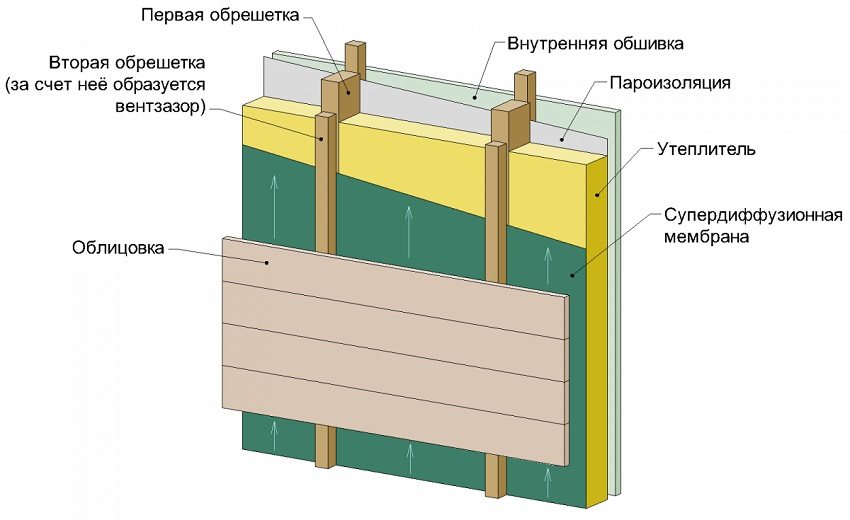
Ventilated facade
Insulation for a ventilated facade is assembled from the following layers:
- waterproofing;
- insulation;
- wind protection;
- finishing facade cladding (lining, siding, panels).
Installation of insulation as part of a ventilated facade is the most preferable option, since heat losses are minimized due to wind protection. Also, waterproofing provides additional protection of the wall surface from moisture.
The use of a ventilated facade is possible with most types of buildings, materials and configurations of external walls and varieties of facade finishes. This option is most common when installing insulation for the walls of the house outside under siding. Also, this method of installation is the best for insulation outside the walls of wooden houses: from a log or from a bar.
Regardless of the type and type of material used as a heat insulator, any of the mentioned installation options must cope with the main tasks - insulation of the room, waterproofing of walls, protection from wind and drafts, as well as heat preservation.
The undoubted advantage of most of the materials mentioned in the article is the ability to independently install them as heaters for the walls of the house outside. Photo and video clips, as well as other instructions, will be very useful in this case.